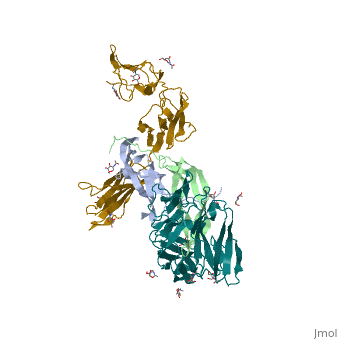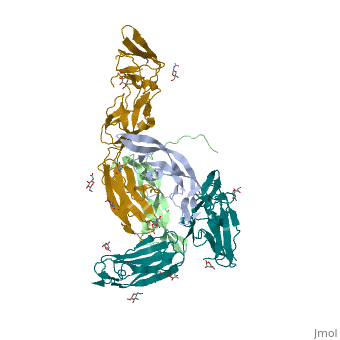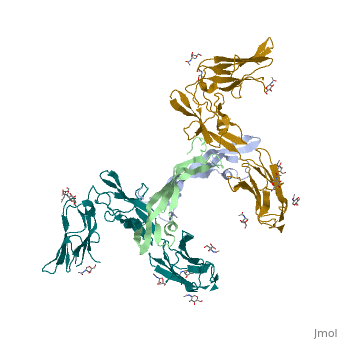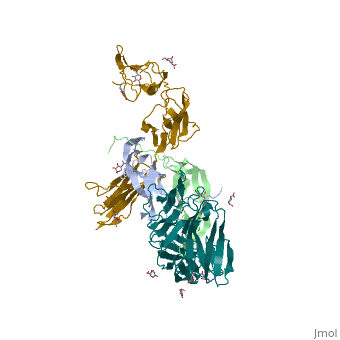
3D structure of the kinase domain of Activin receptor1 (Acvr1) complex with inhibitor shows with the protein including a and a [1]. Water molecule is shown as red sphere.
Rabbit [2]. Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
The structure of the complex between M-CSF and its receptor shows that a . There are [3]. .
The via the conserved kinase DFG motif (colored in salmon) and its gatekeeper threonine residue (colored in magenta)[4].
Lapatinib is a EGFR inhibitor used in breast cancer treatment. EGFRs are overexpressed in many types of human carcinomas including lung, pancreatic, and breast cancer, and are often mutated. This overexpression leads to excessive activation of the anti-apoptotic Ras signaling cascade, resulting in uncontrolled DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. The is responsible for activating this Ras signaling cascade. Upon binding ligands like Epidermal Growth Factor, EGFR dimerizes and autophosphorylates several tyrosine residues at its C-terminal domain. Upon phosphorylation, EGFR undergoes a significant conformational shift, revealing an additional binding site capable of binding and activating downstream signaling proteins.
Gefitinib inhibits the EGFR by located within the kinase domain. Residues Lys745, Leu788, Ala743, Thr790, Gln791, Met193, Pro794, Gly796, Asp800, Ser719, Glu762, & Met766 tightly bind the inhibitor. Unable to bind ATP, EGFR is incapable of autophosphorylating its C-terminal tyrosines, and the uncontrolled cell-proliferation signal is terminated.
Erlotinib inhibits the EGFR by located within the kinase domain. EGFR uses residues Asp831, Lys721, Thr766, Leu820, Gly772, Phe771, Leu694, Pro770, Met769, Leu768, Gln767 & Ala719 to tightly bind the inhibitor. Unable to bind ATP, EGFR is incapable of autophosphorylating its C-terminal tyrosines, and the uncontrolled cell-proliferation signal is terminated.
See also Herceptin - Mechanism of Action
Ephrins (Eph) are the membrane-bound ligands of ephrin receptors. The binding of Eph and ephrin receptors is achieved via cell-cell interaction. Eph/Eph receptor signaling regulates embryonic development, guidance of axon growth, long-term potentiation, angiogenesis and stem-cell differentiation [5]. Eph-A5 is implicated in spinal cord injury. Eph-A1 is implicated in myocardial injury and renal reperfusion injury. (PDB code 3mx0).[6]
. Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
.
