We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ku protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
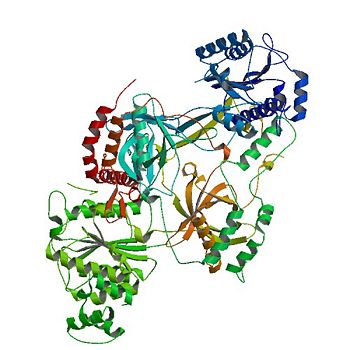
<scene name='56/567269/Ku_heterodimer/3'>heterodimer</scene> | <scene name='56/567269/Ku_heterodimer/3'>heterodimer</scene> | ||
composed of a | composed of a | ||
| - | <scene name='56/567269/Ku70_subunit/3'>Ku70 subunit</scene> | + | <scene name='56/567269/Ku70_subunit/3'>Ku70 subunit</scene> or '''X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6''' |
| - | and a <scene name='56/567269/Ku80_subunit/3'>Ku80 subunit</scene> | + | and a <scene name='56/567269/Ku80_subunit/3'>Ku80 subunit</scene> or '''X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5''' |
. This contributes to genomic integrity through its ability to bind DNA double-strand breaks and facilitate repair by the non-homologous end-joining pathway. The crystal structure of the human Ku heterodimer was determined both alone and | . This contributes to genomic integrity through its ability to bind DNA double-strand breaks and facilitate repair by the non-homologous end-joining pathway. The crystal structure of the human Ku heterodimer was determined both alone and | ||
<scene name='56/567269/Bound_dna/3'>bound to a 55-nucleotide DNA</scene> | <scene name='56/567269/Bound_dna/3'>bound to a 55-nucleotide DNA</scene> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Ku protein
Updated on 14-October-2021
1jey, 5y58 – hKu70 + Ku80 + DNA – human
1jeq – hKu70 + Ku80
7axz – hKu70 + Ku80 – Cryo EM
6zh6 – hKu80 + DNA-dependent protein kinase – Cryo EM
7k0y, 7k1j, 7k1k, 7k1n – hKu70 + Ku80 + DNA-dependent protein kinase – Cryo EM
6erf, 6erg, 6erh – hKu70 + Ku80 + non-homologous end-joining factor + DNA
1jjr – hKu70 C terminal - NMR
1rw2, 1q2z – hKu80 C terminal - NMR
6tyt, 6tyu, 6tyv, 6tyw, 6tyx, 6tyz – hKu80 von Willebrand domain 1-242 (mutant) + peptide
7lt3 – hKu70 + Ku80 in NHEJ synaptic complex – Cryo EM
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 Walker JR, Corpina RA, Goldberg J. Structure of the Ku heterodimer bound to DNA and its implications for double-strand break repair. Nature. 2001 Aug 9;412(6847):607-14. PMID:11493912 doi:10.1038/35088000
- ↑ Bennett SM, Neher TM, Shatilla A, Turchi JJ. Molecular analysis of Ku redox regulation. BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Aug 28;10:86. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-86. PMID:19715578 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-86
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Polotnianka RM, Li J, Lustig AJ. The yeast Ku heterodimer is essential for protection of the telomere against nucleolytic and recombinational activities. Curr Biol. 1998 Jul 2;8(14):831-4. PMID:9663392
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bertuch AA, Lundblad V. The Ku heterodimer performs separable activities at double-strand breaks and chromosome termini. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8202-15. PMID:14585978
- ↑ Berg, Jeremy M., John L. Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer. Biochemistry. 7th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman and, 2012. ISBN-10: 1-4292-2936-5