Sandbox Reserved 1716
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
== Warfarin == | == Warfarin == | ||
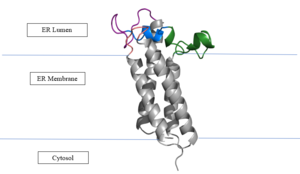
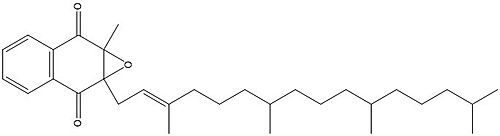
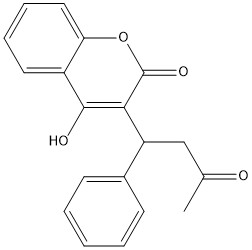
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warfarin Warfarin] is the most common [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_K_antagonist Vitamin K antagonist (VKA)]. Warfarin is a competitive inhibitor, taking the place of Vitamin K Epoxide (VKO) in the active site of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKOR). When warfarin binds in the active site, it causes VKOR to go into the closed conformation. | ||
| + | [[Image:warfarin.jpg|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Warfarin]] | ||
| - | + | === Binding === | |
| - | + | ||
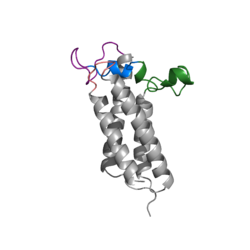
| + | Warfarin still forms Hydrogen bonds with <scene name='90/904322/Tyr_asn_binding_warfarin/2'>Asn80 and Tyr139</scene>. The specific bonds are between Asn80 and the 2-ketone group of warfarin and Tyr139 with the 4-hydroxyl group of warfarin. The rest of the pocket is hydrophobic interactions. The H bonds are necessary for the recognition of the ligand in the binding site of VKOR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is a slight difference in the way in which warfarin binds compared to VKO. Warfarin binds are a slightly different angle. This creates a difference in how the cap loop and anchor domain interact, and that noticeable difference is with <scene name='90/904322/Arg58/3'>Arg58</scene>. With VKO, Arg58, located in the cap loop, directly interacts with <scene name='90/904322/Arg58_vko/3'>Glu67</scene> when VKO is bound. When warfarin binds, Arg58 is found inserted between <scene name='90/904322/Arg58_warfarin/1'>Glu67 and His68</scene> of the anchor domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Disease === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vitamin K antagonists play a big role in the treatment of thromboembolic diseases, like a stroke or heart attack. Warfarin is the most common medication for this treatment, acting as a blood thinner. Warfarin binding in VKOR overall prevents the triggering of coagulation factors that form blood clots. | ||
| - | scene name='90/904321/Closedconformation/4'>Warfarin Binding</scene> | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 29 March 2022
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel AM, Li W. Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science. 2020 Nov 5. pii: science.abc5667. doi: 10.1126/science.abc5667. PMID:33154105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667
- ↑ Olson RE. The function and metabolism of vitamin K. Annu Rev Nutr. 1984;4:281-337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.001433. PMID:6380538 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.001433
- ↑ Wu S, Chen X, Jin DY, Stafford DW, Pedersen LG, Tie JK. Warfarin and vitamin K epoxide reductase: a molecular accounting for observed inhibition. Blood. 2018 Aug 9;132(6):647-657. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901. Epub 2018, May 9. PMID:29743176 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901
- ↑ Chatron N, Abi Khalil R, Benoit E, Lattard V. Structural Investigation of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKORC1) Binding Site with Vitamin K. Biochemistry. 2020 Apr 7;59(13):1351-1360. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b01084. Epub, 2020 Mar 23. PMID:32182040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.9b01084
- ↑ Shen G, Cui W, Cao Q, Gao M, Liu H, Su G, Gross ML, Li W. The catalytic mechanism of vitamin K epoxide reduction in a cellular environment. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100145. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401. Epub 2020, Dec 10. PMID:33273012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401