User:Michael O'Shaughnessy/ TS
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
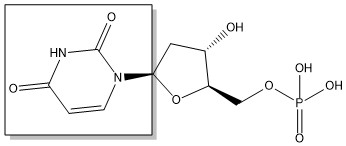
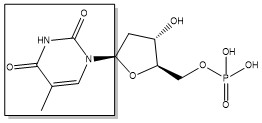
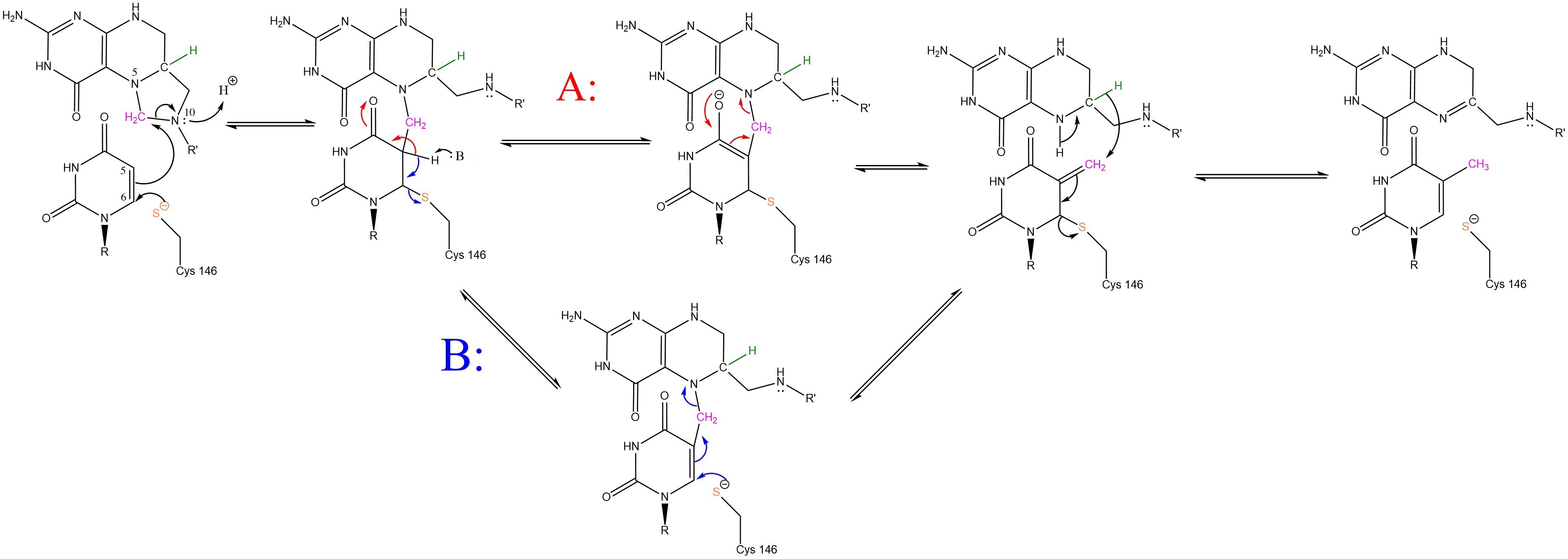
| - | The enzyme | + | The enzyme Thymidylate Synthase (TS) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group and a hydride from 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 2-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate, resulting in the formation of thymidine 5'-monophosphate and dihydrofolate. This is the only de novo source of dTMP in humans. |
2-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate(dUMP) + 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate(CH<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>F) ⇌ thymidine 5'-monophosphate(dTMP) + Dihydrofolate(H<sub>2</sub>F) | 2-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate(dUMP) + 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate(CH<sub>2</sub>H<sub>4</sub>F) ⇌ thymidine 5'-monophosphate(dTMP) + Dihydrofolate(H<sub>2</sub>F) | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | Thymidyalte synthase has a critical role in cell division as the sole producer of thymine in the body. | |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| + | Due to its role in cell division, thymidylate synthase has become a popular target for anticancer drugs. Indirect inhibition of thymidylate synthase by the drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is one of the most used inhibitors for study of TS function. <ref></ref> | ||
| + | |||
<StructureSection load= '7jxf' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load= '7jxf' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 15:55, 6 April 2022
Contents |
Overview
The enzyme Thymidylate Synthase (TS) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group and a hydride from 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 2-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate, resulting in the formation of thymidine 5'-monophosphate and dihydrofolate. This is the only de novo source of dTMP in humans.
2-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate(dUMP) + 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate(CH2H4F) ⇌ thymidine 5'-monophosphate(dTMP) + Dihydrofolate(H2F)
Function
Thymidyalte synthase has a critical role in cell division as the sole producer of thymine in the body.
Disease
Relevance
Due to its role in cell division, thymidylate synthase has become a popular target for anticancer drugs. Indirect inhibition of thymidylate synthase by the drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is one of the most used inhibitors for study of TS function. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
refs with no name must have content
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(01)00067-9