Histones
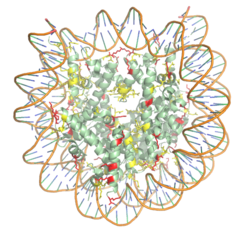
Figure 1. The nucleosome structure consisting of the histone octamer and DNA. Arginine residues are shown in yellow, lysine residues are shown in red. PDB: 3kwq
are proteins found in the cell nucleus that are the key building blocks of
chromatin, and are essential for proper DNA packaging and regulation of
transcription. In the first step of
DNA packaging, two copies of the four core histone proteins (
H1,
H2A,
H3, and
H4) form an
octamer that DNA wraps around, forming the
nucleosome. 20-24% of residues making up the histone octamer are arginine and lysine, causing a net positive charge, especially at the outer surfaces of the histone core where negatively charged DNA is bound (Figure 1).
[1][2] The positively charged residues of the histone core tails are often subject to chemical modifications that can regulate the processes of DNA repair, replication, transcription, and heterochromatin maintenance.
Histone Modification
Histones can be reversibly modified in a variety of ways, including: methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination. These modifications all result in either the condensation or relaxation of DNA and consequently repressing or activating transcription. Histone acetylation is a histone modification that involves the transfer of an acetyl group from the co-factor Acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) to the ε-amino group of a lysine residue in a histone protein. This reaction is catalyzed by various histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzymes. Lysine acetylation is an important epigenetic marker as it removes the positive charge of the lysine, thus reducing the strength of the interaction between DNA and hisotones. The net effect of acetylation is the relaxation of the DNA into euchromatin which is more transcriptionally active.
HAT1 Background
HAT1 catalyzes the acetylation of lysine residues and was the first of the enzymes to be identified in the HAT family. [3] Deletion of the HAT gene caused a loss of acetylation on H4K5 and H4K12, leading to the conclusion that HAT1 is the sole enzyme responsible for this conserved histone modification.[4] The HAT2 enzyme was later identified as a binding partner for HAT1 and it modulates the substrate specificity of HAT1.[3] The HAT1/HAT2 complex is highly specific for H4K12 acetylation.
HAT1/HAT2 Complex Structure
The structure of the from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was determined by X-ray diffraction at 2.0Å resolution. The complex was crystallized in the presence of coenzyme A (CoA) and the histone H4 N-terminal peptide (residues 1-48). The complex has four components (HAT1, HAT2, H4 peptide, and CoA) seen with a 1:1:1:1 stoichiometry. While residues 1-48 of the yeast H4 protein were included in the crystallization, only residues 9-46 were well resolved in the refined structure. Similarly, residues 1-4 in the HAT1 subunit and residues 1-6, 87-104, and 391-401 in the HAT2 subunit were not resolved.[3]
HAT1 is not catalytically active until it binds with HAT2 to form the complex.[5] The includes 317 residues and contains the binding site for acetyl coenzyme A. is 401 residues and forms a beta-propeller structure with C7 symmetry. Bound to the HAT1-HAT2 complex is a comprised of residues 9-46 of the histone protein H4.
The HAT1 and HAT2 is stabilized by multiple salt bridges, hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces among hydrophobic side chains. Many of these are between a short helix spanning in HAT1 and several loops connecting β-strands in the propeller of HAT2. The HAT1 helix is important for the heterodimer formation as its deletion abolishes the in vitro interaction between HAT1 and HAT2.[3] Outside of the helix, three specific interactions at the interface involving hydrogen bonds help stabilize the complex: 1) The side chain atoms of with the main chain nitrogen of Ala202 in HAT1, 2) The side chain of with main chain atoms of Leu288 and Phe205 respectively, and 3) Between the side-chains of . Finally, the at the interface of the complex appears to be critical for the complex formation. This core consists of aromatic residues from HAT1 and leucine residues from HAT2, however it does not form any obvious ring stacking.
