Introduction
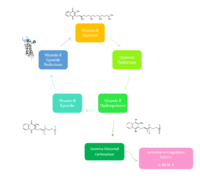
Figure 2. Overview of Vitamin K Cycle: The cycle begins with
Vitamin K Quinone. Vitamin K Quinone is reduced by enzyme Quinone Reductase. This leaves Vitamin K Hydroquinone which can either lead to
Gamma Carboxylaseactivity that will activate Blood Coagulation Factors II, VII, IX, and X. After this, Vitamin K Epoxide is left over. Vitamin K Epoxide is reduced by the enzyme Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase to reform Vitamin K Quinone.
VKOR WIKI(VKOR) is an endoplasmic membrane enzyme that generates the active form of Vitamin K to support blood coagulation. VKOR homologs are integral membrane thiol oxidoreductases Thiol OxidoReductase due to the function of VKOR being dependent on thiol residues and disulfide bonding. The Vitamin K Cycle and the VKOR enzyme specifically are common drug targets for thromboembolic diseases. This is because, as pictured, the vitamin K cycle is required to activate blood coagulant factors II, VII, IX, and X. Coagulant factor activation promotes blood clotting, which in high amounts can be dangerous and cause thromboembolic diseases such as stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and/or pulmonary embolism. Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is found and primarily synthesized in the liver. It is embedded in the membrane known as the endoplasmic reticulum.
Reaction
In the Vitamin K Cycle (Fig 1), there are two primary enzymes, the latter enzyme is Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. Four conserved cysteines: Cys43, Cys51, Cys132, and Cys135 will aid in a redox reaction that will allow for Vitamin K Epoxide to be reduced back to Vitamin K Quinone. VKOR begins and ends in an open conformation and is fully oxidized. The second step is a partially oxidized state where Catalytic Cysteines 51 and 132 share a disulfide bond. No ligand is within the active site at either of these stages. In the third stage Vitamin K Epoxide binds to the active site and VKOR becomes closed and is still partially oxidized. Cysteine 51 and 132 still share a disulfide bond, and Cysteine 135 binds to Vitamin K Epoxide. When Cysteine43 forms a disulfide bond with Cysteine 51, Cysteine 132 will bind to Cysteine 135. Cysteine 135 will form the disulfide bond with Cysteine132 and kick its extra electrons to Vitamin K Epoxide. The transfer of electrons opens up the epoxide ring, which is reforming Vitamin K Quinone. This is another fully oxidized state of VKOR. Then, the cycle restarts at the beginning in an open conformation to release the Vitamin K Quinone.
Structure
The VKOR enzyme is made up of four transmembrane helices: T1, T2, T3, and T4.(Grey) Each of these helices come together to form a central ligand binding pocket. This central pocket is the active site where conserved Cysteines: C132 and C135 are located. In the cap domain are important regions that are significant for Vitamin K binding, and the overall function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase, including the Anchor(Green), Cap Sequence (Blue), Beta Hairpin (Purple), and 3-4 Loop (Pink).
The attaches to the cap domain of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Enzyme and is partially embedded in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. This both stabilizes the enzyme in the membrane, and stabilizes the cap domain over the active site.
The is two parts: The cap helix and the cap loop. When the enzyme is reducing Vitamin K Epoxide or being inhibited by Vitamin K Antagonists, this cap region swings downward over the active site. The cap region is directly attached to the anchor.
The Beta Hairpin is only seen in the closed conformation of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. When in the open conformation the beta hairpin is referred to as the luminal helix (yellow). The Beta hairpin is significant due to the fact that it contains the other two conserved cysteines necessary for the function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase: Cysteine43 and Cysteine51. The beta hairpin/luminal helix is directly connected to the cap region.
The 3-4 Loop is the sequence of residues between Transmembrane Helix 3 and Transmembrane Helix 4. In the open conformation the loop does not have significant interactions with the rest of the cap domain, however in the closed conformation Loop 3-4 has many hydrogen reactions with the Cap Loop. This allows for the stabilization when VKOR is closed.
