This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Transmembrane protease serine 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
=== Gene === | === Gene === | ||
| - | The ''TMPRSS2'' gene resides on chromosome 21 at the band 21q22.3, and is split into | + | The ''TMPRSS2'' gene resides on chromosome 21 at the band 21q22.3, extends aproximately 43.59 kb and is split into 14 exons. |
This gene is conserved in a wide variety of animals, such as chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' and frog. | This gene is conserved in a wide variety of animals, such as chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' and frog. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This gene presents two alternative splicing variants resulting in a 3.25 kb and 3.21 kb transcripts, respectively. | ||
=== Protein === | === Protein === | ||
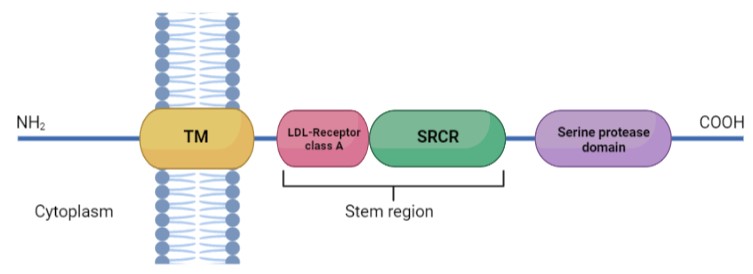
| - | + | TMPRSS2 is a 492 amino acid single-pass type II membrane protein. This protein is defined by the presence of an N-terminal cytoplasmic domain, a transmembrane helical domain, and three extracellular domains: <ref>DOI 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206987</ref> | |
| - | *Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-receptor class A domain | + | *Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-receptor class A domain: which forms a binding site for calcium |
*Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain (SRCR) | *Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain (SRCR) | ||
*Peptidase S1 domain, also known as serine protease domain (SPD) | *Peptidase S1 domain, also known as serine protease domain (SPD) | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 29 November 2021
TMPRSS2 is a membrane protein belonging to the type II transmembrane serine protease (TTSP) family. It is functionally classified as a trypsin-like protease (TLP). [1] Serine proteases are known to be involved in many physiological and pathological processes.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sgrignani J, Cavalli A. Computational Identification of a Putative Allosteric Binding Pocket in TMPRSS2. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 30;8:666626. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626., eCollection 2021. PMID:33996911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.666626
- ↑ Evnin LB, Vasquez JR, Craik CS. Substrate specificity of trypsin investigated by using a genetic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6659-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6659. PMID:2204062 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.17.6659
- ↑ Singh N, Decroly E, Khatib AM, Villoutreix BO. Structure-based drug repositioning over the human TMPRSS2 protease domain: search for chemical probes able to repress SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein cleavages. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Oct 1;153:105495. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105495. Epub, 2020 Jul 28. PMID:32730844 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105495
- ↑ Lam DK, Dang D, Flynn AN, Hardt M, Schmidt BL. TMPRSS2, a novel membrane-anchored mediator in cancer pain. Pain. 2015 May;156(5):923-930. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000130. PMID:25734995 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000130
- ↑ St John J, Powell K, Conley-Lacomb MK, Chinni SR. TMPRSS2-ERG Fusion Gene Expression in Prostate Tumor Cells and Its Clinical and Biological Significance in Prostate Cancer Progression. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2012 Apr 26;4(4):94-101. doi: 10.4172/1948-5956.1000119. PMID:23264855 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/1948-5956.1000119
- ↑ Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J, Kuefer R, Lee C, Montie JE, Shah RB, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005 Oct 28;310(5748):644-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1117679. PMID:16254181 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1117679
- ↑ Carrere S, Verger A, Flourens A, Stehelin D, Duterque-Coquillaud M. Erg proteins, transcription factors of the Ets family, form homo, heterodimers and ternary complexes via two distinct domains. Oncogene. 1998 Jun 25;16(25):3261-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201868. PMID:9681824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201868
- ↑ Yu J, Yu J, Mani RS, Cao Q, Brenner CJ, Cao X, Wang X, Wu L, Li J, Hu M, Gong Y, Cheng H, Laxman B, Vellaichamy A, Shankar S, Li Y, Dhanasekaran SM, Morey R, Barrette T, Lonigro RJ, Tomlins SA, Varambally S, Qin ZS, Chinnaiyan AM. An integrated network of androgen receptor, polycomb, and TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusions in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Cell. 2010 May 18;17(5):443-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.03.018. PMID:20478527 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.03.018
- ↑ Farooqi AA, Hou MF, Chen CC, Wang CL, Chang HW. Androgen receptor and gene network: Micromechanics reassemble the signaling machinery of TMPRSS2-ERG positive prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2014 Apr 17;14:34. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-14-34. eCollection, 2014. PMID:24739220 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1475-2867-14-34
- ↑ Thunders M, Delahunt B. Gene of the month: TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2). J Clin Pathol. 2020 Dec;73(12):773-776. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206987. Epub , 2020 Sep 1. PMID:32873700 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206987
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Paula R. Mallavibarrena, Ines Muniesa-Martinez, Laura Aleixos Juan, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky