Sandbox Reserved 1716
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Significant Cysteines== | ==Significant Cysteines== | ||
| + | |||
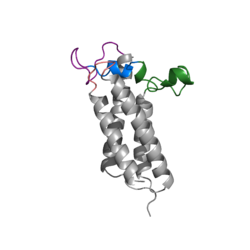
| + | A set of four cysteines is consistently conserved in all VKOR homologs. In the human homolog (HsVKOR) these cysteines are Cys43, Cys51, Cys132, and Cys 135. In the Pufferfish homolog (TrVKORL) these cysteines, due to Cryo-EM differences,are Cys52, Cys55, Cys141, and Cys144. These cysteines are the key factor that allow for Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase to perform its function, which is to open the epoxide ring on Vitamin K Epoxide in order to re-make Vitamin K Quinone. In the closed conformation, that is induced when Vitamin K binds in the hydrophobic pocket, Cys-132 binds to Cys-51 and Cys-135 will bind to the 3' hydroxyl group on Vitamin K Epoxide, which allows for the electron transfer to open up the epoxide ring. | ||
<scene name='90/904321/Cys52disulfidecys55/3'>Disulfide Bond Cysteine52-Cysteine55 TrVKORL</scene> | <scene name='90/904321/Cys52disulfidecys55/3'>Disulfide Bond Cysteine52-Cysteine55 TrVKORL</scene> | ||
==Vitamin K Epoxide== | ==Vitamin K Epoxide== | ||
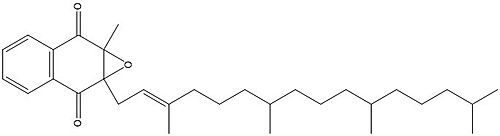
[[Image:Vitamin K epoxide.jpg|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Vitamin K Epoxide structure]] | [[Image:Vitamin K epoxide.jpg|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Vitamin K Epoxide structure]] | ||
| + | |||
As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle, necessary for blood coagulation. In the cycle, Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) reduces Vitamin K epoxide to quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. What is occurring is VKOR donated electrons to Vitamin K epoxide, and those electrons come from the S-H of one of the cysteine pairs discussed above. The one cysteine pair has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate can occur. | As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle, necessary for blood coagulation. In the cycle, Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) reduces Vitamin K epoxide to quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. What is occurring is VKOR donated electrons to Vitamin K epoxide, and those electrons come from the S-H of one of the cysteine pairs discussed above. The one cysteine pair has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate can occur. | ||
Revision as of 19:57, 27 March 2022
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677