The transmembrane helices are located in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Luminal Region, which is the region between the ER Lumen and the Cytosol. Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is unstable in-vitro. To determine its structure an extra protein, sfGFP: superfolder green flourescent protein, was appended to the N and C termini of Vitamin K Epoxide. For the visualizing VKOR, this protein has been removed from the structural scenes.
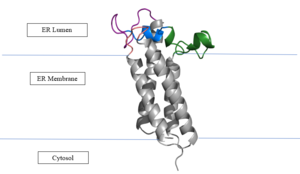
Figure 3. Orientation in Endoplasmic Reticulum: The cap region is partially oriented in the ER Lumen, however the active site remains within the ER membrane. The Beta Hairpin, Loop 3-4, Cap Loop are all in the ER Lumen. The Anchor is partially within the ER lumen, and partially embedded in the ER membrane. The anchor is what attaches the cap domain and stabilizes it, which allows the cap domain to cover the active site.
The reaction catalyzed by VKOR is a redox reaction. Vitamin K Epoxide => Vitamin K Quinone Vitamin K Epoxide is reduced by transferring two electrons through a disulfide bond. These disulfide bonds come from the conserved cysteines. This redox reaction that is catalyzed by VKOR produces Vitamin K Quinone.
Transmembrane Helices
The Transmembrane region has four helices, labeled 1-4. Transmembrane Helix 2 (TM2) and 4 (TM4) contribute to the binding of Vitamin K to the hydrophobic pocket for reduction. Asparagine 83 on TM2 and Tyrosine 142 on TM4 hydrogen bond to Vitamin K Epoxide to hold it in the correct orientation for reduction. The angle in which Vitamin K Epoxide binds in the central pocket is significant to the placement of the beta hairpin, and loop 3-4, Cysteine residues C51-C132 will donate their electrons to Vitamin K Epoxide (Fig. 4) to open the epoxide ring, and reform Vitamin K Quinone (Fig. 2).
Cap Domain
The cap domain of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase plays an intricate role in its function. When Vitamin K Epoxide (or a similar substrate) binds in the hydrophobic pocket of VKOR, the cap domain undergoes a conformational change that will allow for specific cysteine residues to be able to open the epoxide ring and to recreate Vitamin K Quinone. The catalytic cycle begins in an open fully oxidized conformation. This conformation has slightly different parts. These include the Anchor (green), the cap region (blue), 3-4 Loop (pink), and luminal helix (yellow). When Vitamin K Epoxide binds, the entire cap domain undergoes a slight conformation change, but the luminal helix has a larger change. The luminal helix (yellow) bends forward where specific cysteines on this region are in proximity to other important cysteines. The luminal helix is then referred to as the beta hairpin (purple).
Catalytic Cysteines
A set of four catalytic are required for Vitamin K Epoxide reduction and are consistently conserved in all VKOR homologs. In the human homolog (HsVKOR) these cysteines are Cys43, Cys51, Cys132, and Cys 135. In the Pufferfish homolog (TrVKORL) these cysteines, due to Cryo-EM differences,are Cys52, Cys55, Cys141, and Cys144. These cysteines donate their electrons to the epoxide ring on Vitamin K Epoxide which reforms Vitamin K Quinone. In the closed active conformation, that is induced when Vitamin K binds in the hydrophobic pocket. (NEED TO FINISH)
Vitamin K Epoxide
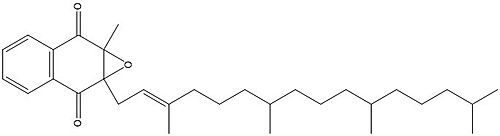
Figure 4. Vitamin K Epoxide structure
As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle, necessary for blood coagulation. In the cycle, Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) reduces Vitamin K epoxide to quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. What is occurring is VKOR donated electrons to Vitamin K epoxide, and those electrons come from the S-H of one of the cysteine pairs discussed above. The one cysteine pair has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate can occur.
