|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
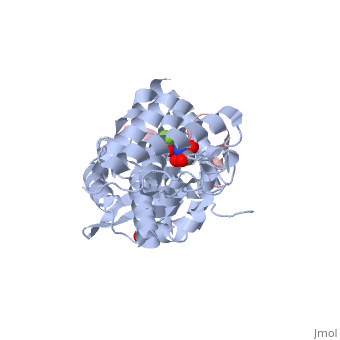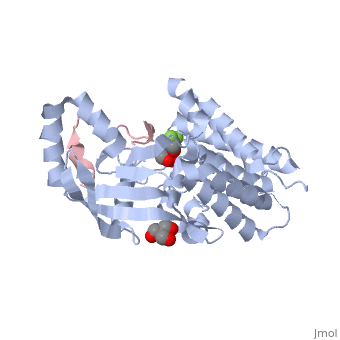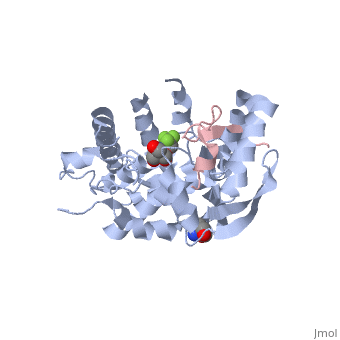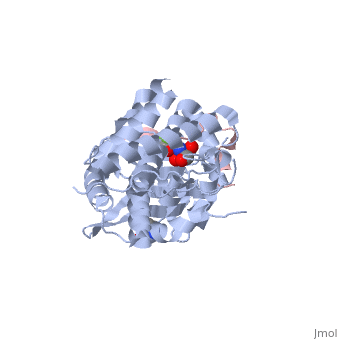
| | ==The structure of the type III effector AvrB complexed with a high-affinity RIN4 peptide== | | ==The structure of the type III effector AvrB complexed with a high-affinity RIN4 peptide== |
| - | <StructureSection load='2nud' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2nud]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2nud' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2nud]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2nud]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psesg Psesg]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2NUD OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2NUD FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2nud]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psesg Psesg]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2NUD OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2NUD FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ETF:TRIFLUOROETHANOL'>ETF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=TRS:2-AMINO-2-HYDROXYMETHYL-PROPANE-1,3-DIOL'>TRS</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ETF:TRIFLUOROETHANOL'>ETF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=TRS:2-AMINO-2-HYDROXYMETHYL-PROPANE-1,3-DIOL'>TRS</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1nh1|1nh1]], [[2nun|2nun]]</td></tr> | + | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[1nh1|1nh1]], [[2nun|2nun]]</div></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">avrB ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=318 PSESG])</td></tr> | + | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">avrB ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=318 PSESG])</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2nud FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2nud OCA], [http://pdbe.org/2nud PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2nud RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2nud PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2nud ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2nud FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2nud OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2nud PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2nud RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2nud PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2nud ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/RIN4_ARATH RIN4_ARATH]] Essential regulator of plant defense, which plays a central role in resistance in case of infection by a pathogen. It is a common target for both type III avirulence proteins from P.syringae (AvrB, AvrRpm1 and AvrRpt2) and for the plant Resistance (R) proteins RPM1 and RPS2. In strains carrying the appropriate R gene for avirulence proteins of the pathogen, its association with avirulence proteins triggers a defense system including the hypersensitive response, which limits the spread of disease. In contrast, in plants lacking appropriate R genes, its association with avirulence proteins of the pathogen impairs the defense system and leads to the pathogen multiplication.<ref>PMID:11955429</ref> <ref>PMID:12581526</ref> <ref>PMID:12581527</ref> | + | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/RIN4_ARATH RIN4_ARATH]] Essential regulator of plant defense, which plays a central role in resistance in case of infection by a pathogen. It is a common target for both type III avirulence proteins from P.syringae (AvrB, AvrRpm1 and AvrRpt2) and for the plant Resistance (R) proteins RPM1 and RPS2. In strains carrying the appropriate R gene for avirulence proteins of the pathogen, its association with avirulence proteins triggers a defense system including the hypersensitive response, which limits the spread of disease. In contrast, in plants lacking appropriate R genes, its association with avirulence proteins of the pathogen impairs the defense system and leads to the pathogen multiplication.<ref>PMID:11955429</ref> <ref>PMID:12581526</ref> <ref>PMID:12581527</ref> |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 32: |
