This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1712
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
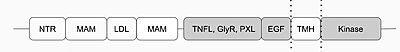
| - | [[Image:2d_image.jpg|400 px|center|thumb| | + | [[Image:2d_image.jpg|400 px|center|thumb|Fig.1 Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase and its domains. ]] |
===Conformational Change=== | ===Conformational Change=== | ||
In order for the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) to move across the membrane to bind with the second monomer, it has to undergo a conformational change. The Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Activating Ligand (ALKAL) binds to the binding surface on the ALK. This induces a conformational change which allows for the PXL and the GlyR domains to hinge forward. The kinase is now ready to move across the membrane and attach to the other kinase to be fully activated. | In order for the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) to move across the membrane to bind with the second monomer, it has to undergo a conformational change. The Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Activating Ligand (ALKAL) binds to the binding surface on the ALK. This induces a conformational change which allows for the PXL and the GlyR domains to hinge forward. The kinase is now ready to move across the membrane and attach to the other kinase to be fully activated. | ||
Revision as of 19:34, 22 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
| |||||||||||