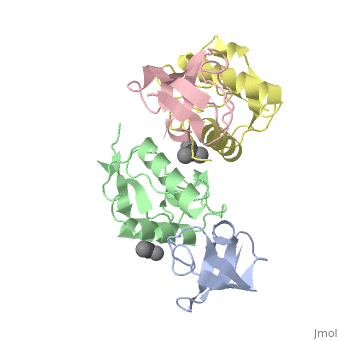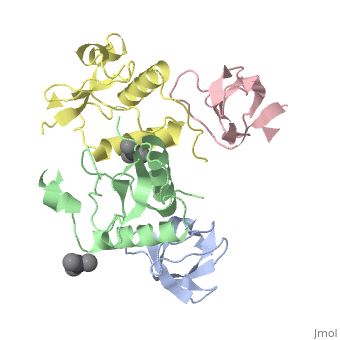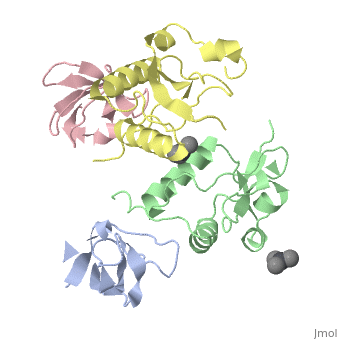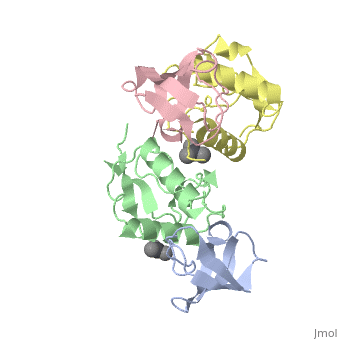| Structural highlights
Function
[FYN_HUMAN] Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays a role in many biological processes including regulation of cell growth and survival, cell adhesion, integrin-mediated signaling, cytoskeletal remodeling, cell motility, immune response and axon guidance. Inactive FYN is phosphorylated on its C-terminal tail within the catalytic domain. Following activation by PKA, the protein subsequently associates with PTK2/FAK1, allowing PTK2/FAK1 phosphorylation, activation and targeting to focal adhesions. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and motility through phosphorylation of CTNNB1 (beta-catenin) and CTNND1 (delta-catenin). Regulates cytoskeletal remodeling by phosphorylating several proteins including the actin regulator WAS and the microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and MAPT. Promotes cell survival by phosphorylating AGAP2/PIKE-A and preventing its apoptotic cleavage. Participates in signal transduction pathways that regulate the integrity of the glomerular slit diaphragm (an essential part of the glomerular filter of the kidney) by phosphorylating several slit diaphragm components including NPHS1, KIRREL and TRPC6. Plays a role in neural processes by phosphorylating DPYSL2, a multifunctional adapter protein within the central nervous system, ARHGAP32, a regulator for Rho family GTPases implicated in various neural functions, and SNCA, a small pre-synaptic protein. Participates in the downstream signaling pathways that lead to T-cell differentiation and proliferation following T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation. Also participates in negative feedback regulation of TCR signaling through phosphorylation of PAG1, thereby promoting interaction between PAG1 and CSK and recruitment of CSK to lipid rafts. CSK maintains LCK and FYN in an inactive form. Promotes CD28-induced phosphorylation of VAV1.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [NEF_HV1BR] Factor of infectivity and pathogenicity, required for optimal virus replication. Alters numerous pathways of T-lymphocytes function and down-regulates immunity surface molecules in order to evade host defense and increase viral infectivity. Alters the functionality of other immunity cells, like dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages and NK cells. One of the earliest and most abundantly expressed viral proteins (By similarity).[20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] In infected CD4(+) T-lymphocytes, down-regulates the surface MHC-I, mature MHC-II, CD4, CD28, CCR5 and CXCR4 molecules. Mediates internalization and degradation of host CD4 through the interaction of with the cytoplasmic tail of CD4, the recruitment of AP-2 (clathrin adapter protein complex 2), internalization through clathrin coated pits, and subsequent transport to endosomes and lysosomes for degradation. Diverts host MHC-I molecules to the trans-Golgi network-associated endosomal compartments by an endocytic pathway to finally target them for degradation. MHC-I down-regulation may involve AP-1 (clathrin adapter protein complex 1) or possibly Src family kinase-ZAP70/Syk-PI3K cascade recruited by PACS2. In consequence infected cells are masked for immune recognition by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Decreasing the number of immune receptors also prevents reinfection by more HIV particles (superinfection).[31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] Bypasses host T-cell signaling by inducing a transcriptional program nearly identical to that of anti-CD3 cell activation. Interaction with TCR-zeta chain up-regulates the Fas ligand (FasL). Increasing surface FasL molecules and decreasing surface MHC-I molecules on infected CD4(+) cells send attacking cytotoxic CD8+ T-lymphocytes into apoptosis (By similarity).[42] [43] [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] [51] [52] Plays a role in optimizing the host cell environment for viral replication without causing cell death by apoptosis. Protects the infected cells from apoptosis in order to keep them alive until the next virus generation is ready to strike. Inhibits the Fas and TNFR-mediated death signals by blocking MAP3K5. Interacts and decreases the half-life of p53, protecting the infected cell against p53-mediated apoptosis. Inhibits the apoptotic signals regulated by the Bcl-2 family proteins through the formation of a Nef/PI3-kinase/PAK2 complex that leads to activation of PAK2 and induces phosphorylation of Bad (By similarity).