(3fxx).[7]
Ephrin Type-A Receptor
The includes the N-terminal ephrin (Ligand)-binding domain (LBD), a cysteine-rich domain (CRD), and 2 fibronectin Type-III Repeats (FN3). EphA binds ephrins with . Most ephrins have a similar rigid structure which , AB, CD, FG, & GH. The LBD of EphA4 is said to be a “structural chameleon” able bind both A and B class ephrins. This explains why Ephrin Type-A receptors exhibit cross-class reactivity. The includes four important loops, the BC, DE, GH, & JK loops. EphA4 binds the GH loop of the ephrin ligand created by the EphA4 DE and JK loops. It is these loops, DE and JK, which undergo the greatest conformational shifts when binding either EphrinA2 or EphrinB2. , EphA4-Arg 162 forms a hydrogen bond with EphrinA2-Leu 138, while EphA4-Met 164 and EphA4-Leu 166 participate in hydrophobic interactions with EphrinA2-Leu 138 and EphrinA2-PHe 136. Although in the same binding pocket, the local interactions are significantly different. Most notably, the α-helix present in the EphA4-EphrinA2 JK loop is disrupted in the EphA4-EphrinB2 structure. This is due to that would occur between EphrinB2-Trp 122 and EphA4 Met 164. Instead, EphA4-Arg 162 and EphrinB2-Trp 122 form hydrophobic stacking interactions which stabilize the receptor-ligand complex. A morph of the movements EphA4 undergoes to bind EphrinA2 and EphrinB2 can be .
Eph-Ephrin complexes form two unique heterotetrameric assemblies consisting of distinct EphA2-EphA2 interfaces. is generated by . The 2nd involves complex and in the region .[8] These two heterotetramers generate a (). The proximity of kinase domains in an eph-ephrin tetramer, favors transphosphorylation of tyrosines in the cytoplasmic domains. Phosphorylation promotes kinase activity by orienting the activation segment of the kinase domain in a way that favors subsrate binding and subsequent signaling.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a glycoprotein composed of only . The sulfur of the cysteine residues links to form disulfide bonds. These disulfide bonds help keep EPO's structure. Helix A is connected to Helix D by , while Helix A and Helix B are connected by . EPO’s structure was determined in 1993. It is made up of four alpha helixes. EPO is produced mainly in the kidney, but further research has shown the brain and liver still produce small amounts.
The of the blood marrow is part of the hematipoietic cytokine family. This receptor has a single transmembrane domain, that forms a homodimer complex until it is activated by the binding of EPO. This receptor is 484 amino acids long and weigh 52.6 kDa. Once the homodimer is formed after the binding, autophosphorlation of the Jak2 kinases, which activates other cellular processes. This transmembrane receptor has two extracellular domains. This receptor has two disulfide bonds that are formed from 4 cystine residues, . The intracellular domain of this receptor does not possess any enzymatic activity like other receptors. When EPO comes in contact with the extracellular domains form a ligand bond. The extracellular sinding site 1 and Binding site 2 are composed of . When EPO binds, all loops on D1 and D2 of binding site one form a bind with EPO. However loop 4 of D1 on binding site 2 does not participate in the binding of EPO [9]. After the biniding of EPO, 8 tyrosine residues are phosphoralated which activates the . This kinase helps regulate the transcription of different genes and expression of other proteins.
(PDB code 1cn4).[10]
[11]. Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
FGFR consist of an extracellular ligand-binding domain (LBD), transmembrane helix domain and cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase activity domain (TKD) with phosphorylated tyrosine designated PTR. FGFR LBD contains 3 immunoglobulin-like domains D1, D2 and D3. (PDB code 1evt).
For more details see Group:MUZIC:Myostatin. See also Bone morphogenetic protein.
The A loop of the wt receptor contains 2 tyrosines at position 1234 and 1235. When these 2 residues become phosphorylated, the kinase can become active. A unique part of the c-met structure is the pair of . These tyrosines are necessary for normal c-met signaling. When these 2 tyrosines were substituted with with phenylalanine in mice, the mice had an embryonically lethal phenotype and defects were found in placenta, liver, muscles and nerves. In a wt c-met, these sites will become phosphorylated and act as docking sites for many different transducers and adapters. Upon phosphorylation, these tyrosines can bind with Src homology 2 (SH2) domains and phophotyrosine-binding (PTB), and therefore bind many effectors that will cause downstream effects such as cell proliferation, scattering and inhibition of apoptosis. This receptor follows the typical structure of a protein kinase, with a bilobal structure. The N-terminal contains and is linked through a hinge to the C lobe, which is full of α helices. This particular kinase domain is very similar to the domains of the insulin receptor kinase and fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase.[12] This structure is made up of many α-helices that move in the transformation from inactive to active kinase. Some of these helices are conserved in many different tyrosine kinases. C-met does show a divergence from other tyrosine kinases (such as IRK and FGFRK) in the helix formed at the N-terminus, before the core kinase domain, in residues . The αA is in contact with αC and so causes αC to be in a slightly different orientation than in FGFRK and IRK. Residues Leu-1062, Val-1066, and Val-1069 of αA with with residues Leu-1125 and Ile-1129 of αC. There is another between the residues Ile-1053, Leu-1055 and Leu-1058 of αA and Ile-1118 and Val-1121 of αC. Because of the movement of αC during activation of the kinase, it is an assumption that αA is also part of the kinase activation upon ligand binding.
