|
General function
Enkephalins were the first reported evidence of endogenous opioids in the brain, by John Hughes and Hans Kosterlitz in 1975 [1] [2]. They are pentapeptides that can be divided into two groups based on their carboxy-terminal amino acids: methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin.
acts as a neurotransmitter through opioid receptors, more specifically through the classical opioid receptor δ [3]. The main functions of enkephalins include analgesia, but they are also involved in the control of respiratory, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal functions, and participate in neuroendocrine regulation [4] [5] [6].
Enkephalin is generated from the cleavage of the precursor pro-enkephalin, resulting in Met-enkephalin or Leu-enkephalin. The processing of one molecule of pro-enkephalin generates six copies of Met-enkephalin and one copy of Leu-enkephalin [3].
Enkephalin is mainly distributed throughout the central, peripheral and autonomic nervous system in mammals [3]. However, opioid receptors are broadly distributed in the body, such as the cardiac and gastrointestinal systems.
Structure
The main conformations of enkephalin found in crystals have been classified in three categories, described as “extended,” “single bend,” and “double bend.”[7]. The picture below represents molecular models of Leu-enkephalin in the three main conformations found in solid state determinations when the peptide is dissolved in a DMSO/water cryomixture at 275 K. [8].
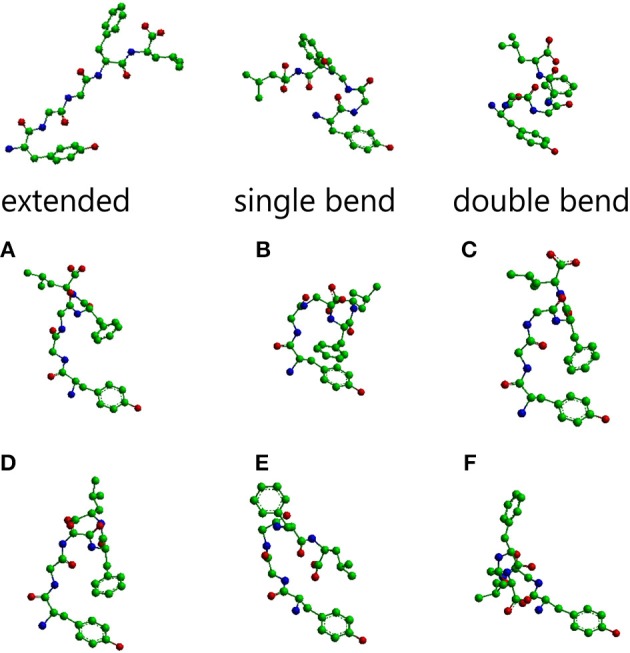
Met-enkephalin amino acid sequence is Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met, while leu-enkephalin amino acid sequence is Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu. As we can see, of leu-enkephalin are on opposite sides of the backbone and point in different directions. A similar conformation was found for met-enkephalin in Bic/PG [4].
Variations in membrane composition seem to have an effect on the conformation adopted by enkephalins [4]. There is common agreement that the orientation of the tyrosine and phenylalanine rings with respect to each other dictates the receptor subtype selectivity [4]. It was originally believed that the μ-selective opiates adopted a folded conformation whereas the δ-opiates preferred an extended form [4] [9]. However, later other studies suggested a folded conformation with the Tyr and Phe aromatic rings in proximity for the δ-selective opiates, whereas the aromatic rings would point in different directions in the μ-type opiates [4] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20].
Physiological functions
Analgesia
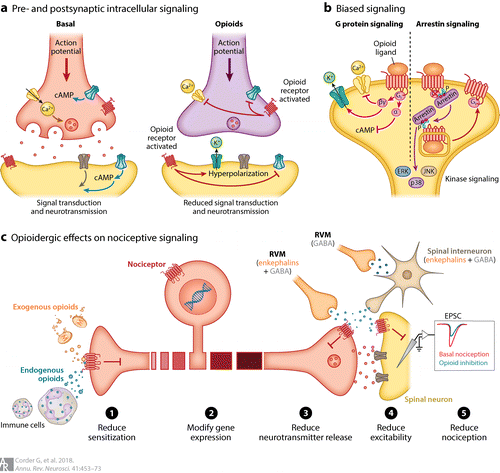
Enkephalins belong to one of the four major families of endogenous opioid ligands [21]. Opioid receptors couple to inhibitory G proteins and when they are activated Gα and Gβγ subunits dissociate and induce a signaling cascade that leads to a reduced neurotransmitter release [21]. All four opioid receptors inhibit N-, P/Q- and L-type voltage-gated calcium channels [21] [22] by the Gβγ subunit, which inhibits the entry of calcium to the pre-synaptic neuron, preventing the fusion of calcium-dependent synaptic vesicules with the membrane terminal and therefore blocking the neurotransmitter release. Transmission of pain signals is thus blocked. Enkephalins can be released from infiltrating immune cells at the site of injuries and from neurons in the central nervous system [21].
