This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1717
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=== Binding === | === Binding === | ||
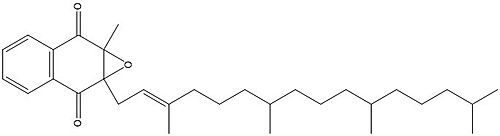
| - | To start, VKOR is in its open conformation. The Vitamin K epoxide enters. The oxygens of the ketones bind to <scene name='90/904322/Asn80_tyr139_vko/ | + | To start, VKOR is in its open conformation. The Vitamin K epoxide enters. The oxygens of the ketones bind to <scene name='90/904322/Asn80_tyr139_vko/3'>Asn80 and Tyr139</scene>. With Vitamin K epoxide in its place, the conformation of VKOR is partially oxidized in regards to the cysteine pairs, which overall leads to the reduction of the substrate. A disulfide bond forms between Cys51 and Cys132, resulting in the closed conformation. This leaves the sulfur on Cys43 and the sulfur on Cys135 protonated. The available hydrogens on these cysteines are utilized in reducing the epoxide. First, the sulfur on Cys51 and Cys43 form a new bond. The hydrogen from Cys43 binds to the oxygen in the epoxide. The sulfur on Cys132 and the sulfur on Cys135 then form a new disulfide bond. The hydrogen that was present on Cys135 forms a new bond with the oxygen of the epoxide. With these cysteine pairs formed, VKOR is left in an open conformation. The end products are the Vitamin K/quinone and water. |
Revision as of 15:21, 29 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||