[53] [54] [55] [56] [57] [58] [59] [60] [61] [62] [63] Extracellular Nef protein targets CD4(+) T-lymphocytes for apoptosis by interacting with CXCR4 surface receptors (By similarity).[64] [65] [66] [67] [68] [69] [70] [71] [72] [73] [74]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The crystal structure of the conserved core of HIV-1 Nef has been determined in complex with the SH3 domain of a mutant Fyn tyrosine kinase (a single amino acid substitution, Arg-96 to isoleucine), to which Nef binds tightly. The conserved PxxP sequence motif of Nef, known to be important for optimal viral replication, is part of a polyproline type II helix that engages the SH3 domain in a manner resembling closely the interaction of isolated peptides with SH3 domains. The Nef-SH3 structure also reveals how high affinity and specificity in the SH3 interaction is achieved by the presentation of the PxxP motif within the context of the folded structure of Nef.
Crystal structure of the conserved core of HIV-1 Nef complexed with a Src family SH3 domain.,Lee CH, Saksela K, Mirza UA, Chait BT, Kuriyan J Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):931-42. PMID:8681387[75]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Rigley K, Slocombe P, Proudfoot K, Wahid S, Mandair K, Bebbington C. Human p59fyn(T) regulates OKT3-induced calcium influx by a mechanism distinct from PIP2 hydrolysis in Jurkat T cells. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):1136-45. PMID:7822789
- ↑ Raab M, Cai YC, Bunnell SC, Heyeck SD, Berg LJ, Rudd CE. p56Lck and p59Fyn regulate CD28 binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, growth factor receptor-bound protein GRB-2, and T cell-specific protein-tyrosine kinase ITK: implications for T-cell costimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8891-5. PMID:7568038
- ↑ Huang J, Tilly D, Altman A, Sugie K, Grey HM. T-cell receptor antagonists induce Vav phosphorylation by selective activation of Fyn kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Sep 26;97(20):10923-9. PMID:11005864
- ↑ Nakamura T, Yamashita H, Takahashi T, Nakamura S. Activated Fyn phosphorylates alpha-synuclein at tyrosine residue 125. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Feb 2;280(4):1085-92. PMID:11162638 doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.4253
- ↑ Wolf RM, Wilkes JJ, Chao MV, Resh MD. Tyrosine phosphorylation of p190 RhoGAP by Fyn regulates oligodendrocyte differentiation. J Neurobiol. 2001 Oct;49(1):62-78. PMID:11536198
- ↑ Taniguchi S, Liu H, Nakazawa T, Yokoyama K, Tezuka T, Yamamoto T. p250GAP, a neural RhoGAP protein, is associated with and phosphorylated by Fyn. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Jun 20;306(1):151-5. PMID:12788081
- ↑ Piedra J, Miravet S, Castano J, Palmer HG, Heisterkamp N, Garcia de Herreros A, Dunach M. p120 Catenin-associated Fer and Fyn tyrosine kinases regulate beta-catenin Tyr-142 phosphorylation and beta-catenin-alpha-catenin Interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(7):2287-97. PMID:12640114
- ↑ Hisatsune C, Kuroda Y, Nakamura K, Inoue T, Nakamura T, Michikawa T, Mizutani A, Mikoshiba K. Regulation of TRPC6 channel activity by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 30;279(18):18887-94. Epub 2004 Feb 3. PMID:14761972 doi:10.1074/jbc.M311274200
- ↑ Meriane M, Tcherkezian J, Webber CA, Danek EI, Triki I, McFarlane S, Bloch-Gallego E, Lamarche-Vane N. Phosphorylation of DCC by Fyn mediates Netrin-1 signaling in growth cone guidance. J Cell Biol. 2004 Nov 22;167(4):687-98. PMID:15557120 doi:jcb.200405053
- ↑ Badour K, Zhang J, Shi F, Leng Y, Collins M, Siminovitch KA. Fyn and PTP-PEST-mediated regulation of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) tyrosine phosphorylation is required for coupling T cell antigen receptor engagement to WASp effector function and T cell activation. J Exp Med. 2004 Jan 5;199(1):99-112. PMID:14707117 doi:10.1084/jem.20030976
- ↑ Zamora-Leon SP, Bresnick A, Backer JM, Shafit-Zagardo B. Fyn phosphorylates human MAP-2c on tyrosine 67. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 21;280(3):1962-70. Epub 2004 Nov 9. PMID:15536091 doi:10.1074/jbc.M411380200
- ↑ Yang C, Zhou W, Jeon MS, Demydenko D, Harada Y, Zhou H, Liu YC. Negative regulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase itch via Fyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2006 Jan 6;21(1):135-41. PMID:16387660 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.11.014
- ↑ Tang X, Feng Y, Ye K. Src-family tyrosine kinase fyn phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhancer-activating Akt, preventing its apoptotic cleavage and promoting cell survival. Cell Death Differ. 2007 Feb;14(2):368-77. Epub 2006 Jul 14. PMID:16841086 doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402011