Stress response regulation
Several studies showed the importance of enkephalins in anxiety and stress. A polymorphism in the gene encoding neutral endopeptidase involved in enkephalin metabolism, was identified in patients with anxiety disorders [23] [24]. Moreover, an enkephalin KO mice model had increased anxiety with the elevated plus maze (EPM), open field (OF) and light-dark box (LDB) tests, as well as an exaggerated startle response (SR), which is an unconscious defensive response to unexpected or threatened stimuli, and a reduced duration in the social interaction test (SI) [23] [25] [26] [27]. This suggests that a reduced enkephalin neurotransmission relates with the expression of anxiety. However, in other studies it appears that enkephalins enhanced the reactivity to chronic stress, as enkephalin KO mice were resistant to anxiety and depression-like behaviors after a chronic mild unpredictable stress [23] [28]. It seems that enkephalins have different effects on anxiety and stress and this might depend on the central nervous system region. In response to stress, Corticotropin-Releasing Factor (CRF) is released and stimulates the production of endogenous opioids such as endorphins and enkephalins. Enkephalin has been found to modulate the release of CRF from the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus [3]. More knowledge on enkephalin pathways and their role is needed in order to fully understand stress regulation and a variety of stress- and anxiety- related disorders.
Formation of social memory
Enkephalin has a depressant or inhibitory function of neuronal communication, and it is produced by VIP neurons [29], located in a small area of the hippocampus called CA2, which is known to be involved in the formation of social memory [30]. In mice, it is observed that VIP neurons show greater activity during the encounter with an unknown individual than against another relative and also when faced with a new object [31]. With the release of enkephalin by VIP interneurons in CA2, a special type of plasticity is induced, called ITDP (Input-timing-dependent plasticity), which is essential for the formation of social memory [32].
CA2 dysfunction has been linked to schizophrenia in humans and is believed to contribute to social memory deficits. We know from mouse models of schizophrenia that the CA2 zone is poorly regulated in this pathology, and that these mice cannot form social memory. This group is currently studying how enkephalin-mediated plasticity can be used to rescue the ability to form social memory in these animals.
Pathophysiology
Due to the wide distribution of the endogenous opioid system in the human body, its dysregulation has a high number of implications. One example of pain dysregulation is fibromyalgia, which is a widespread pain in the absence of identifiable peripheral pathology [33]. It appears that the endogenous opioid system is involved in some aspects of pain in fibromyalgia [34]. The concentration of endogenous opioids in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with fibromyalgia seems to be higher, which leads to a decreased availability and affinity of Mu-opioid receptors (MOR) [34]. This translates into an increase in pain neurotransmission.
The enkephalin signaling pathway regulates various neural functions and can be altered by neurodegenerative disorders. In Alzheimer's disease (AD), elevated enkephalin levels may reflect compensatory processes or contribute to cognitive impairments. The therapeutic potential of reducing enkephalin production or signaling merits further exploration[35].
Decreased plasma met-enkephalin levels are vasogenic mediators in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc), and will associate with clinical manifestations of SSc-related vascular and fibrogenic injuries[36].
Proenkephalin (PENK) represents a novel biomarker for kidney function. PENK plasma concentration appears to accurately represent glomerular filtration rate in patients diagnosed with sepsis or cardiac diseases. Increased PENK concentration is found to be associated with Accurate Kidney Injury and cardiac diseases. Moreover, the predominant receptor of enkephalins, the δ-opioid receptor, is expressed with the highest density in the kidney, suggesting that enkephalins could also exert a direct effect on kidney function[37].
Clinical relevance
Met-Enkephalin (MENK) may contribute to immune responses against tumors and viral infections by activating multiple types of immune cells, enabling them to secrete various cytokines or directly kill target cells. The nuclear membrane of certain cancer cells expressed receptors to which MENK bound, resulting in marked growth inhibition of cancer cells in vitro[38].
Activation of δ opioid receptors acts against oxidative stress in the central nervous system and promotes neuron survival. Enkephalin is able to cross the blood-brain barrier; it has been hypothesized to be a promising strategy to promote neuron regeneration, especially in brain damage caused by stroke [39]. Multifunctional fluorinated enkephalin analog, LYS739 can be considered as a potential lead for ischemic stroke research and may provide advantages given the multimeric peptide-opiate structure[40].