Two other notable structures are Vitamin K Quinone (Fig. 5) and Vitamin K Hydroquinone (Fig. 6). Vitamin K Quinone is the product that is released after the reaction with Vitamin K Epoxide and VKOR. (Fig. 2)
Figure 5. Vitamin K Quinone structure
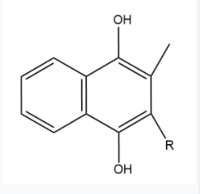
Figure 6. Vitamin K Hydroquinone structure
Binding
To start, VKOR is in its . The Vitamin K epoxide enters through the isoprenyl- chain tunnel. The oxygens of the ketones bind to . With Vitamin K epoxide in its place, the conformation of VKOR is partially oxidized in regards to the cysteine pairs, which overall leads to the reduction of the substrate. A disulfide bond forms between Cys51 and Cys132, resulting in the closed conformation. This leaves the sulfur on Cys43 and the sulfur on Cys135 protonated. The available hydrogens on these cysteines are utilized in reducing the epoxide. First, the sulfur on Cys51 and Cys43 form a new bond. The hydrogen from Cys43 binds to the oxygen in the epoxide. The sulfur on Cys132 and the sulfur on Cys135 then form a new disulfide bond. The hydrogen that was present on Cys135 forms a new bond with the oxygen of the epoxide. With these cysteine pairs formed, VKOR is left in an open conformation. The end products are the Vitamin K/quinone and water.
Warfarin
Warfarin is the most common Vitamin K antagonist (VKA). Warfarin is a competitive inhibitor, taking the place of Vitamin K Epoxide (VKO) in the active site of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKOR). When warfarin binds in the active site, it causes VKOR to go into the closed conformation.
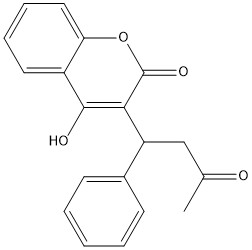
Figure 7. 2-Dimensional structure of Warfarin
Binding
Warfarin still forms Hydrogen bonds with . The specific bonds are between Asn80 and the 2-ketone group of warfarin and Tyr139 with the 4-hydroxyl group of warfarin. The rest of the pocket is hydrophobic interactions. The H bonds are necessary for the recognition of the ligand in the binding site of VKOR.
There is a slight difference in the way in which warfarin binds compared to VKO. Warfarin binds are a slightly different angle. This creates a difference in how the cap loop and anchor domain interact, and that noticeable difference is with . With VKO, Arg58, located in the cap loop, directly interacts with when VKO is bound. When warfarin binds, Arg58 is found inserted between of the anchor domain.
Disease
Vitamin K Antagonists play a big role in the treatment of thromboembolic diseases, like a stroke or heart attack. Warfarin is the most common medication for this treatment, acting as a blood thinner. Warfarin binding in VKOR overall prevents the triggering of coagulation factors that form blood clots.
References
[1] Goodstadt, L., & Ponting, C. P. (2004). Vitamin K epoxide reductase: homology, active site and catalytic mechanism. Trends in biochemical sciences, 29(6), 289–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2004.04.004
Rishavy, M.A., Usubalieva, A., Hallgren, K.W., & Berkner, K.L. (2011). Novel insidht into the mechanism of the vitamin K oxidoreductas (VKOR): Electron relay through Cy43 and Cys51 reduces VKOR to allow vitamin K reduction and facilitation of vitamin K-dependent protein caroxylation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(9), 7267-7278. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.172213
[2] Liu, S., Li, S., Shen, G., Sukumar, N., Krezel, A. M., & Li, W. (2021). Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science (New York, N.Y.), 371(6524), eabc5667. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667
[3] Shen, G., Cui, W., Cao, Q., Gao, M., Liu, H., Su, G., Gross, M. L., & Li, W. (2021). The catalytic mechanism of vitamin K epoxide reduction in a cellular environment. The Journal of biological chemistry, 296, 100145. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401
Silverman, R.B. (1981). Chemical model studies for the mechanism of vitamin K epoxide reductase. The Journal of American Chemistry Society, 103(19), 5939-5941.
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]