The particular structure of the hepatocyte growth factor tyrosine kinase domain is one harboring a human cancer mutation. The 2
are replaced by a phenylalanine and aspartate, respectively. This mutation normally causes the receptor to be constitutively active, and is found in HNSC (Head, Neck squamous cell) carcinoma. Although there is no longer phosphorylation at these sites, it is believed that the negative charge of the aspartate resembles the negative phosphate that would normally cause activation, and therefore keeps the protein in its active form. [13] There is a 3rd mutation at Tyr-1194 which is substituted for a . This is shown to point into the formed by Lys-1198 and Leu-1195 from αE. [14] This structure is conserved in the wild type protein, suggesting that the mutation at residue 1149 is not changing the structure at this position.
is a staurosporine analog. Staurosporine is an inhibitor of many Ser/Thr Kinases, and has been shown to also inhibit c-Met activation by inhibiting its autophosphorylation. The structures of K-252a and staurosporine are very similar, with the main difference being that K-252a has a furanose instead of a pyranose structure. The binding of K-252a causes the c-Met to adopt an inhibitory conformation of the A-loop, specifically with residues . This segment blocks the place where the substrate tyrosine side chain would bind, if the protein were in an active conformation. Residues
also enhance this inhibitory conformation, as they constrain αC into a conformation that does not allow the catalytic placement of keeping αC in an inactive conformation. In an active kinase, Glu-1127 would form a salt bridge with Lys-1110.
Residues 1229-1230 pass through the triphosphate subsite of bound ATP blocking ATP binding. The K-252a itself binds in the adenosine pocket, therefore also inhibiting the binding of ATP. The binding of K-252a is very favorable. This is probably due to polar interactions as well as a change in conformation upon binding. There is a concerted conformational change in the complex upon K-252a binding. One of these changes involves the A-loop, specifically residues . In the Apo-Met structure, the side chain of Met-1229 would pass through the ring of the inhibitor, and so, in order to make room for K-252a, the segment must move, with residues 1229 and 1230 moving by 3-4 Å. In order to make room for the side chain of Tyr-1230, moves by 8 Å toward . Arg-1208, which in the uninhibited complex would stack with tyr-1230, now stacks with
. K-252a binds in the adenosine pocket. It has 4 hydrogen bonds to the enzyme, with of these mimicking hydrogen bonds of an adenine base. There is a hydrogen bond between the K-252a nitrogen and the carbonyl oxygen of Pro-1158, and another between the K252-a carbonyl oxygen and the hydrogen of the amide of Met-1160. There are 2 more hydrogen bonds between the 3' hydroxyl and carbonyl oxygen and the of the A loop. There are also many hydrophobic interactions between the interface of the enzyme and K-252a. The residues involved in this are Ile-1084, Gly-1085, Phe-1089, Val-1092, Ala-1108, Lys-1110, and Leu-1140 (); Leu-1157, Pro-1158, Tyr-1159, and Met-1160 (); and Met-1211, Ala-1226, Asp-1228, Met-1229, and Tyr-1230 (). Met-1229, Met-1211 and Met-1160 all make up the for the indolocarbazole plane as they are all within van der Waals distance of it.
In c-Met, there are 2 tyrosines located in the C-terminal tail sequence, which, upon phosphorylation, act as the docking sites for many signal transducers. These tyrosines correspond to residues . Both of these sites interact with SH2, MBD and PTD domains of signal transducers. The residues form an extended conformation, which is seen in other phosphopeptides that bind to SH2 domains. Residues
form a type I β turn, which is similar to sequences that bind to Shc-PTB domians. Whether binding to SH2 domains or PTB domains, upon binding, these motifs would move to avoid clashes with the C lobe. The 3rd binding motif is found in residues , which form a type II β turn, and is similar to pohsphopeptides that bind Grb2. When comparing the unphosphorylated conformation of the motif to one that is phosphorylated, and bound to the Grb2 complex, there is a peptide flip between the bind of . This suggests that when Grb2 docks onto c-Met, there is a change in orientation of this motif. These 3 binding motifs of the mutated structure are very similar to binding motifs that would be recognized by their binding partners, implying that the C-terminal supersite of this structure is very similar to that of an active c-met.