The main and most known effect of enkephalins is analgesia, which makes the therapeutic use of enkephalins to treat pain one their main clinical relevant aspect. However, enkephalins have a relatively low stability in-vivo, due to their degradation by endogenous peptidases [3]. Two approaches have been proposed to this issue: the first one is the chemical modification of enkephalins while preserving their analgesic efficacy. One example of this is the design of D-Ala-methionine-enkephalin in 1976 by Pert et al. [41]. Kropotova et al. in 2020 have designed different modified enkephalins that are less accessible to endopeptidases [42]. Squalene-based nanoparticles have opened exciting perspectives for drug delivery due to their biodegradability and their non-toxicity as Leu-Enkephalin Nanomedicines for pain alleviation. LENK-SQ bioconjugates show exclusively peripheral activity (no BBB penetration) so no CNS addiction and take advantage of the inflammatory process to optimize drug concentrations at the site of injury [43].
The second approach to increase enkephalin stability in-vivo is the blocking of the peptidases themselves, such as enkephalinase and aminopeptidase. One example is DENKIs [3].Dual Enkephalinase Inhibitors (DENKIs) are a novel therapeutic approach for opioid use disorders. This class of compounds physiologically activates the endogenous opioid system by inhibiting the enzymes responsible for the breakdown of enkephalins, protecting endogenous enkephalins, increasing their half-lives and physiological actions [44].
References
- ↑ John Hughes, Terry Smith, Barry Morgan, Linda Fothergill, Purification and properties of enkephalin — The possible endogenous ligand for the morphine receptor, Life Sciences,
Volume 16, Issue 12,1975,Pages 1753-1758,ISSN 0024-3205,https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(75)90268-4.
- ↑ Hans W. Kosterlitz, John Hughes,
Some thoughts on the significance of enkephalin, the endogenous ligand, Life Sciences, Volume 17, Issue 1, 1975, Pages 91-96, ISSN 0024-3205, https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(75)90243-X.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Cullen JM, Cascella M. Physiology, Enkephalin. [Updated 2021 Mar 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557764/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Marcotte, I., Separovic, F., Auger, M., & Gagné, S. M. (2004). A multidimensional 1H NMR investigation of the conformation of methionine-enkephalin in fast-tumbling bicelles. Biophysical journal, 86(3), 1587–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74226-5
- ↑ Cesselin, F. 1997. Endomorphines, Récepteurs des Opioïdes et Nociception. In Douleurs: Bases Fondamentales, Pharmacologie, Douleurs Aiguës, Douleurs Chroniques, Thérapeutiques. L. Brasseur, M. Chauvin, G. Guilbaud, and P. Guesnon, editors. Maloine, Paris, France.
- ↑ Fuxe, K., Borroto-Escuela, D. O., Romero-Fernandez, W., Diaz-Cabiale, Z., Rivera, A., Ferraro, L., Tanganelli, S., Tarakanov, A. O., Garriga, P., Narváez, J. A., Ciruela, F., Guescini, M., & Agnati, L. F. (2012). Extrasynaptic neurotransmission in the modulation of brain function. Focus on the striatal neuronal-glial networks. Frontiers in physiology, 3, 136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00136
- ↑ Deschamps J. R., George C., Flippen-Anderson J. L. (1996). Structural studies of opioid peptides: a review of recent progress in x-ray diffraction studies. Biopolymers 40, 121–139. 10.1002/bip.360400102
- ↑ Amodeo P., Naider F., Picone D., Tancredi T., Temussi P. A. (1998). Conformational sampling of bioactive conformers: a low temperature NMR study of 15N-Leu-enkephalin. J. Pept. Sci. 4, 253–265.
- ↑ Hansen, P. E., and B. A. Morgan. 1984. Structure-activity relationships in enkephalin peptides. In Opioid Peptides: Biology, Chemistry, and Genetics, Vol. 6. S. Udenfriend and J. Meienhofer, editors. Academic Press, Orlando, FL.
- ↑ Belleney, J., G. Gacel, M. C. Fournié-Zalusky, B. Maigret, and B. P. Roques. 1989. δ opioid receptor selectivity induced by conformational constraints in linear enkephalin-related peptides: 1H 400-MHz NMR study and theoretical calculations. Biochemistry. 28:7392–7400.
- ↑ Groth, M., J. Malicka, C. Czaplewski, S. Oldziej, L. Lankiewicz, W. Wiczk, and A. Liwo. 1999. Maximum entropy approach to the determination of solution conformation of flexible polypeptides by global conformational analysis and NMR spectroscopy: application to DNS1-c-[D-A2bu2, Trp4, Leu5]-enkephalin and DNS1-c-[D-A2bu2, Trp4, D-Leu5]enkephalin. J. Biomol. NMR. 15:315–330.
