We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1709
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<scene name='90/904314/Cap_Domain/1'>VKOR Cap Domain</scene> | <scene name='90/904314/Cap_Domain/1'>VKOR Cap Domain</scene> | ||
Closed conformation | Closed conformation | ||
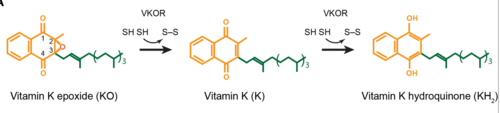
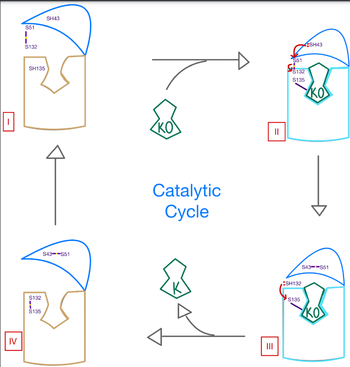
| - | A key part of VKOR is the function of the cap domain | + | A key part of VKOR is the function of the <scene name='90/904314/Cap_Domain/1'>VKOR Cap Domain</scene>, which is located at the top of VKOR towards the intracellular part of the membrane. The cap domain assists with activating Vitamin K as it induces the structural change of VKOR from the open conformation to the closed conformation when the substrate binds. This initiates a domino effect through the [https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0021925820001386?token=9F8E1964241D20488CA55E035D35D9A5D650A7B3FDAD9A5579598A8DC00127539BE71CF1785B117102144AC1F41ABB6C&originRegion=us-east-1&originCreation=20220329001707/ catalytic mechanism]. The cap domain has critical interactions that stabilize the closed conformation including a <scene name='90/904314/Disulfide_bridge_stabilization/1'>Disulfide Bridge </scene> between S43 and S51, and polar interactions from D44. |
| - | + | ||
<scene name='90/904314/Disulfide_bridge_stabilization/1'>Disulfide Bridge Stabilization</scene> | <scene name='90/904314/Disulfide_bridge_stabilization/1'>Disulfide Bridge Stabilization</scene> | ||
=== Anchor === | === Anchor === | ||
Revision as of 00:39, 29 March 2022
| |||||||||||
References
1. Li, Weikai et al. “Structure of a bacterial homologue of vitamin K epoxide reductase.” Nature vol. 463,7280 (2010): 507-12. doi:10.1038/nature08720.
2. Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel AM, Li W. Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science. 2021 Jan 1;371(6524):eabc5667. doi: 10.1126/science.abc5667. Epub 2020 Nov 5. PMID: 33154105; PMCID: PMC7946407.
3. “Warfarin.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 10 Feb. 2022, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warfarin.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644