Sandbox Reserved 1712
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
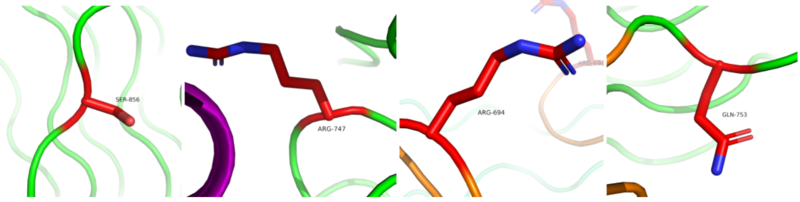
There are many <scene name='90/904317/Premutationresidues/1'>residues that could be mutated</scene> that would cause constitutive receptor activation, enhancement between the interaction of receptors or stabilization of active receptors are known to relate to oncogenic potentials (Figure 4). The <scene name='90/904317/His694/2'>His694</scene> that is mutated to an arginine is known to be a gain-of-function in lung adenocarcinoma which can lead to constitutive activation of ALK. The <scene name='90/904317/Phe856/1'>Phe856</scene> that is mutated to the a serine may cause a gain-of-function mutation that is linked to acute myeloid leukemia. When the <scene name='90/904317/Arg753/1'>Arg753</scene> is mutated to a glutamate it is commonly identified in histiocytic neoplasms. The <scene name='90/904317/Gly747/1'>Gly747</scene> changing to arginine could cause possible oncogenic potentials which are not specified yet. The F856S and R753Q mutations are known to increase cytokine-dependent cell proliferation in certain cells. <ref>DOI:10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5</ref> | There are many <scene name='90/904317/Premutationresidues/1'>residues that could be mutated</scene> that would cause constitutive receptor activation, enhancement between the interaction of receptors or stabilization of active receptors are known to relate to oncogenic potentials (Figure 4). The <scene name='90/904317/His694/2'>His694</scene> that is mutated to an arginine is known to be a gain-of-function in lung adenocarcinoma which can lead to constitutive activation of ALK. The <scene name='90/904317/Phe856/1'>Phe856</scene> that is mutated to the a serine may cause a gain-of-function mutation that is linked to acute myeloid leukemia. When the <scene name='90/904317/Arg753/1'>Arg753</scene> is mutated to a glutamate it is commonly identified in histiocytic neoplasms. The <scene name='90/904317/Gly747/1'>Gly747</scene> changing to arginine could cause possible oncogenic potentials which are not specified yet. The F856S and R753Q mutations are known to increase cytokine-dependent cell proliferation in certain cells. <ref>DOI:10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5</ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:Mutations.png|800 px|left|thumb|Figure 4: Mutated residues on ALK that contribute to stabilization of the active state of ALK, leading to many types of cancers. From left to right: F856S, G747R, H694R, R753Q]] | + | [[Image:Mutations.png|800 px|left|thumb|Figure 4: Mutated residues on ALK that contribute to stabilization of the active state of ALK, leading to many types of cancers. From left to right: F856S, G747R, H694R, R753Q [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7N00 PDB: 7N00]]] |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 29 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
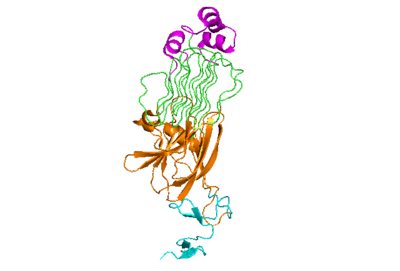
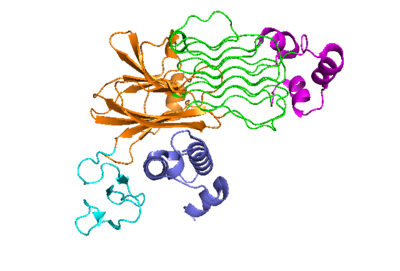
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Huang H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 2;19(11). pii: ijms19113448. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113448. PMID:30400214 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113448
- ↑ Murray PB, Lax I, Reshetnyak A, Ligon GF, Lillquist JS, Natoli EJ Jr, Shi X, Folta-Stogniew E, Gunel M, Alvarado D, Schlessinger J. Heparin is an activating ligand of the orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ALK. Sci Signal. 2015 Jan 20;8(360):ra6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005916. PMID:25605972 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005916
- ↑ Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ De Munck S, Provost M, Kurikawa M, Omori I, Mukohyama J, Felix J, Bloch Y, Abdel-Wahab O, Bazan JF, Yoshimi A, Savvides SN. Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors. Nature. 2021 Oct 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. PMID:34646012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5