- ↑ Castano J, Solanas G, Casagolda D, Raurell I, Villagrasa P, Bustelo XR, Garcia de Herreros A, Dunach M. Specific phosphorylation of p120-catenin regulatory domain differently modulates its binding to RhoA. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(5):1745-57. Epub 2006 Dec 28. PMID:17194753 doi:10.1128/MCB.01974-06
- ↑ Solheim SA, Torgersen KM, Tasken K, Berge T. Regulation of FynT function by dual domain docking on PAG/Cbp. J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 1;283(5):2773-83. Epub 2007 Dec 4. PMID:18056706 doi:10.1074/jbc.M705215200
- ↑ Harita Y, Kurihara H, Kosako H, Tezuka T, Sekine T, Igarashi T, Hattori S. Neph1, a component of the kidney slit diaphragm, is tyrosine-phosphorylated by the Src family tyrosine kinase and modulates intracellular signaling by binding to Grb2. J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 4;283(14):9177-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707247200. Epub 2008, Feb 7. PMID:18258597 doi:10.1074/jbc.M707247200
- ↑ Harita Y, Kurihara H, Kosako H, Tezuka T, Sekine T, Igarashi T, Ohsawa I, Ohta S, Hattori S. Phosphorylation of Nephrin Triggers Ca2+ Signaling by Recruitment and Activation of Phospholipase C-{gamma}1. J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8951-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806851200. Epub 2009 , Jan 29. PMID:19179337 doi:10.1074/jbc.M806851200
- ↑ Uchida Y, Ohshima T, Yamashita N, Ogawara M, Sasaki Y, Nakamura F, Goshima Y. Semaphorin3A signaling mediated by Fyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of collapsin response mediator protein 2 at tyrosine 32. J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27393-401. Epub 2009 Aug 3. PMID:19652227 doi:M109.000240
- ↑ Goh YM, Cinghu S, Hong ET, Lee YS, Kim JH, Jang JW, Li YH, Chi XZ, Lee KS, Wee H, Ito Y, Oh BC, Bae SC. Src kinase phosphorylates RUNX3 at tyrosine residues and localizes the protein in the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 26;285(13):10122-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.071381. Epub 2010, Jan 25. PMID:20100835 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.071381
- ↑ Chowers MY, Spina CA, Kwoh TJ, Fitch NJ, Richman DD, Guatelli JC. Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2906-14. PMID:8151761
- ↑ Aiken C, Konner J, Landau NR, Lenburg ME, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853-64. PMID:8124721
- ↑ Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A. Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2907-12. PMID:10684310
- ↑ Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV. Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11081-7. PMID:11070003
- ↑ Swigut T, Shohdy N, Skowronski J. Mechanism for down-regulation of CD28 by Nef. EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1593-604. PMID:11285224 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1593
- ↑ Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, Ichijo H, Greene WC. HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell. Nature. 2001 Apr 12;410(6830):834-8. PMID:11298454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071111
- ↑ Greenway AL, McPhee DA, Allen K, Johnstone R, Holloway G, Mills J, Azad A, Sankovich S, Lambert P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2692-702. PMID:11861836
- ↑ Larsen JE, Massol RH, Nieland TJ, Kirchhausen T. HIV Nef-mediated major histocompatibility complex class I down-modulation is independent of Arf6 activity. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jan;15(1):323-31. Epub 2003 Nov 14. PMID:14617802 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0578
- ↑ Michel N, Allespach I, Venzke S, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus establishes superinfection immunity by a dual strategy to downregulate cell-surface CCR5 and CD4. Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 26;15(8):714-23. PMID:15854903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.058
- ↑ Venzke S, Michel N, Allespach I, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. Expression of Nef downregulates CXCR4, the major coreceptor of human immunodeficiency virus, from the surfaces of target cells and thereby enhances resistance to superinfection. J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11141-52. Epub 2006 Aug 23. PMID:16928758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01556-06
- ↑ Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):121-33. PMID:18005690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.004
- ↑ Chowers MY, Spina CA, Kwoh TJ, Fitch NJ, Richman DD, Guatelli JC. Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2906-14. PMID:8151761
- ↑ Aiken C, Konner J, Landau NR, Lenburg ME, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853-64. PMID:8124721
