Esterification
From Proteopedia
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
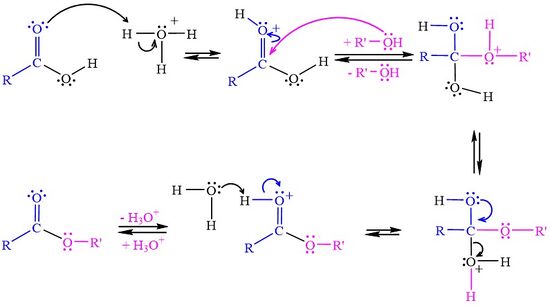
The <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 1 10; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>reaction starts</text></jmolLink></jmol> when the carboxylic acid accepts a proton from the strong acid catalyst. | The <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 1 10; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>reaction starts</text></jmolLink></jmol> when the carboxylic acid accepts a proton from the strong acid catalyst. | ||
| - | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> | + | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. |
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol>, the zzzz. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol>, the zzzz. | ||
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol>, the aaaa. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol>, the aaaa. | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 18 July 2021
Contents |
Esterification
Esterification is a chemical reaction of an acid with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR').
Usually esterification refers to reaction between an organic (carboxylic) acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR') and water and called Fischer esterification.
The chemical reaction for Fischer esterification is given below:
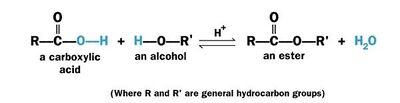
Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol
Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol |
| Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate |
The when the carboxylic acid accepts a proton from the strong acid catalyst. In the the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. In the , the zzzz. In the , the aaaa. In the , the bbbb.
An animated example of this reaction is shown. Please click on the buttons below to animate the reaction with different representations. Use the popup button to enlarge the view and the quality button to turn on anti-aliasing.
The animation was originally done by Prof. Dr. Verena Pietzner; for details, see her web site ChiLe[1]. The implementation into Proteopedia was done by Prof. Jaime Prilusky, Prof. Joel L. Sussman and Veronika Pelekhov.
See also
SN1 reaction: Substitution of Cl− and tert-Butanol
SN2 reaction: substitution of Cl− and methanol