The histone H4 peptide that represents the substrate binds both the HAT1 and HAT2 subunits, and may be represented as . The N-terminal segment of H4 is largely glycine residues and makes few specific interactions with HAT1. In this segment, the target lysine (H4K12) inserts into the active site of HAT1 to access acetyl-CoA.[5] The segment is amphipathic and interacts exclusively with HAT2, residing in a groove formed by the HAT2 N-terminal helix (residues 10-24), and a shorter, acidic helix (residues 333-339). The central segment of the H4 peptide makes no interactions with either HAT1 or HAT2.
Acetyl-CoA Binding Site
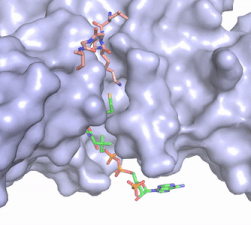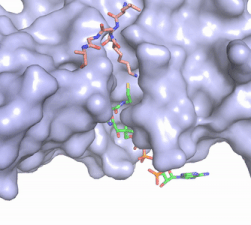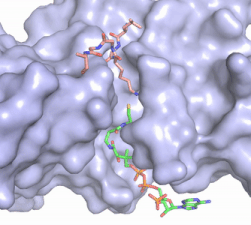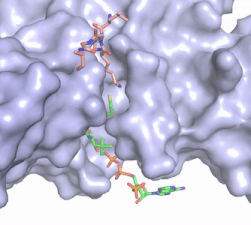
Figure 2. Coenzyme A (CoA, green sticks) and the histone H4 peptide substrate (pink sticks) are shown in the binding groove of HAT1. The movie was made in PyMol using 4psw.pdb, then converted to gif format using EZgif.
The CoA molecule is buried in a deep channel in the HAT1 subunit, where the free rotation of several bonds in the
pantetheine group give the molecule a bent conformation (Figure 2). The conserved Arg/Gln-X-X-Gly-X-Gly/Ala (residues 227-232) of CoA containing proteins wraps around the 5'-diphosphate moiety of the CoA. This motif also positions the negatively charged β-phosphate group of CoA at the N-terminal dipole of the helix spanning residues 230-245, further stabilizing the interaction. The of CoA rests in the hydrophobic pocket formed by the side chains of residues Ile-217,Pro-257 and Phe-261. In the HAT1-Acetyl coenzyme A structure determined without HAT2 and the H4 substrate (PDB: 1bob) the main chain atoms of were revealed to play a critical role in binding to acetyl-CoA. The carbonyl oxygen of Phe220 hydrogen bonds to the amine of the β-mercaptoethylamine group of the co-factor, while the Phe220 amide nitrogen hydrogen bonds to the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA.
[6] The latter interaction has important implications for the mechanism as described below.
Mechanism
After many structural studies, the complete catalytic mechanism for HAT1 remains unclear. In particular, the identity of the general base needed to deprotonate the substrate lysine is uncertain. In a previous study a structural overlay of HAT1 and Gcn5, a better-understood HAT enzyme, found a conserved glutamate residue in the active site of both enzymes. Mutation of this glutamate (equivalent to Glu255 in 2psw.pdb) was shown to decrease the catalytic ability of HAT1, identifying it to be important for catalysis. [3] Given the proximity of this mechanism could be supported by structure of the HAT1-HAT2 complex with histone H4, however it would require a 180° shift in the direction of the side chains to act as a general base that deprotonates H4-Lys12, enhancing its nucleophilic character.
