Growth factors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The <scene name='80/801744/Cv/4'>kinase domain of M-CSF receptor interacts with a drug-designed inhibitor</scene> via the conserved kinase DFG motif (colored in salmon) and its gatekeeper threonine residue (colored in magenta)<ref>PMID:23493555</ref>. | The <scene name='80/801744/Cv/4'>kinase domain of M-CSF receptor interacts with a drug-designed inhibitor</scene> via the conserved kinase DFG motif (colored in salmon) and its gatekeeper threonine residue (colored in magenta)<ref>PMID:23493555</ref>. | ||
*[[Epidermal growth factor]] and [[Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor]] | *[[Epidermal growth factor]] and [[Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor]] | ||
| + | [[Lapatinib]] is a EGFR inhibitor used in breast cancer treatment. EGFRs are overexpressed in many types of human carcinomas including lung, pancreatic, and breast cancer, and are often mutated. This overexpression leads to excessive activation of the anti-apoptotic [[Ras]] signaling cascade, resulting in uncontrolled [[DNA_Replication|DNA synthesis]] and cell proliferation. The <scene name='Lapatinib/Egfr/1'>EGFR tyrosine kinase domain</scene> is responsible for activating this Ras signaling cascade. Upon binding ligands like Epidermal Growth Factor, EGFR dimerizes and autophosphorylates several tyrosine residues at its C-terminal domain. Upon phosphorylation, EGFR undergoes a significant conformational shift, revealing an additional binding site capable of binding and activating downstream signaling proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Gefitinib]] inhibits the EGFR by <scene name='Gefitinib/Bound/1'>binding to the ATP-binding site</scene> located within the kinase domain. Residues Lys745, Leu788, Ala743, Thr790, Gln791, Met193, Pro794, Gly796, Asp800, Ser719, Glu762, & Met766 tightly bind the inhibitor. Unable to bind ATP, EGFR is incapable of autophosphorylating its C-terminal tyrosines, and the uncontrolled cell-proliferation signal is terminated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Erlotinib]] inhibits the EGFR by <scene name='Erlotinib/Bound/1'>binding to the ATP-binding site</scene> located within the kinase domain. EGFR uses residues Asp831, Lys721, Thr766, Leu820, Gly772, Phe771, Leu694, Pro770, Met769, Leu768, Gln767 & Ala719 to tightly bind the inhibitor. Unable to bind ATP, EGFR is incapable of autophosphorylating its C-terminal tyrosines, and the uncontrolled cell-proliferation signal is terminated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Herceptin - Mechanism of Action]] | ||
| + | |||
*[[Ephrin]] and [[Ephrin receptor]] | *[[Ephrin]] and [[Ephrin receptor]] | ||
*[[Erythropoietin]] and [[Erythropoietin receptor]] | *[[Erythropoietin]] and [[Erythropoietin receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 27 July 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mohedas AH, Wang Y, Sanvitale CE, Canning P, Choi S, Xing X, Bullock AN, Cuny GD, Yu PB. Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants. J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7900-15. doi: 10.1021/jm501177w. Epub 2014 Sep 4. PMID:25101911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm501177w
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
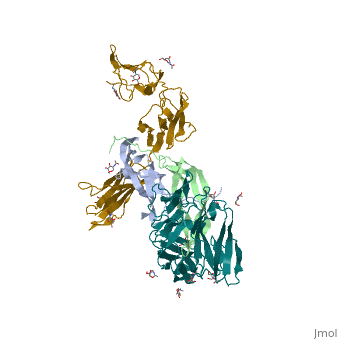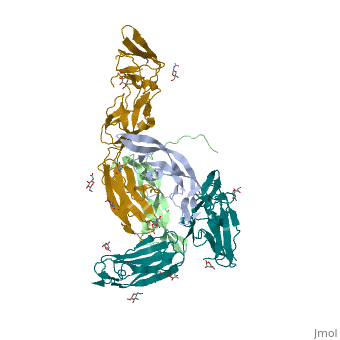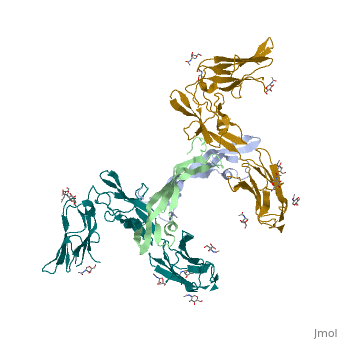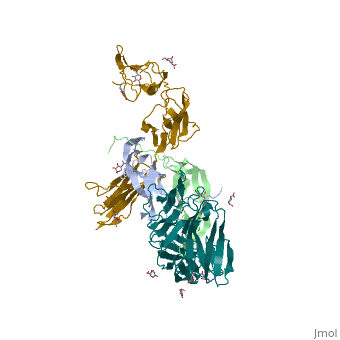
- ↑ Felix J, De Munck S, Verstraete K, Meuris L, Callewaert N, Elegheert J, Savvides SN. Structure and Assembly Mechanism of the Signaling Complex Mediated by Human CSF-1. Structure. 2015 Jul 21. pii: S0969-2126(15)00272-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019. PMID:26235028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019
- ↑ Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Zhang J, Burton EA, Habets G, Zhang Y, Powell B, West BL, Matusow B, Tsang G, Shellooe R, Carias H, Nguyen H, Marimuthu A, Zhang KY, Oh A, Bremer R, Hurt CR, Artis DR, Wu G, Nespi M, Spevak W, Lin P, Nolop K, Hirth P, Tesch GH, Bollag G. Design and pharmacology of a highly specific dual FMS and KIT kinase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 14. PMID:23493555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219457110