Sandbox Reserved 1713
From Proteopedia
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
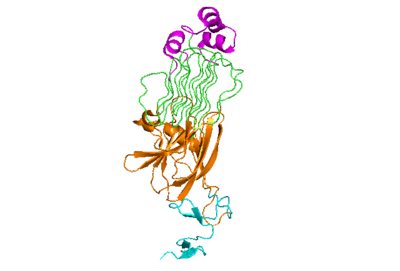
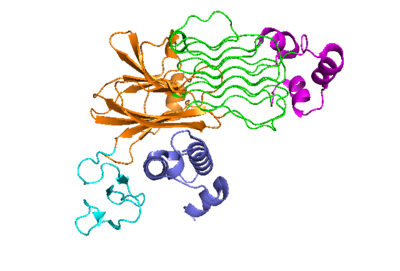
The anaplastic lymphoma kinase activating ligand (ALKAL) binds to the <scene name='90/904318/Alk-alkal_binding_surface/2'>binding surface</scene> on the ALK at the TNFL domain. This induces a conformational change which allows for the PXL and the GlyR domains to hinge forward.<ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8</ref> (Figure 2) ALK's TNFL has <scene name='90/904318/Binding_surface_with_residues/3'>residues</scene> E978, E974, E859, and Y966 that form salt bridges with R123, R133, R136, R140, and R117 on ALKAL that allow for activation, leading to <scene name='90/904317/Dimer_full_colored/3'>dimerization</scene> of two ALK-ALKAL monomers. | The anaplastic lymphoma kinase activating ligand (ALKAL) binds to the <scene name='90/904318/Alk-alkal_binding_surface/2'>binding surface</scene> on the ALK at the TNFL domain. This induces a conformational change which allows for the PXL and the GlyR domains to hinge forward.<ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8</ref> (Figure 2) ALK's TNFL has <scene name='90/904318/Binding_surface_with_residues/3'>residues</scene> E978, E974, E859, and Y966 that form salt bridges with R123, R133, R136, R140, and R117 on ALKAL that allow for activation, leading to <scene name='90/904317/Dimer_full_colored/3'>dimerization</scene> of two ALK-ALKAL monomers. | ||
===Membrane Guidance of ALKAL to ALK=== | ===Membrane Guidance of ALKAL to ALK=== | ||
| - | The negatively charged phosphate groups on the cell membrane interact with a highly conserved positively charged <scene name='90/904318/Alkalbindingsurfacewmembrane/1'>helix</scene> on ALKAL that faces the membrane. These <scene name='90/904318/Alkal1membraneinteraction/2'>residues that interact with the cell membrane</scene> guides ALKAL to ALK and correctly positions ALKAL for its binding surface to face ALK's binding surface, which allows for a more favorable interaction. <ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8</ref> | + | The negatively charged phosphate groups on the cell membrane interact with a highly conserved positively charged <scene name='90/904318/Alkalbindingsurfacewmembrane/1'>helix</scene> on ALKAL that faces the membrane. These <scene name='90/904318/Alkal1membraneinteraction/2'>residues that interact with the cell membrane</scene> guides ALKAL to ALK and correctly positions ALKAL for its <scene name='90/904318/Alk-alkal_binding_surface/2'>binding surface to face ALK's binding surface</scene>, which allows for a more favorable interaction. <ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8</ref> |
===Role of Activated ALK=== | ===Role of Activated ALK=== | ||
Once the ALKAL binds with ALK and dimerizes with another ALK-ALKAL complex, this activated conformation also initiates a conformational change of the intracellular kinase domain of ALK. This causes an autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues of this domain, activating a signaling cascade with its kinase activity. | Once the ALKAL binds with ALK and dimerizes with another ALK-ALKAL complex, this activated conformation also initiates a conformational change of the intracellular kinase domain of ALK. This causes an autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues of this domain, activating a signaling cascade with its kinase activity. | ||
Revision as of 20:07, 12 April 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
Background
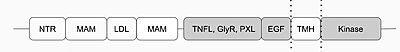
The anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) was first discovered in 1994 as a tyrosine kinase in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) cells.[1] The specific type of tyrosine kinase ALK is classified as is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) and like other RTKs, it's an integral protein with extracellular and intracellular domains and is involved in transmembrane signaling and communication within the cell. ALK is commonly expressed in the development of the nervous system. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor (ALKr) is the extracellular portion of the RTK that includes a binding surface for a ligand to bind. When the ALK activating ligand (ALKAL) binds to ALKr, this causes a conformational change of ALK, allowing two ALK-ALKAL complexes to interact with each other, which will then allow intracellular kinase domain of ALK to phosphorylate a tyrosine residue on a downstream enzyme, which will activate this enzyme and activate a signaling cascade. Abnormal forms of ALK are closely related to the formation of several cancers. [2]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Huang H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 2;19(11). pii: ijms19113448. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113448. PMID:30400214 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113448
- ↑ Huang H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 2;19(11). pii: ijms19113448. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113448. PMID:30400214 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113448
- ↑ Murray PB, Lax I, Reshetnyak A, Ligon GF, Lillquist JS, Natoli EJ Jr, Shi X, Folta-Stogniew E, Gunel M, Alvarado D, Schlessinger J. Heparin is an activating ligand of the orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ALK. Sci Signal. 2015 Jan 20;8(360):ra6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005916. PMID:25605972 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005916
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ De Munck S, Provost M, Kurikawa M, Omori I, Mukohyama J, Felix J, Bloch Y, Abdel-Wahab O, Bazan JF, Yoshimi A, Savvides SN. Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors. Nature. 2021 Oct 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. PMID:34646012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5
- ↑ Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7