- ↑ Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A. Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2907-12. PMID:10684310
- ↑ Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV. Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11081-7. PMID:11070003
- ↑ Swigut T, Shohdy N, Skowronski J. Mechanism for down-regulation of CD28 by Nef. EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1593-604. PMID:11285224 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1593
- ↑ Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, Ichijo H, Greene WC. HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell. Nature. 2001 Apr 12;410(6830):834-8. PMID:11298454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071111
- ↑ Greenway AL, McPhee DA, Allen K, Johnstone R, Holloway G, Mills J, Azad A, Sankovich S, Lambert P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2692-702. PMID:11861836
- ↑ Larsen JE, Massol RH, Nieland TJ, Kirchhausen T. HIV Nef-mediated major histocompatibility complex class I down-modulation is independent of Arf6 activity. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jan;15(1):323-31. Epub 2003 Nov 14. PMID:14617802 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0578
- ↑ Michel N, Allespach I, Venzke S, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus establishes superinfection immunity by a dual strategy to downregulate cell-surface CCR5 and CD4. Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 26;15(8):714-23. PMID:15854903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.058
- ↑ Venzke S, Michel N, Allespach I, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. Expression of Nef downregulates CXCR4, the major coreceptor of human immunodeficiency virus, from the surfaces of target cells and thereby enhances resistance to superinfection. J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11141-52. Epub 2006 Aug 23. PMID:16928758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01556-06
- ↑ Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):121-33. PMID:18005690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.004
- ↑ Chowers MY, Spina CA, Kwoh TJ, Fitch NJ, Richman DD, Guatelli JC. Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2906-14. PMID:8151761
- ↑ Aiken C, Konner J, Landau NR, Lenburg ME, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853-64. PMID:8124721
- ↑ Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A. Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2907-12. PMID:10684310
- ↑ Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV. Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11081-7. PMID:11070003
- ↑ Swigut T, Shohdy N, Skowronski J. Mechanism for down-regulation of CD28 by Nef. EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1593-604. PMID:11285224 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1593
- ↑ Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, Ichijo H, Greene WC. HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell. Nature. 2001 Apr 12;410(6830):834-8. PMID:11298454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071111
- ↑ Greenway AL, McPhee DA, Allen K, Johnstone R, Holloway G, Mills J, Azad A, Sankovich S, Lambert P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2692-702. PMID:11861836
- ↑ Larsen JE, Massol RH, Nieland TJ, Kirchhausen T. HIV Nef-mediated major histocompatibility complex class I down-modulation is independent of Arf6 activity. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jan;15(1):323-31. Epub 2003 Nov 14. PMID:14617802 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0578
- ↑ Michel N, Allespach I, Venzke S, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus establishes superinfection immunity by a dual strategy to downregulate cell-surface CCR5 and CD4. Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 26;15(8):714-23. PMID:15854903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.058
- ↑ Venzke S, Michel N, Allespach I, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. Expression of Nef downregulates CXCR4, the major coreceptor of human immunodeficiency virus, from the surfaces of target cells and thereby enhances resistance to superinfection. J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11141-52. Epub 2006 Aug 23. PMID:16928758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01556-06
- ↑ Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):121-33. PMID:18005690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.004
- ↑ Chowers MY, Spina CA, Kwoh TJ, Fitch NJ, Richman DD, Guatelli JC. Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2906-14. PMID:8151761
- ↑ Aiken C, Konner J, Landau NR, Lenburg ME, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853-64. PMID:8124721
