User:Cristiane Custodio Ross Matheus/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Ohr gene regulation== | ==Ohr gene regulation== | ||
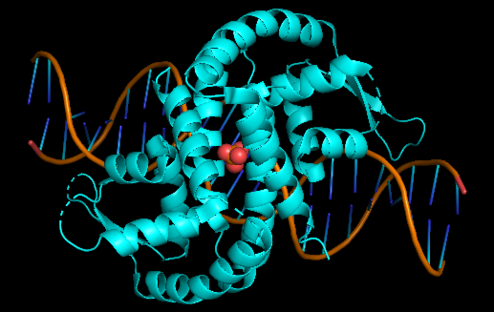
OhrR is a transcriptional factor characterized by being a repressive protein and the main regulatory factor of the Ohr gene in most microorganisms. This protein is found on the promoter of the Ohr gene and has its structure altered when oxidized when it comes into contact with hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrites. With the change of conformation generated by the oxidation of OhrR occurs its detachment from the promoter of the gene, making it more accessible to RNA polymerase, resulting in an overexpression of the Ohr gene. In addition to OhrR were also found in some microorganisms different regulatory means for the Ohr gene. An example is positive regulation by the alternative sigma factor, present in some microorganisms | OhrR is a transcriptional factor characterized by being a repressive protein and the main regulatory factor of the Ohr gene in most microorganisms. This protein is found on the promoter of the Ohr gene and has its structure altered when oxidized when it comes into contact with hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrites. With the change of conformation generated by the oxidation of OhrR occurs its detachment from the promoter of the gene, making it more accessible to RNA polymerase, resulting in an overexpression of the Ohr gene. In addition to OhrR were also found in some microorganisms different regulatory means for the Ohr gene. An example is positive regulation by the alternative sigma factor, present in some microorganisms | ||
| + | [[Image:Screenshot 20211212-110409~2.png|right|494px]]<br /> | ||
==Structural features== | ==Structural features== | ||
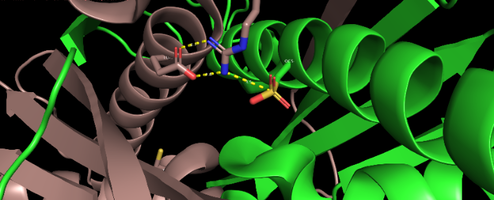
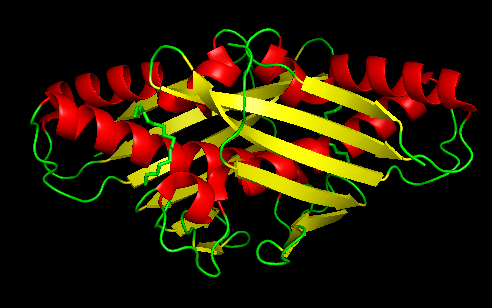
Ohr presents distinct structural and biochemical characteristics when compared to cys-based mammalian peroxidases. This protein has a barrel-like structure formed by a tightly folded homodhermer, in which two β sheets of six ribbons involve two αhelix. There are two active sites in the enzyme that are located at the dye interface on opposite sides of the protein.The architecture of the Ohr catalytic site is composed of two cysteines, peroxidatic and resolution. Peroxidatic cysteine, located in one of α central helixs, has as function the direct reaction with hydroperoxides, forming a sulphenic acid. This in turn condenses with resolution cysteine to form an intramoleculardisulfide bond. In addition to the two cys amino acids there is also the presence of a catalytic arginine and a glutamate that has extreme importance in the activity of the enzyme Ohr, since they help stabilize the Cys in its thiolato state through polar interactions, increasing its nucleophilicity.The carboxylic group of catalytic glutamate guides the Guanidine group of Arginine towards Cysteine, in a configuration that seems to be ideal for the reduction of organic hydroperoxides. This described stabilization process is the so-called closed state of the catalytic triad. In the open state, there is a disruption of interactions and consequent conformational change that ends up exposing the residue to the solvent, the latter being the most conducive to the reduction of Ohr | Ohr presents distinct structural and biochemical characteristics when compared to cys-based mammalian peroxidases. This protein has a barrel-like structure formed by a tightly folded homodhermer, in which two β sheets of six ribbons involve two αhelix. There are two active sites in the enzyme that are located at the dye interface on opposite sides of the protein.The architecture of the Ohr catalytic site is composed of two cysteines, peroxidatic and resolution. Peroxidatic cysteine, located in one of α central helixs, has as function the direct reaction with hydroperoxides, forming a sulphenic acid. This in turn condenses with resolution cysteine to form an intramoleculardisulfide bond. In addition to the two cys amino acids there is also the presence of a catalytic arginine and a glutamate that has extreme importance in the activity of the enzyme Ohr, since they help stabilize the Cys in its thiolato state through polar interactions, increasing its nucleophilicity.The carboxylic group of catalytic glutamate guides the Guanidine group of Arginine towards Cysteine, in a configuration that seems to be ideal for the reduction of organic hydroperoxides. This described stabilization process is the so-called closed state of the catalytic triad. In the open state, there is a disruption of interactions and consequent conformational change that ends up exposing the residue to the solvent, the latter being the most conducive to the reduction of Ohr | ||
[[Image:OHR.png|center|494px]]<br /> | [[Image:OHR.png|center|494px]]<br /> | ||
| - | [[Image:Screenshot 20211212-110409~2.png|center|494px]]<br /> | ||
==3D structures of Ohr== | ==3D structures of Ohr== | ||
[[Organic hydroperoxide resistance protein]] | [[Organic hydroperoxide resistance protein]] | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 12 December 2021
| |||||||||||
References
<CUSSIOL, Jose Renato Rosa. Caracterização funcional de uma nova proteína antioxidante: Ohr (Organic Hidroperoxide Resistance Protein). Vias de redução e expressão em Xylella fastidiosa. 2010. 218 f. Tese (Doutorado) - Curso de Biociências, Departamento de Biologia Evolutiva e Genética, Usp, São Paulo, 2010. Disponível em: https://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/41/41131/tde-21072010-161740/publico/Jose_Renato_Cussiol_versao_completa.pdf. Acesso em: 13 nov. 2021./>