- ↑ Hruby, V. J., L.-F. Kao, B. M. Pettitt, and M. Karplus. 1988. The conformational properties of the δ-opioid peptide [D-Pen2,D-Pen5]enkephalin in aqueous solution determined by NMR and energy minimization calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110:3351–3359.
- ↑ Keys, C., P. Payne, P. Amsterdam, L. Toll, and G. Loew. 1988. Conformational determinants of high affinity δ receptor binding of opioid peptides. Mol. Pharmacol. 33:528–536.
- ↑ Kolp, B., F. Andreae, W. M. F. Fabian, and H. Sterk. 1996. Combined use of NMR, distance geometry and MD calculations for the conformational analysis of opioid peptides of the type [D(L)-Cys2, D(L)-Cys5]enkephalin. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 48:443–451.
- ↑ Lomize, A. L., I. D. Pogozheva, and H. I. Mosberg. 1996. Development of a model for the δ-opioid receptor pharmacophore. 3. Comparison of the cyclic tetrapeptide Tyr-c[D-Cys-Phe-D-Pen]OH with other conformationally constrained δ-receptor selective ligands. Biopolymers. 38:221–234.
- ↑ Mosberg, H. I. 1999. Complementarity of δ opioid ligand pharmacophore and receptor models. Biopolymers. 51:426–439.
- ↑ Shenderovitch, M. D., G. V. Nikiforovich, and A. A. Golbraikh. 1991. Conformational features responsible for the binding of cyclic analogues of enkephalin to opioid receptors. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 37:241–251.
- ↑ Tourwé, D., K. Verschueren, A. Frycia, P. Davis, F. Porreca, V. J. Hruby, G. Toth, H. Jaspers, P. Verheyden, and G. Van Binst. 1995. Conformational restriction of Tyr and Phe side chains in opioid peptides: information about preferred and bioactive side-chain topology. Biopolymers. 38:1–12.
- ↑ Wang, Y., and K. Kuczera. 1996. Molecular dynamics simulations of cyclic and linear DPDPE: influence of the disulfide bond on peptide flexibility. J. Phys. Chem. 100:2555–2563.
- ↑ Yamazaki, T., S. Ro, M. Goodman, N. N. Chung, and P. W. Schiller. 1993. A topochemical approach to explain morphiceptin bioactivity. J. Med. Chem. 36:708–719.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 Corder, G., Castro, D. C., Bruchas, M. R., & Scherrer, G. (2018). Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain. Annual review of neuroscience, 41, 453–473. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061522
- ↑ Rusin, K. I., Giovannucci, D. R., Stuenkel, E. L., & Moises, H. C. (1997). Kappa-opioid receptor activation modulates Ca2+ currents and secretion in isolated neuroendocrine nerve terminals. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 17(17), 6565–6574. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-17-06565.1997
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Henry, M. S., Gendron, L., Tremblay, M. E., & Drolet, G. (2017). Enkephalins: Endogenous Analgesics with an Emerging Role in Stress Resilience. Neural plasticity, 2017, 1546125. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1546125
- ↑ Comings, D. E., Dietz, G., Gade-Andavolu, R., Blake, H., Muhleman, D., Huss, M., Saucier, G., & MacMurray, J. P. (2000). Association of the neutral endopeptidase (MME) gene with anxiety. Psychiatric genetics, 10(2), 91–94. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041444-200010020-00007
- ↑ Ragnauth, A., Schuller, A., Morgan, M., Chan, J., Ogawa, S., Pintar, J., Bodnar, R. J., & Pfaff, D. W. (2001). Female preproenkephalin-knockout mice display altered emotional responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(4), 1958–1963. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.041598498
- ↑ Bilkei-Gorzo, A., Racz, I., Michel, K., Zimmer, A., Klingmüller, D., & Zimmer, A. (2004). Behavioral phenotype of pre-proenkephalin-deficient mice on diverse congenic backgrounds. Psychopharmacology, 176(3-4), 343–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1904-9
- ↑ König, M., Zimmer, A. M., Steiner, H., Holmes, P. V., Crawley, J. N., Brownstein, M. J., & Zimmer, A. (1996). Pain responses, anxiety and aggression in mice deficient in pre-proenkephalin. Nature, 383(6600), 535–538. https://doi.org/10.1038/383535a0
- ↑ Melo, I., Drews, E., Zimmer, A., & Bilkei-Gorzo, A. (2014). Enkephalin knockout male mice are resistant to chronic mild stress. Genes, brain, and behavior, 13(6), 550–558. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12139
- ↑ Blasco-Ibáñez JM, Martínez-Guijarro FJ, Freund TF. Enkephalin-containing interneurons are specialized to innervate other interneurons in the hippocampal CA1 region of the rat and guinea-pig. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:1784–95.
- ↑ Oliva A, Fernández-Ruiz A, Leroy F, Siegelbaum SA. Hippocampal CA2 sharp-wave ripples reactivate and promote social memory. Nature. 2020;587:264–9.
- ↑ Leroy, F., de Solis, C.A., Boyle, L.M. et al. Enkephalin release from VIP interneurons in the hippocampal CA2/3a region mediates heterosynaptic plasticity and social memory. Mol Psychiatry (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01124-y
- ↑ Leroy F, Brann DH, Meira T, Siegelbaum SA. Input-timing-dependent Plasticity in the Hippocampal CA2 region and its potential role in social memory. Neuron. 2017;95:1089–102.e5.
- ↑ Clauw D. J. (2014). Fibromyalgia: a clinical review. JAMA, 311(15), 1547–1555. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3266
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Schrepf, A., Harper, D. E., Harte, S. E., Wang, H., Ichesco, E., Hampson, J. P., Zubieta, J. K., Clauw, D. J., & Harris, R. E. (2016). Endogenous opioidergic dysregulation of pain in fibromyalgia: a PET and fMRI study. Pain, 157(10), 2217–2225. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000633
- ↑ William J. Meilandt, Gui-Qiu Yu, Jeannie Chin, Erik D. Roberson, Jorge J. Palop, Tiffany Wu et alii (et al.). Enkephalin elevations contribute to neuronal and behavioral impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience 2008;28:5007-5017.
- ↑ McNearney TA, Sluka KA, Ahn C, Reveille JD, Fischbach M, Mayes MD. Plasma endogenous enkephalin levels in early systemic sclerosis: clinical and laboratory associations. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010;28(2 Suppl 58):S7-S11.
- ↑ Remi Beunders, Joachim Struck, Alan H B Wu, Alexander Zarbock, Salvatore Di Somma, Ravindra L Mehta, Jay L Koyner, Mitra K Nadim, Alan S Maisel, Patrick T Murray, Sean-Xavier Neath, Allan Jaffe, Peter Pickkers, Proenkephalin (PENK) as a Novel Biomarker for Kidney Function, The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine, Volume 2, Issue 3, 1 November 2017, Pages 400–412, https://doi.org/10.1373/jalm.2017.023598
- ↑ Wang DM, Wang GC, Yang J, Plotnikoff NP, Griffin N, Han YM, Qi RQ, Gao XH and Shan FP: Inhibition of the growth of human melanoma cells by methionine enkephalin. Mol Med Rep 14: 5521-5527, 2016
- ↑ Liu, Y., Fu, N., Su, J., Wang, X., & Li, X. (2019). Rapid Enkephalin Delivery Using Exosomes to Promote Neurons Recovery in Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Neuronal p53/Caspase-3. BioMed research international, 2019, 4273290. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4273290
- ↑ Rashedul Islam, M., Yang, L., Sun Lee, Y., J Hruby, V., T Karamyan, V., & J Abbruscato, T. (2016). Enkephalin-fentanyl multifunctional opioids as potential neuroprotectants for ischemic stroke treatment. Current pharmaceutical design, 22(42), 6459-6468.
- ↑ Pert, C. B., Pert, A., Chang, J. K., & Fong, B. T. (1976). (D-Ala2)-Met-enkephalinamide: a potent, long-lasting synthetic pentapeptide analgesic. Science (New York, N.Y.), 194(4262), 330–332. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.968485
- ↑ Kropotova, E. S., Ivleva, I. S., Karpenko, M. N., & Mosevitsky, M. I. (2020). Design of enkephalin modifications protected from brain extracellular peptidases providing long-term analgesia. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 28(1), 115184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115184
- ↑ Lepetre-Mouelhi S., Feng J., Couvreur P. (2021) New Enkephalin Nanomedicines for Pain Alleviation, Overcoming the Side Effects of Morphine. In: J.M. Abadie M., Pinteala M., Rotaru A. (eds) New Trends in Macromolecular and Supramolecular Chemistry for Biological Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57456-7_10
- ↑ Alvarez-Perez, B, Poras, H, Maldonado, R. THE INHIBITION OF ENKEPHALIN CATABOLISM BY DUAL ENKEPHALINASE INHIBITOR: A NOVEL POSSIBLE THERAPEUTIC APPROACH FOR OPIOID USE DISORDERS. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. Accepted Author Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15656
|