Line 32: |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| - | *[[Avirulence protein|Avirulence protein]] | + | *[[Avirulence protein 3D structures|Avirulence protein 3D structures]] |
| - | *[[Type III effector AvrB complexed with a high-affinity RIN4 peptide|Type III effector AvrB complexed with a high-affinity RIN4 peptide]]
| + | |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| | [[Category: Psesg]] | | [[Category: Psesg]] |
| | [[Category: Dangl, J L]] | | [[Category: Dangl, J L]] |
| Structural highlights
Function
[RIN4_ARATH] Essential regulator of plant defense, which plays a central role in resistance in case of infection by a pathogen. It is a common target for both type III avirulence proteins from P.syringae (AvrB, AvrRpm1 and AvrRpt2) and for the plant Resistance (R) proteins RPM1 and RPS2. In strains carrying the appropriate R gene for avirulence proteins of the pathogen, its association with avirulence proteins triggers a defense system including the hypersensitive response, which limits the spread of disease. In contrast, in plants lacking appropriate R genes, its association with avirulence proteins of the pathogen impairs the defense system and leads to the pathogen multiplication.[1] [2] [3]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector protein avirulence protein B (AvrB) is delivered into plant cells, where it targets the Arabidopsis RIN4 protein (resistance to Pseudomonas maculicula protein 1 [RPM1]-interacting protein). RIN4 is a regulator of basal host defense responses. Targeting of RIN4 by AvrB is recognized by the host RPM1 nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat disease resistance protein, leading to accelerated defense responses, cessation of pathogen growth, and hypersensitive host cell death at the infection site. We determined the structure of AvrB complexed with an AvrB-binding fragment of RIN4 at 2.3 A resolution. We also determined the structure of AvrB in complex with adenosine diphosphate bound in a binding pocket adjacent to the RIN4 binding domain. AvrB residues important for RIN4 interaction are required for full RPM1 activation. AvrB residues that contact adenosine diphosphate are also required for initiation of RPM1 function. Nucleotide-binding residues of AvrB are also required for its phosphorylation by an unknown Arabidopsis protein(s). We conclude that AvrB is activated inside the host cell by nucleotide binding and subsequent phosphorylation and, independently, interacts with RIN4. Our data suggest that activated AvrB, bound to RIN4, is indirectly recognized by RPM1 to initiate plant immune system function.
Type III effector activation via nucleotide binding, phosphorylation, and host target interaction.,Desveaux D, Singer AU, Wu AJ, McNulty BC, Musselwhite L, Nimchuk Z, Sondek J, Dangl JL PLoS Pathog. 2007 Mar;3(3):e48. PMID:17397263[4]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Mackey D, Holt BF 3rd, Wiig A, Dangl JL. RIN4 interacts with Pseudomonas syringae type III effector molecules and is required for RPM1-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2002 Mar 22;108(6):743-54. PMID:11955429
- ↑ Axtell MJ, Staskawicz BJ. Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell. 2003 Feb 7;112(3):369-77. PMID:12581526
- ↑ Mackey D, Belkhadir Y, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Dangl JL. Arabidopsis RIN4 is a target of the type III virulence effector AvrRpt2 and modulates RPS2-mediated resistance. Cell. 2003 Feb 7;112(3):379-89. PMID:12581527
- ↑ Desveaux D, Singer AU, Wu AJ, McNulty BC, Musselwhite L, Nimchuk Z, Sondek J, Dangl JL. Type III effector activation via nucleotide binding, phosphorylation, and host target interaction. PLoS Pathog. 2007 Mar;3(3):e48. PMID:17397263 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030048
|