We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Replication Termination Protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
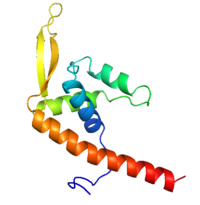
[[Image:RTP.png|200px|left|thumb| Diagram of RTP monomer with secondary structure highlighted.]] | [[Image:RTP.png|200px|left|thumb| Diagram of RTP monomer with secondary structure highlighted.]] | ||
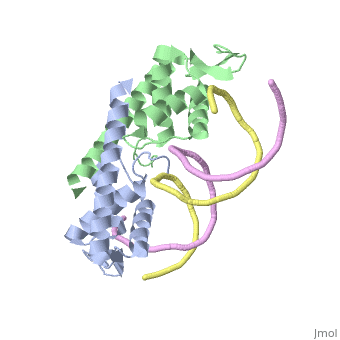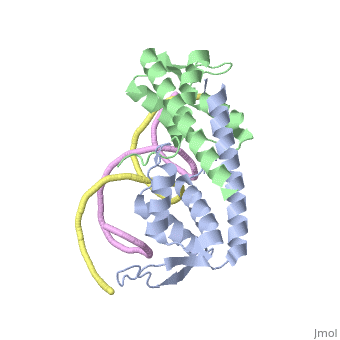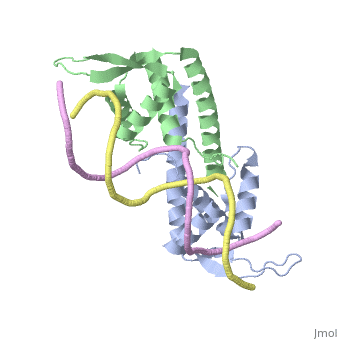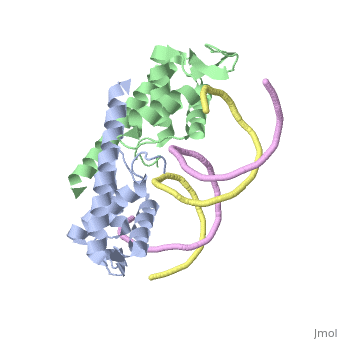
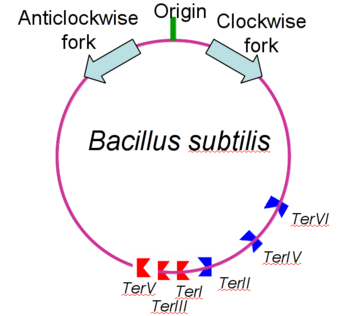
| - | The '''replication termination protein''' (RTP) is one of only two well-defined proteins known to be involved in arresting DNA replication forks, the other being a protein known as tus (termination utilisation substance) from E. coli <ref> Kamada K, Horiuchi T, Ohsumi K, Shimamoto N, Morkikawa K, (1996) Structure of a replication-terminator protein complexed with DNA. Nature, 383:598-603 </ref>. RTP was discovered in ''Bacillus subtilis'' and has been identified as a DNA binding protein of the winged helix family that forms a dimer of 29kDa. This dimeric form has been shown to have an exceptionally high affinity for its cognate binding sites( Kd ~10-11M-1)<ref> Wilce et. al. (2001) Structure of the RTP−DNA complex and the mechanism of polar replication fork arrest. Nature Structural Biology, 8:206-210 </ref>, otherwise known as Termination sites (Ter sites). These Ter sites are found in multiple locations in the ''B. subtilis'' genome <ref> Gautam A. et.al. (2001) A single domain of the replication termination protein of ''Bacillus subtilis'' is involved in arresting both DnaB helicase and RNA polymerase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276:23471-23479</ref>. For more details see:<br /> | + | The '''replication termination protein''' or '''replication terminator protein'''(RTP) is one of only two well-defined proteins known to be involved in arresting DNA replication forks, the other being a protein known as tus (termination utilisation substance) from E. coli <ref> Kamada K, Horiuchi T, Ohsumi K, Shimamoto N, Morkikawa K, (1996) Structure of a replication-terminator protein complexed with DNA. Nature, 383:598-603 </ref>. RTP was discovered in ''Bacillus subtilis'' and has been identified as a DNA binding protein of the winged helix family that forms a dimer of 29kDa. This dimeric form has been shown to have an exceptionally high affinity for its cognate binding sites( Kd ~10-11M-1)<ref> Wilce et. al. (2001) Structure of the RTP−DNA complex and the mechanism of polar replication fork arrest. Nature Structural Biology, 8:206-210 </ref>, otherwise known as Termination sites (Ter sites). These Ter sites are found in multiple locations in the ''B. subtilis'' genome <ref> Gautam A. et.al. (2001) A single domain of the replication termination protein of ''Bacillus subtilis'' is involved in arresting both DnaB helicase and RNA polymerase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276:23471-23479</ref>. For more details see:<br /> |
*[[RTP and Tus]]<br /> | *[[RTP and Tus]]<br /> | ||
*[[Rtp and Tus DNA Binding]]<br /> | *[[Rtp and Tus DNA Binding]]<br /> | ||
Revision as of 08:02, 13 February 2022
| |||||||||||
3D structures of replication termination protein
Updated on 13-February-2022
1bm9 – BsRTP – Bacillus subtilis
1j0r, 2dqr - BsRTP (mutant)
2dpd - BsRTP + DNA
1f4k, 2dpu, 2efw – BsRTP (mutant) + DNA
1ecr – Tus + DNA – Escherichia coli
References
- ↑ Kamada K, Horiuchi T, Ohsumi K, Shimamoto N, Morkikawa K, (1996) Structure of a replication-terminator protein complexed with DNA. Nature, 383:598-603
- ↑ Wilce et. al. (2001) Structure of the RTP−DNA complex and the mechanism of polar replication fork arrest. Nature Structural Biology, 8:206-210
- ↑ Gautam A. et.al. (2001) A single domain of the replication termination protein of Bacillus subtilis is involved in arresting both DnaB helicase and RNA polymerase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276:23471-23479
- ↑ Noirot P (2007). "Replication of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome". In Graumann P. Bacillus: Cellular and Molecular Biology. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-12-7
- ↑ Duggin I.G. (2006) DNA Replication Fork Arrest by the Bacillus subtilis RTP–DNA Complex Involves a Mechanism that Is Independent of the Affinity of RTP–DNA Binding. Journal of Molecular Biology, 361:1-6
- ↑ Vivian JP, Porter CJ, Wilce JA, Wilce MCJ, (2007) An asymmetric structure of the Bacillus subtilise Replication Terminator Protein in Complex with DNA. J. Mol. Bio, 370:481-491
- ↑ Vivian JP, Porter CJ, Wilce JA, Wilce MCJ, (2007) An asymmetric structure of the Bacillus subtilise Replication Terminator Protein in Complex with DNA. J. Mol. Bio, 370:481-491
- ↑ Bastia D. (1995) Crystal structure of the replication terminator protein from b. subtilis at 2.6 A. Cell 80: 651-660
- ↑ Wilce et. al. (2001) Structure of the RTP−DNA complex and the mechanism of polar replication fork arrest. Nature Structural Biology, 8:206-210
- ↑ Kaplan D.L., Bastia D. (2009). Mechanisms of polar arrest of a replication fork. Molecular Microbiology 72: 279-284
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Craig Mooney, Joel L. Sussman