Growth factors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
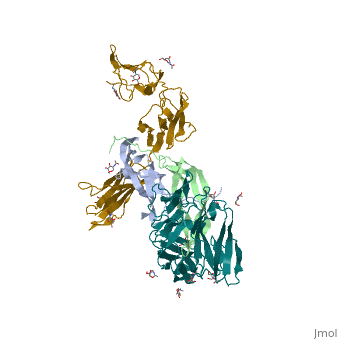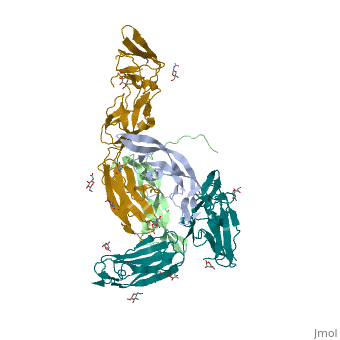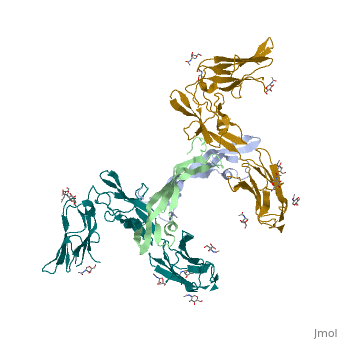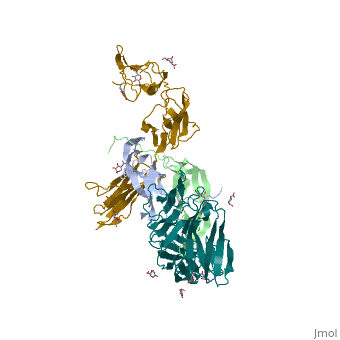
Each monomer contains a central antiparallel beta sheet, with the canonical <scene name='41/411433/Knot_new/3'>cysteine knot </scene> found in other VEGFs. <ref>PMID:1396586</ref> The knot consists of an eight residue ring formed by the backbone of residues 57-61 and 102-104 and intramolecular disulfide bridges Cys57-Cys102 and Cys61-Cys104, and a third bridge, Cys26-Cys68, that passes perpendicularly through the ring. Each VEGF-E monomer contains an amino terminal alpha helix and three solvent accessible loop regions, L2, <scene name='41/411433/Vegf-e_l1_l3/3'>L1 and L3 </scene>. | Each monomer contains a central antiparallel beta sheet, with the canonical <scene name='41/411433/Knot_new/3'>cysteine knot </scene> found in other VEGFs. <ref>PMID:1396586</ref> The knot consists of an eight residue ring formed by the backbone of residues 57-61 and 102-104 and intramolecular disulfide bridges Cys57-Cys102 and Cys61-Cys104, and a third bridge, Cys26-Cys68, that passes perpendicularly through the ring. Each VEGF-E monomer contains an amino terminal alpha helix and three solvent accessible loop regions, L2, <scene name='41/411433/Vegf-e_l1_l3/3'>L1 and L3 </scene>. | ||
| - | are able to form a complex hydrogen bond network as well as extensive hydrophobic contacts with VEGFR making these loops ideal receptor specificity determinants. Residues: P34, S36, T43, P50, R46, D63, E64, and E67 make up the <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor/Vegf-e_binding_site/1'>VEGF-E binding pocket </scene>and are critical for binding to VEGFR-2 as determined by alanine mutagenesis.<ref> PMID:16672228</ref> Further, the salt bridge between <scene name='41/411433/Vegf-e_salt_bridge/4'>R46 and E64 </scene> is believed to be the source of VEGF-E’s VEGFR-2 specificity by preventing binding to VEGFR-1. <ref>PMID:15272021</ref> | + | are able to form a complex hydrogen bond network as well as extensive hydrophobic contacts with VEGFR making these loops ideal receptor specificity determinants. Residues: P34, S36, T43, P50, R46, D63, E64, and E67 make up the <scene name='Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor/Vegf-e_binding_site/1'>VEGF-E binding pocket </scene>and are critical for binding to VEGFR-2 as determined by alanine mutagenesis.<ref> PMID:16672228</ref> Further, the salt bridge between <scene name='41/411433/Vegf-e_salt_bridge/4'>R46 and E64 </scene> is believed to be the source of VEGF-E’s VEGFR-2 specificity by preventing binding to VEGFR-1. <ref>PMID:15272021</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | [[Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor]]s (VEGFRs) are [[tyrosine kinase receptors]] responsible for binding with [[VEGF]] to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects. The tyrosine kinase domain of VEGFR-2 is separated into 2 segments with a 70 amino acid long kinase insert region. Upon binding VEGFA and subsequent dimerization, VEGFR-2 is autophosphoryalted at the carboxy terminal tail and kinase insert region, 6 tyrosine residues of VEGFR2 are autophosphorylated. <scene name='41/411436/Cv/2'>Auto-phosphorylation of residues 1054 and 1059</scene> within the activation loop of VEGFR2 leads to increased kinase activity. <scene name='41/411436/Cv/4'>Anti-tumor inhibitor binding site</scene> ([[3c7q]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Bevacizumab]]. | ||
| + | |||
*[[TGF-beta receptor|Transforming Growth Factor and its receptor]] | *[[TGF-beta receptor|Transforming Growth Factor and its receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 5 August 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mohedas AH, Wang Y, Sanvitale CE, Canning P, Choi S, Xing X, Bullock AN, Cuny GD, Yu PB. Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants. J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7900-15. doi: 10.1021/jm501177w. Epub 2014 Sep 4. PMID:25101911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm501177w
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
- ↑ Felix J, De Munck S, Verstraete K, Meuris L, Callewaert N, Elegheert J, Savvides SN. Structure and Assembly Mechanism of the Signaling Complex Mediated by Human CSF-1. Structure. 2015 Jul 21. pii: S0969-2126(15)00272-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019. PMID:26235028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019