- ↑ Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A. Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2907-12. PMID:10684310
- ↑ Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV. Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11081-7. PMID:11070003
- ↑ Swigut T, Shohdy N, Skowronski J. Mechanism for down-regulation of CD28 by Nef. EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1593-604. PMID:11285224 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1593
- ↑ Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, Ichijo H, Greene WC. HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell. Nature. 2001 Apr 12;410(6830):834-8. PMID:11298454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071111
- ↑ Greenway AL, McPhee DA, Allen K, Johnstone R, Holloway G, Mills J, Azad A, Sankovich S, Lambert P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2692-702. PMID:11861836
- ↑ Larsen JE, Massol RH, Nieland TJ, Kirchhausen T. HIV Nef-mediated major histocompatibility complex class I down-modulation is independent of Arf6 activity. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jan;15(1):323-31. Epub 2003 Nov 14. PMID:14617802 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0578
- ↑ Michel N, Allespach I, Venzke S, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus establishes superinfection immunity by a dual strategy to downregulate cell-surface CCR5 and CD4. Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 26;15(8):714-23. PMID:15854903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.058
- ↑ Venzke S, Michel N, Allespach I, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. Expression of Nef downregulates CXCR4, the major coreceptor of human immunodeficiency virus, from the surfaces of target cells and thereby enhances resistance to superinfection. J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11141-52. Epub 2006 Aug 23. PMID:16928758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01556-06
- ↑ Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):121-33. PMID:18005690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.004
- ↑ Chowers MY, Spina CA, Kwoh TJ, Fitch NJ, Richman DD, Guatelli JC. Optimal infectivity in vitro of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires an intact nef gene. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2906-14. PMID:8151761
- ↑ Aiken C, Konner J, Landau NR, Lenburg ME, Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853-64. PMID:8124721
- ↑ Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A. Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol. 2000 Mar;74(6):2907-12. PMID:10684310
- ↑ Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV. Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11081-7. PMID:11070003
- ↑ Swigut T, Shohdy N, Skowronski J. Mechanism for down-regulation of CD28 by Nef. EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1593-604. PMID:11285224 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1593
- ↑ Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, Ichijo H, Greene WC. HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell. Nature. 2001 Apr 12;410(6830):834-8. PMID:11298454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35071111
- ↑ Greenway AL, McPhee DA, Allen K, Johnstone R, Holloway G, Mills J, Azad A, Sankovich S, Lambert P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(6):2692-702. PMID:11861836
- ↑ Larsen JE, Massol RH, Nieland TJ, Kirchhausen T. HIV Nef-mediated major histocompatibility complex class I down-modulation is independent of Arf6 activity. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Jan;15(1):323-31. Epub 2003 Nov 14. PMID:14617802 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0578
- ↑ Michel N, Allespach I, Venzke S, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus establishes superinfection immunity by a dual strategy to downregulate cell-surface CCR5 and CD4. Curr Biol. 2005 Apr 26;15(8):714-23. PMID:15854903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.058
- ↑ Venzke S, Michel N, Allespach I, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. Expression of Nef downregulates CXCR4, the major coreceptor of human immunodeficiency virus, from the surfaces of target cells and thereby enhances resistance to superinfection. J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11141-52. Epub 2006 Aug 23. PMID:16928758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01556-06
- ↑ Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):121-33. PMID:18005690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.004
- ↑ Lee CH, Saksela K, Mirza UA, Chait BT, Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the conserved core of HIV-1 Nef complexed with a Src family SH3 domain. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):931-42. PMID:8681387
|