This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Fel d 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Chains 1 and 2 are two antiparallel polypeptides, linked via 3 interchain disulfide bonds, formed between cysteine residues at positions Cys3-Cys73, Cys44-Cys48, and Cys70-Cys7, at chains 1 and 2, respectively, in chains 1 and 2, respectively<ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | Chains 1 and 2 are two antiparallel polypeptides, linked via 3 interchain disulfide bonds, formed between cysteine residues at positions Cys3-Cys73, Cys44-Cys48, and Cys70-Cys7, at chains 1 and 2, respectively, in chains 1 and 2, respectively<ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | ||
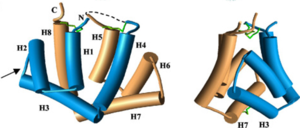
| - | [[Image:Monomero.png | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 1.'''General structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two distinct orientations, rotated 90° about the vertical axis<ref name="[1]"/>.]] | + | [[Image:Monomero.png | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 1.''' General structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two distinct orientations, rotated 90° about the vertical axis<ref name="[1]"/>.]] |
Chain 1 has about 8kDa, composed of a residue of 70 amino acids and chain 2 has about 10 kDa, which can be composed of a residue of 90 amino acids, found preferably in the sebaceous glands, or composed of a residue of 92 amino acids, which is expressed by the salivary glands. Its glycan portion is found in chain 2 and the recombinant structure of Fel d 1 reveals that the N33 residue is located in the loop connecting the H2 and H3 helices and that the side chain is exposed to the solvent<ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | Chain 1 has about 8kDa, composed of a residue of 70 amino acids and chain 2 has about 10 kDa, which can be composed of a residue of 90 amino acids, found preferably in the sebaceous glands, or composed of a residue of 92 amino acids, which is expressed by the salivary glands. Its glycan portion is found in chain 2 and the recombinant structure of Fel d 1 reveals that the N33 residue is located in the loop connecting the H2 and H3 helices and that the side chain is exposed to the solvent<ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | ||
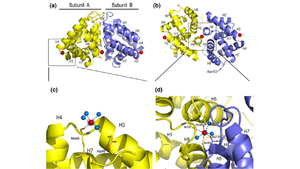
| - | [[Image:Ca2.png | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 2.'''General structure of the Fel d 1 tetramer. (a) Schematic view of the Fel d 1 tetramer (1 + 2). The two heterodimeric subunits A and B, each composed of the linked 1 and 2 chains, that form the tetramer are yellow and blue, respectively. The three Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions are indicated as red balls. (b) Schematic view of the Fel d 1 tetramer following an approximately 90° rotation about the horizontal axis. (c) Calcium binding sites 1 and 2. (d) Calcium binding site 3<ref name="[2]"/>.]] | + | [[Image:Ca2.png | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 2.''' General structure of the Fel d 1 tetramer. (a) Schematic view of the Fel d 1 tetramer (1 + 2). The two heterodimeric subunits A and B, each composed of the linked 1 and 2 chains, that form the tetramer are yellow and blue, respectively. The three Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions are indicated as red balls. (b) Schematic view of the Fel d 1 tetramer following an approximately 90° rotation about the horizontal axis. (c) Calcium binding sites 1 and 2. (d) Calcium binding site 3<ref name="[2]"/>.]] |
Figure 1 shows the general structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two different orientations, rotated 90° around the vertical axis. Chains 1 and 2 correspond to the gold and blue helices respectively. The dotted line indicates the disordered loop (residues 75 to 92). The three disulfide bridges connecting chains 1 and 2 are shown in green. An arrow indicates the unique glycosylation site at residue N33<ref name="[1]"/>. | Figure 1 shows the general structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two different orientations, rotated 90° around the vertical axis. Chains 1 and 2 correspond to the gold and blue helices respectively. The dotted line indicates the disordered loop (residues 75 to 92). The three disulfide bridges connecting chains 1 and 2 are shown in green. An arrow indicates the unique glycosylation site at residue N33<ref name="[1]"/>. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
=='''Treatment'''== | =='''Treatment'''== | ||
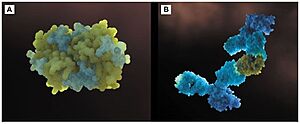
| - | [[Image:Anticorpos.jpg | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 4'''(a) Three-dimensional configuration of Fel d 1 (b) Fel d 1 linked to two anti-Fel d 1 IgY antibodies <ref name="[3]"/>.]] | + | [[Image:Anticorpos.jpg | thumb | 300px | '''Figure 4.''' (a) Three-dimensional configuration of Fel d 1 (b) Fel d 1 linked to two anti-Fel d 1 IgY antibodies <ref name="[3]"/>.]] |
Immunotherapy, or allergy vaccination, which is based on repeated subcutaneous injections of cat hair extracts has been shown to be effective in the curative treatment of allergy. However, in addition to being a time-consuming treatment, it can cause serious side effects such as asthma attacks and anaphylactic shock <ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | Immunotherapy, or allergy vaccination, which is based on repeated subcutaneous injections of cat hair extracts has been shown to be effective in the curative treatment of allergy. However, in addition to being a time-consuming treatment, it can cause serious side effects such as asthma attacks and anaphylactic shock <ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | ||
Additionally, to add to the immunotherapy treatment, there is a cat food supplemented with anti-Fel d 1 IgY, which significantly reduces active Fel d 1 levels. Figure 4 shows the three-dimensional configuration of Fel d 1 (a) and the structure of Fel d 1 linked to two anti-Fel d 1 IgY antibodies (b) <ref name="[3]"/>. | Additionally, to add to the immunotherapy treatment, there is a cat food supplemented with anti-Fel d 1 IgY, which significantly reduces active Fel d 1 levels. Figure 4 shows the three-dimensional configuration of Fel d 1 (a) and the structure of Fel d 1 linked to two anti-Fel d 1 IgY antibodies (b) <ref name="[3]"/>. | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 6 December 2021
1PUO - Fel d 1: The major cat allergen
| |||||||||||