- ↑ Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Zhang J, Burton EA, Habets G, Zhang Y, Powell B, West BL, Matusow B, Tsang G, Shellooe R, Carias H, Nguyen H, Marimuthu A, Zhang KY, Oh A, Bremer R, Hurt CR, Artis DR, Wu G, Nespi M, Spevak W, Lin P, Nolop K, Hirth P, Tesch GH, Bollag G. Design and pharmacology of a highly specific dual FMS and KIT kinase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 14. PMID:23493555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219457110
- ↑ Egea J, Klein R. Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007 May;17(5):230-8. Epub 2007 Apr 8. PMID:17420126 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2007.03.004
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120
- ↑ Davis TL, Walker JR, Allali-Hassani A, Parker SA, Turk BE, Dhe-Paganon S. Structural recognition of an optimized substrate for the ephrin family of receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS J. 2009 Aug;276(16):4395-404. PMID:19678838 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07147.x
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120
- ↑ Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B, Zhan H, Osslund TD, Chirino AJ, Zhang J, Finer-Moore J, Elliott S, Sitney K, Katz BA, Matthews DJ, Wendoloski JJ, Egrie J, Stroud RM. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature. 1998 Oct 1;395(6701):511-6. PMID:9774108 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/26773
- ↑ Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B, Zhan H, Osslund TD, Chirino AJ, Zhang J, Finer-Moore J, Elliott S, Sitney K, Katz BA, Matthews DJ, Wendoloski JJ, Egrie J, Stroud RM. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature. 1998 Oct 1;395(6701):511-6. PMID:9774108 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/26773
- ↑ Kulahin N, Kiselyov V, Kochoyan A, Kristensen O, Kastrup JS, Berezin V, Bock E, Gajhede M. Dimerization effect of sucrose octasulfate on rat FGF1. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2008 Jun 1;64(Pt, 6):448-52. Epub 2008 May 16. PMID:18540049 doi:10.1107/S174430910801066X
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Hung IC, Chang SS, Chang PC, Lee CC, Chen CY. Memory enhancement by traditional Chinese medicine? J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Dec 19. PMID:23249175 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.741052
- ↑ Dinarello CA. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108-15. PMID:3277884
- ↑ Naismith JH, Devine TQ, Kohno T, Sprang SR. Structures of the extracellular domain of the type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Structure. 1996 Nov 15;4(11):1251-62. PMID:8939750
- ↑ Robinson CJ, Stringer SE. The splice variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors. J Cell Sci. 2001 Mar;114(Pt 5):853-65. PMID:11181169
- ↑ Muller YA, Li B, Christinger HW, Wells JA, Cunningham BC, de Vos AM. Vascular endothelial growth factor: crystal structure and functional mapping of the kinase domain receptor binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 8;94(14):7192-7. PMID:9207067
- ↑ Keyt BA, Nguyen HV, Berleau LT, Duarte CM, Park J, Chen H, Ferrara N. Identification of vascular endothelial growth factor determinants for binding KDR and FLT-1 receptors. Generation of receptor-selective VEGF variants by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 8;271(10):5638-46. PMID:8621427
- ↑ Oefner C, D'Arcy A, Winkler FK, Eggimann B, Hosang M. Crystal structure of human platelet-derived growth factor BB. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3921-6. PMID:1396586
- ↑ Pieren M, Prota AE, Ruch C, Kostrewa D, Wagner A, Biedermann K, Winkler FK, Ballmer-Hofer K. Crystal structure of the Orf virus NZ2 variant of vascular endothelial growth factor-E. Implications for receptor specificity. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 14;281(28):19578-87. Epub 2006 May 3. PMID:16672228 doi:10.1074/jbc.M601842200
- ↑ Errico M, Riccioni T, Iyer S, Pisano C, Acharya KR, Persico MG, De Falco S. Identification of placenta growth factor determinants for binding and activation of Flt-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 15;279(42):43929-39. Epub 2004 Jul 21. PMID:15272021 doi:10.1074/jbc.M401418200