Esterification
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='' scene='88/887592/Esterification_with_fifth_step/1'> | ||
==Esterification== | ==Esterification== | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol' scene='88/887592/Esterification_with_fifth_step/1'> | ||
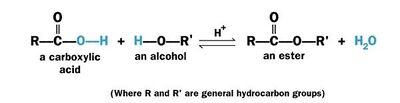
Esterification is a chemical reaction of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid acid] with an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcohol alcohol] (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR'). | Esterification is a chemical reaction of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid acid] with an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcohol alcohol] (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR'). | ||
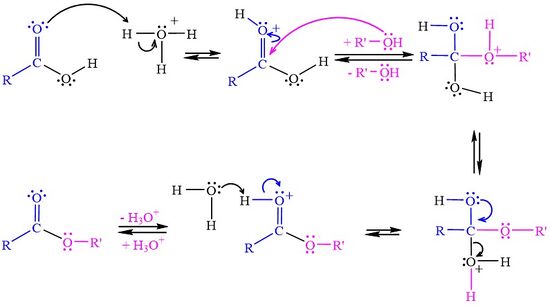
Usually esterification refers to reaction between an organic (carboxylic) acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR') and water and called '''Fischer esterification'''. | Usually esterification refers to reaction between an organic (carboxylic) acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR') and water and called '''Fischer esterification'''. | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 18 July 2021
Esterification
| |||||||||||
See also
SN1 reaction: Substitution of Cl− and tert-Butanol
SN2 reaction: substitution of Cl− and methanol