Memory-Enhancement by Traditional Chinese Medicine? [15]
(IGF-IR, in darkmagenta) activation is critical for IGF-I to elicit desirable cognitive functions. Molecular dynamics simulation revealed that the Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) ligands were secured at the opening of the IGF-IR binding site for the duration of the MD. was stabilized by , was stabilized by , and was stabilized by (key residues are colored in yellow).
Interleukin (IL) is a cytokine which functions in the immune system. IL families are denoted by numbers[16].
IL-1 is a group of 11 cytokines which regulate immune and inflammatory response. See Interleukin-1 beta.
IL-2 is a cytokine made by leukocytes. It is used in cancer therapy to boost the immune system.
IL-3 improves the body's natural response to disease by stimulating the differentiation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells into myeloid or lymphoid progenitor cells.
IL-4 induces the differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0) to Th2 cells.
IL-5 stimulates B cell growth and increases immunoglobulin secretion.
IL-6 is both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and anti-inflammatory myokine.
IL-7 is a cytokine important for B and T cells development.
IL-8 induces chemotaxis and phagocytosis.
IL-10 see Interleukin-10 and Inflammation & Rheumatoid Arthritis.
IL-11 involved in the stimulation of megakaryocyte maturation.
IL-12 induces the differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0) to Th1 cells. See Interleukin-12.
IL-13 induces the differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0) to Th2 cells.
IL-15 see Interleukin-15.
IL-16 acts as chemoattractant, modulator of T cell activity and inhibitor of HIV replication.
IL-17 recruits monocytes and neutrophils to the site of inflammation.
IL-18 induces cell-mediated immunity following infection by microbial lipopolysaccharides.
IL-19 induces activation of the signal transducer and activator of STAT3.
IL-21 has potent effect on natural killer cells.
IL-22 stimulates inflammatory responses like S100 and defensin.
IL-23 induces activation of the signal transducer and activator of STAT4.
IL-24 induces activation of the signal transducer and activator of STAT1 and STAT3.
IL-28 has a role in the immune defense against viruses.
IL-29 similar to IL-28.
IL-33 induces helper T cells, mast cells, eosinophils and basophils to produce type 2 cytokines.
IL-34 increases growth or survival of monocytes.
IL-36 acts on naïve CD4+ T cells.
IL-37 has a role in inhibiting both innate and adaptive immune responses.
The complex between NT3 and p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) shows a . There are 3 sites of interactions between NT3 and p75NTR - site 1, site 2 and site 3.
.
.
.
TrkA. Trk stands for Topomyosin-Related Kinase. TrkA ligand - nerve growth factor activates the receptor by stabilizing homodimer formation which initiates transautophosphorylation. . An , conserved in all neutrophins, forms the most important binding determinant between TrkA and its ligand - nerve growth factor - which forms the active homodimer of the receptor. .
TRK-A contains an extracellular ligand binding domain (LBD), a transmembrane helix and an intracellular region which contains the kinase domain. The kinase domain (4yne) contains the tripeptide DFG which flips out in TRK-A inactivated form. (4yne). The structure of the complex of TRK-A with the phenylpyrrolidine derivative shows the inhibitor forming hydrogen bonds to Met620 and Lys572 residues and π-π interactions of it with Phe617 and Phe 698.
The (2ifg) is a 2:2 dimer. The C-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain interacts with the NGF. The extracellular domain of TRK-A contains flanked by (in yellow), 2 immunoglobulin-like domains and the nerve growth factor (NGF) binding domain.
. TrkB and neutrotrophin-4/5 interact via a and via a .
The biological assembly of human tumor necrosis factor is (PDB entry 2az5). .
TRAIL-R2 is called DR5. (1d0g).
The extracellular domain of TNFR contains 2 to 6 cysteine-rich domains (CRD). The . The CRDs are involved in binding of TNF[17]. . Water molecules are shown as red spheres.
See also: