Introduction
Histone deacetylase 8 () is an enzyme that plays a role in controlling gene expression. Specifically, HDAC8 removes an acetyl group from the ε-amino-Lys 382 of the N-terminal extension of Histone 4. [1] Histone core particles consist of eight monomer proteins that an octamer complex. Each histone monomer has a net positive charge which enhances the interaction with negatively-charged DNA. This prevents transcription factors from accessing DNA, thus decreasing gene expression. Chromatin remodeling by the addition or removal of an acetyl group on a histone is an example of epigenetic regulation. Histone Acetylase 1 (HAT1) catalyzes the addition of an acetyl group onto a lysine residue in a histone. The lack of charge on the acetylated lysine weakens the interaction between DNA and histones. This subsequently allows transcription factors to access to bind DNA, increasing the potential for gene expression. HDAC8 reverses this reaction by catalyzing the removal of these acetyl groups from the Lys to reclaim the positive charge of the histone. This again allows the histone to interact with the negative charge on the DNA. As a result, DNA binds more tightly to the histone protein, repressing transcription.
HDAC Enzymes and Homology
There are four major classes of HDAC proteins (I,II, III, and IV). Other than the Class III “sirtuins” that utilize a NAD+ cofactor-dependent mechanism [2], all other HDAC classes use Zn2+-assisted catalysis to activate a water molecule for nucleophilic attack.[3] While Classes I, II, and IV do have some major distinctions such as size of the protein, in general, they share homology at the catalytic site. HDAC8 is classified as a Class I HDAC alongside HDACs 1-3. In fact, within Class I HDACs, there are many invariant residues involved in the catalytic site (such as His-Asp dyads), Zn-binding, and ligand binding pocket (such as Asp101) (Figure 1). [1] The structure reported here is of Human HDAC8, a 377 residue, Class I HDAC.
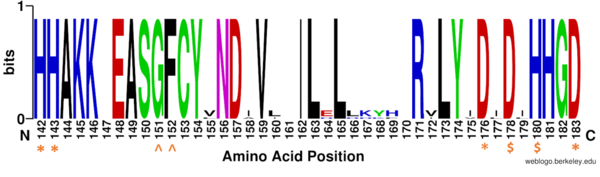
Figure 1: Weblogo representation comparing conservation of residues (143-182 in HDAC8) to homologous sequences in all class I HDACs. Active site residues (asterisk), zinc binding (dollar), and binding pocket residues (caret) are invariant across class I HDACs. Other conserved residues not shown include active site residue Tyr306, zinc binding residue Asp267, and binding pocket residue Asp101. Other conserved residues in the Weblogo image serve as a 'scaffold' for the active site residues, while residues from 158 to 170 are part of an α-helix that transits away from the active site before looping back to it.
HDAC8 Structure
The crystal structure of human HDAC8 was determined to 2.0Å resolution using x-ray crystallography. [1] The structure includes two structural K+ ions and one catalytic Zn2+ ion. HDAC8 is bound to a p53 derived as opposed to the natural histone substrate. This peptide includes a at its C terminus. The HDAC8 secondary structure consists of a with eight parallel β-strands located between 13 .
Zinc Ion
The pentacoordinated Zn2+ ion involved in the metalloenzyme catalysis is tethered to the protein through interactions with . This positions the metal ion to favorably interact with the catalytic water and acetylated lysine substrate. [1] The Zn2+ ion lowers the pKa of the water molecule, activating it as a nucleophile. By binding to both the nucleophile and the substrate simultaneously, the Zn2+ ion also assists the deacetylation process by lowering the entropy of the reaction. Thus, the Zn2+ polarizes the carbonyl of the acetyl-lysine and stabilizes the transition state.[4]
Key Residues
The of HDAC8 possesses two catalytic dyads, His143/Asp183 and His142/Asp176, which activate the catalytic water nucleophile. The mutation of the native Tyr306 to Phe306 in the PDB:2v5w structure was observed to render the protein mostly inactive. Thus, it has been proposed that the hydroxyl group of the tyrosine side chain may be in the oxyanion hole and is critical for stabilization of the transition state. This mutation was essential for the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex that allowed the determination of the crystal structure. [1]
Binding Pocket
By encasing the nonpolar, four-carbon side-chain of the substrate Lys residue, Phe152 and Phe208 engage in hydrophobic Van der Waals interactions with the ligand at different ends of the . Trp141 and Met274 contribute to the overall shape through general hydrophobic interactions.[5] Finally, the carbonyl oxygen of hydrogen bonds with the amide hydrogen of the acetylated lysine to stabilize the ligand in the relatively hydrophobic tunnel.[1]
At the rim of the active site, is involved in two hydrogen bonds between the side-chain carbonyl oxygens and two consecutive backbone amide hydrogens of the incoming peptide derived ligand. This results in the ligand assuming a cis backbone conformation with respect to the substrate lysine. In addition, extensive interactions among many other polar atoms near the rim of the active site help keep the ligand lodged in the hydrophobic tunnel.[1]
Additional Features
There are two bound in the HDAC8 structure. The first K+ is 7Å away from the active site while the second lies toward the exterior of the HDAC8.[6]. It is suggested that the K+ nearer to the active site is of importance because it is tethered to the enzyme by the main chain carbonyl oxygens of which stabilizes the Zn2+ in the active site. Furthermore, the K+ increases the overall positive charge in the active site and this could help stabilize the oxyanion hole that is formed in the transition state.[6]
The (amino acid residues 30-36) may play a role in substrate binding. It is suggested that this loop has high flexibility that enables HDAC8 to more efficiently recognize different ligands. [4] Furthermore, phosphorylation of by protein kinase A (PKA) has been shown to induce formation a salt bridge interaction with Lys36 in the L1-loop. This interaction will stabilize a L1-loop conformational change that can interfere with the interaction between HDAC8 and the target histone. Ultimately this change can prohibit substrate binding, thus regulating the HDAC8 activity.[4]
Mechanism
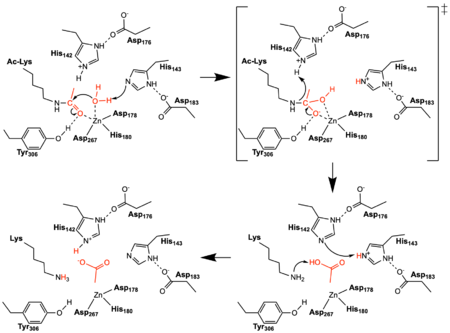
Figure 2: The reaction mechanism catalyzed by HDAC8. The reacting water, acetyl group, and acetate product are shown in red. Tyr306 was mutated to Phe306 to determine the structure in the PDB file 2v5w.
Once the substrate is bound in the active site through interactions with , the bound water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetylated lysine sidechain found in the N terminus of histone proteins (Figure 2). The catalytic water molecule is made acidic through its coordination by the active site Zn
2+ which lowers its pK
a. The first of , His143 and Asp183, shift electron density so that His143 acts as a general base to remove a proton from the acidic water thus creating a nucleophilic hydroxyl ion. The transition state is a tetrahedral oxyanion that is stabilized by the Zn
2+ ion as well as the hydroxyl sidechain of Tyr306. The second catalytic dyad consists of His142 and Asp176 and acts to protonate the lysine sidechain leaving group after collapse of the transition state. The enzyme then resets by shuttling protons between the two histidine residues and between the acetate and lysine products.
[7]
Medical Relevance
HDAC Inhibitors
While there are several classes of
HDAC inhibitors that are used to target different HDAC enzymes, many have common structural motifs that include a zinc-binding moiety, a surface recognition or capping group, and a connecting straight chain alkyl, vinyl, or aryl linker (Figure 3). Such deactivate the enzymes through interactions with the Zn
2+ ion in the active site.
[8]. The capping group is generally hydrophobic and interacts with such as Phe152, Met174, Phe208, Pro273, and Tyr306 residues.
[9][10].
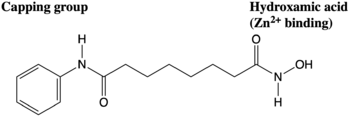
Figure 3. The anticancer agent Vorinostat is an example of an HDAC inhibitor that is currently undergoing clinical trials.
Clinical Application
A variety of HDAC inhibitors are of interest for use as a cancer treatment. HDACs are over expressed in tumor tissue, implying that high amounts of these enzymes are reacting with and deacetylating the p53 protein of which the substrate is derived. The p53 protein is a tumor suppressor that, when deacetylated, is rendered inactive, no longer upregulating genes responsible for cell death, arrest of growth, or DNA repair [11]. A variety of HDAC inhibitors have been developed as potential anticancer agents. Current types of HDAC inhibitors include hydroxamic acids, electrophilic ketones, short chain fatty acids, boronic acid based compounds, benzofuranone, cyclic peptides, and sulfonamides. Of these, two HDAC inhibitors, Vorinostat and Romidepsin have been tested in the clinic as potential anticancer therapeutics.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Vannini, A., Volpari, C., Gallinari, P., Jones, P., Mattu, M., Carfí, A., ... & Di Marco, S. (2007). Substrate binding to histone deacetylases as shown by the crystal structure of the HDAC8–substrate complex. EMBO reports, 8(9), 879-884. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401047
- ↑ Sauve AA, Youn DY. Sirtuins: NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase mechanism and regulation. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2012 Dec;16(5-6):535-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.003., Epub 2012 Oct 23. PMID:23102634 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.003
- ↑ DesJarlais, R., & Tummino, P. J. (2016). Role of histone-modifying enzymes and their complexes in regulation of chromatin biology. Biochemistry, 55(11), 1584-1599. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Somoza J, Skene R. Structural snapshots of human HDAC8 provide insights into the class I histone deacetylases. Structure, 12(7), 1325-1334.2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2004.04.012
- ↑ Whitehead, L., Dobler, M. R., Radetich, B., Zhu, Y., Atadja, P. W., Claiborne, T., ... & Shao, W. (2011). Human HDAC isoform selectivity achieved via exploitation of the acetate release channel with structurally unique small molecule inhibitors. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 19(15), 4626-4634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2011.06.030
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Vannini, A., Volpari, C., Filocamo, G., Casavola, E. C., Brunetti, M., Renzoni, D., ... & Steinkühler, C. (2004). Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(42), 15064-15069. https://dx.doi.org/10.1073%2Fpnas.0404603101
- ↑ Seto, E., & Yoshida, M. (2014). Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 6(4), a018713. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018713
- ↑ Tabackman AA, Frankson R, Marsan ES, Perry K, Cole KE. Structure of 'linkerless' hydroxamic acid inhibitor-HDAC8 complex confirms the formation of an isoform-specific subpocket. J Struct Biol. 2016 Sep;195(3):373-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2016.06.023. Epub 2016, Jun 29. PMID:27374062 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2016.06.023
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a chemical genetics approach to understanding cellular functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct-Dec;1799(10-12):717-25. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.008. Epub 2010 Jun 8. PMID:20594930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.008
- ↑ Vannini A, Volpari C, Filocamo G, Casavola EC, Brunetti M, Renzoni D, Chakravarty P, Paolini C, De Francesco R, Gallinari P, Steinkuhler C, Di Marco S. Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 19;101(42):15064-9. Epub 2004 Oct 11. PMID:15477595
- ↑ Reed SM, Quelle DE. p53 Acetylation: Regulation and Consequences. Cancers (Basel). 2014 Dec 23;7(1):30-69. doi: 10.3390/cancers7010030. PMID:25545885 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cancers7010030



