This is a default text for your page '. Click above on edit this page' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
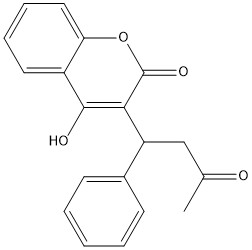
Vitamin K Epoxide
Figure 1. Vitamin K Epoxide structure
As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle, necessary for blood coagulation. In the cycle, Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) reduces Vitamin K epoxide to quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. What is occurring is VKOR donated electrons to Vitamin K epoxide, and those electrons come from the S-H of one of the cysteine pairs discussed above. The one cysteine pair has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate can occur.
Binding
To start, VKOR is in its open conformation. The Vitamin K epoxide enters. The oxygens of the ketones bind to . With Vitamin K epoxide in its place, the conformation of VKOR is partially oxidized in regards to the cysteine pairs, which overall leads to the reduction of the substrate. A disulfide bond forms between Cys51 and Cys132, resulting in the closed conformation. This leaves the sulfur on Cys43 and the sulfur on Cys135 protonated. The available hydrogens on these cysteines are utilized in reducing the epoxide. First, the sulfur on Cys51 and Cys43 form a new bond. The hydrogen from Cys43 binds to the oxygen in the epoxide. The sulfur on Cys132 and the sulfur on Cys135 then form a new disulfide bond. The hydrogen that was present on Cys135 forms a new bond with the oxygen of the epoxide. With these cysteine pairs formed, VKOR is left in an open conformation. The end products are the Vitamin K/quinone and water.
Warfarin
Warfarin is the most common Vitamin K antagonist (VKA). Warfarin is a competitive inhibitor, taking the place of Vitamin K Epoxide (VKO) in the active site of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKOR). When warfarin binds in the active site, it causes VKOR to go into the closed conformation.
Binding
Warfarin still forms Hydrogen bonds with . The specific bonds are between Asn80 and the 2-ketone group of warfarin and Tyr139 with the 4-hydroxyl group of warfarin. The rest of the pocket is hydrophobic interactions. The H bonds are necessary for the recognition of the ligand in the binding site of VKOR.
There is a slight difference in the way in which warfarin binds compared to VKO. Warfarin binds are a slightly different angle. This creates a difference in how the cap loop and anchor domain interact, and that noticeable difference is with . With VKO, Arg58, located in the cap loop, directly interacts with when VKO is bound. When warfarin binds, Arg58 is found inserted between of the anchor domain.
Disease
Vitamin K antagonists play a big role in the treatment of thromboembolic diseases, like a stroke or heart attack. Warfarin is the most common medication for this treatment, acting as a blood thinner. Warfarin binding in VKOR overall prevents the triggering of coagulation factors that form blood clots.
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644