An alternative mechanism (Figure 3) that is better supported by the HAT1-HAT2-histone H4 structure, proposes that the attacking lysine would be deprotonated upon entry into active site due the proximity of the acidic side chains of Glu255 and Asp256. Additionally, there are in the main chain of Ser218, Glu255, and Asp256 which are in hydrogen bonding distance with the ε-amine of the attacking lysine. They will act to withdraw positive charge from the attacking nitrogen improving its nucleophilic nature and perhaps better orient the lone pair electrons for nucleophillic attack. Additionally, the interaction of the Phe220 amide with the carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group enhances the electrophilic nature the carbonyl carbon being attacked. In the second step of the reaction, the lone pair on the lysine attacks the carbonyl carbon of acetyl-CoA, forming an oxyanion containing tetrahedral transition state. The structure does not definitively reveal residues in an oxyanion hole that stabilize the transition state
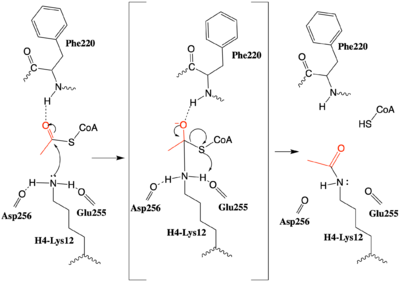
Figure 3: The proposed HAT1 Mechanism with the transferred acetyl group in red. (The carbonyl of Ser218 described in the text and is not shown activating the Lys12 nucleophile)
but superposition of the HAT1-acetyl coenzyme A structure with the HAT1-HAT2-H4 substrate structure suggests , which binds the carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group before attack, is a likely candidate. Finally, upon electron reorganization, the C-S scissile bond breaks leaving the H4Lys12 acetylated and Coenzyme A as products.
Inhibition
Although HAT1 was the first histone acetyltransferase enzyme discovered, its function is poorly understood and the first inhibitor of the enzyme was only described in 2019[7]. The HAT1 inhibitor (H4K12CoA) that is a conjugate of the first 20 residues of the H4 protein, covalently linked to CoA through the lysine 12 side chain. H4K12CoA was found to act as a competitive inhibitor to both the H4 peptide substrate as well as acetyl-CoA. Having this inhibitor now allows for more in depth study of therapeutic targets associated with specific disease states. Additionally, H4K12CoA can be used as tool compound to better elucidate the HAT1 specificity and mechanism regarding epigenetic modification of the H4 histone protein.
References
- ↑ Watson, J D, et al. Molecular Biology of the Gene (Seventh Edition). (2014) Boston, MA: Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company.
- ↑ Watanabe S, Resch M, Lilyestrom W, Clark N, Hansen JC, Peterson C, Luger K. Structural characterization of H3K56Q nucleosomes and nucleosomal arrays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):480-6. Epub 2010 Jan 25. PMID:20100606 doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.009
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Li Y, Zhang L, Liu T, Chai C, Fang Q, Wu H, Agudelo Garcia PA, Han Z, Zong S, Yu Y, Zhang X, Parthun MR, Chai J, Xu RM, Yang M. Hat2p recognizes the histone H3 tail to specify the acetylation of the newly synthesized H3/H4 heterodimer by the Hat1p/Hat2p complex. Genes Dev. 2014 Jun 1;28(11):1217-27. doi: 10.1101/gad.240531.114. Epub 2014 May , 16. PMID:24835250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.240531.114
- ↑ Parthun MR, Widom J, Gottschling DE. The major cytoplasmic histone acetyltransferase in yeast: links to chromatin replication and histone metabolism. Cell. 1996 Oct 4;87(1):85-94. PMID:8858151
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wu H, Moshkina N, Min J, Zeng H, Joshua J, Zhou MM, Plotnikov AN. Structural basis for substrate specificity and catalysis of human histone acetyltransferase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 5;109(23):8925-30. Epub 2012 May 21. PMID:22615379 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114117109
- ↑ Dutnall RN, Tafrov ST, Sternglanz R, Ramakrishnan V. Structure of the yeast histone acetyltransferase Hat1: insights into substrate specificity and implications for the Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:501-7. PMID:10384314
- ↑ Ngo L, Brown T, Zheng YG. Bisubstrate inhibitors to target histone acetyltransferase 1. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13476. PMID:30637990 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.13476



