This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox SN2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
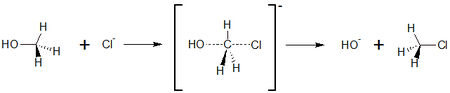
==S<sub>N</sub>2-substitution of chloride and methanol== | ==S<sub>N</sub>2-substitution of chloride and methanol== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='SN2 - Substitution of Cl and Methanol' scene='88/887016/Sn2_cl_rt/ | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='SN2 - Substitution of Cl and Methanol' scene='88/887016/Sn2_cl_rt/6'> |
SN2 reaction is a basic reaction type in organic chemistry. The letter S<sub>N</sub> stands for nulceophilic Substitution, the number 2 stands for bimolecular, with both reactions partners are involved in the reaction rate-determining step. It also exists an S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction; here, only one reaction partner is involved in this step. On the other side, SN2 reactions are characterized by exchanging substituents. The substituent that leaves the molecule is called leaving group. | SN2 reaction is a basic reaction type in organic chemistry. The letter S<sub>N</sub> stands for nulceophilic Substitution, the number 2 stands for bimolecular, with both reactions partners are involved in the reaction rate-determining step. It also exists an S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction; here, only one reaction partner is involved in this step. On the other side, SN2 reactions are characterized by exchanging substituents. The substituent that leaves the molecule is called leaving group. | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 18 July 2021
SN2-substitution of chloride and methanol
| |||||||||||
See also
SN1 reaction: Substitution of Cl− and tert-Butanol
References
- ↑ Wang Y, Song H, Szabo I, Czako G, Guo H, Yang M. Mode-Specific SN2 Reaction Dynamics. J Phys Chem Lett. 2016 Sep 1;7(17):3322-7. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b01457. Epub, 2016 Aug 12. PMID:27505286 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b01457
- ↑ ChiLe Web Site