Isopeptide bond
From Proteopedia
(→Unspecified) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
An ''isopeptide bond'' is an amide bond between the sidechain of one [[amino acid]] and the sidechain or main chain terminus of another amino acid. | An ''isopeptide bond'' is an amide bond between the sidechain of one [[amino acid]] and the sidechain or main chain terminus of another amino acid. | ||
| - | [[Image:Isopeptide-bond.jpg|300px]] | + | <br>[[Image:Isopeptide-bond.jpg|300px]] |
An isopeptide bonds makes a covalent link between polypeptide backbones. This is in contrast to the much more common [[Peptide bond|peptide (''eupeptide'') bonds]] between amino acid main chain atoms that form the polypeptide backbones of proteins. Isopepide bonds are rare. [[Disulfide bonds]] are a much more common form of covalent linkage between polypeptide chains. | An isopeptide bonds makes a covalent link between polypeptide backbones. This is in contrast to the much more common [[Peptide bond|peptide (''eupeptide'') bonds]] between amino acid main chain atoms that form the polypeptide backbones of proteins. Isopepide bonds are rare. [[Disulfide bonds]] are a much more common form of covalent linkage between polypeptide chains. | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 17 May 2021
|
An isopeptide bond is an amide bond between the sidechain of one amino acid and the sidechain or main chain terminus of another amino acid.
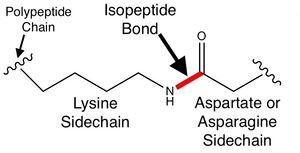
An isopeptide bonds makes a covalent link between polypeptide backbones. This is in contrast to the much more common peptide (eupeptide) bonds between amino acid main chain atoms that form the polypeptide backbones of proteins. Isopepide bonds are rare. Disulfide bonds are a much more common form of covalent linkage between polypeptide chains.
For more, please see Isopeptide bond in Wikipedia.
Contents |
Formation
Spontaneous
Some isopeptide bonds appear to form spontaneously during protein folding. These include the intramolecular (within molecule) isopeptide bonds in pilin monomers[1][2], and intermolecular (between molecule) "chain mail" isopeptide bonds in the capsid of bacteriophage HK97[3].
Enzymatic
Intermolecular (between molecule) isopeptide bonds that link bacterial pilin monomers into long chains of pili are formed enzymatically by a cysteine transpeptidase "sortase"[1]. However, the same pilins have multiple intramolecular (within molecule) isopeptide bonds that appear to form spontaneously[1].
Frequency
A search for isopeptide bond in the keywords records at the PDB returns about 200 hits (April, 2021). This suggests that approximately one model per thousand in the PDB contains isopeptide bonds.
PDB KEYWDS and LINK Records
Structures containing isopeptide bonds usually have "ISOPEPTIDE BOND" in their PDB file KEYWDS record, and sometimes have LINK records (or _struct_conn in their mmCIF files) specifying the isopeptide-bonded residues. Here are the relevant LINK records from 3htl:LINK NZ LYS X 199 CG ASN X 321 1555 1555 1.43 LINK NZ LYS X 363 CG ASN X 482 1555 1555 1.55
Note that link records involving MSE (selenomethionine) generally signify nothing more than MSE being part of a polypeptide chain, but are required because the HETATM MSE residue is covalently linked to the adjacent standard amino acids.
Unspecified Isopeptide Bonds
Some structures that contain isopeptide bonds lack LINK/_struct_conn records specifying these bonds. See examples below.
Examples
Specified
Isopeptide bonds in the following examples are specified in LINK/_struct_conn records.
- The capsid of the HK97 bacteriophage contains isopeptide bonds that cross-link the protein chains into a protein chain mail [4][5][3]. However, these do not occur in the asymmetric unit of 1ohg[6]. They can be visualized in the biological unit, which is the full virus capsid, but that is technically challenging.
- 7cap is a ubiquitin homotrimer. The C-terminal Gly76 is isopeptide linked to Lys48 in each inter-chain interface[7].
- 4mli contains the SpyTag peptide (which can be linked to a protein of interest) forming an isopeptide bond between SpyTag peptide Lys31 and SpyCatcher protein Asp117[8].
- 3htl is a pilus monomer with isopepide bonds Lys199-Asn321 and Lys363-Asn482[9].
Unspecified
Isopeptide bonds in the following examples are not specified in LINK/_struct_conn records.
- 1fma: Molybdopterin synthase, an enzyme with structural similarity to ubiquitin, has Lys118 chain E isopeptide bonded to the carboxy-terminal Gly81 in chain D.
- 5jqf: Lasso peptide sphingopyxin I has Asp9 isopeptide bonded to the amino terminus at Gly1. This bond is cleaved by lasso peptide isopeptidase.
Visualization
FirstGlance in Jmol alerts you to isopeptide binds, and provides links to visualize each one conveniently. Use the links above under Examples to go to a Proteopedia page titled with a PDB code. There, click on "FirstGlance". In FirstGlance, click on "Show more details" in the Molecule Information Tab. Look for "Isopeptide(?) bonds" in the Molecule Information Tab.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kang HJ, Baker EN. Intramolecular isopeptide bonds give thermodynamic and proteolytic stability to the major pilin protein of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 31;284(31):20729-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014514. Epub, 2009 Jun 4. PMID:19497855 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.014514
- ↑ Kang HJ, Baker EN. Intramolecular isopeptide bonds: protein crosslinks built for stress? Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Apr;36(4):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.007. Epub , 2010 Nov 4. PMID:21055949 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.007
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dierkes LE, Peebles CL, Firek BA, Hendrix RW, Duda RL. Mutational analysis of a conserved glutamic acid required for self-catalyzed cross-linking of bacteriophage HK97 capsids. J Virol. 2009 Mar;83(5):2088-98. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02000-08. Epub 2008 Dec 17. PMID:19091865 doi:10.1128/JVI.02000-08
- ↑ Hendrix RW, Johnson JE. Bacteriophage HK97 capsid assembly and maturation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;726:351-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0980-9_15. PMID:22297521 doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-0980-9_15
- ↑ Gilakjan ZA, Kropinski AM. Cloning and analysis of the capsid morphogenesis genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage D3: another example of protein chain mail? J Bacteriol. 1999 Dec;181(23):7221-7. PMID:10572124
- ↑ Wikoff WR, Liljas L, Duda RL, Tsuruta H, Hendrix RW, Johnson JE. Topologically linked protein rings in the bacteriophage HK97 capsid. Science. 2000 Sep 22;289(5487):2129-33. PMID:11000116
- ↑ Hiranyakorn M, Yanaka S, Satoh T, Wilasri T, Jityuti B, Yagi-Utsumi M, Kato K. NMR Characterization of Conformational Interconversions of Lys48-Linked Ubiquitin Chains. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 28;21(15). pii: ijms21155351. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155351. PMID:32731397 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155351
- ↑ Li L, Fierer JO, Rapoport TA, Howarth M. Structural Analysis and Optimization of the Covalent Association between SpyCatcher and a Peptide Tag. J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 23. pii: S0022-2836(13)00666-9. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.021. PMID:24161952 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.021
- ↑ Kang HJ, Paterson NG, Gaspar AH, Ton-That H, Baker EN. The Corynebacterium diphtheriae shaft pilin SpaA is built of tandem Ig-like modules with stabilizing isopeptide and disulfide bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 6;106(40):16967-71. Epub 2009 Sep 21. PMID:19805181
