We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1716
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
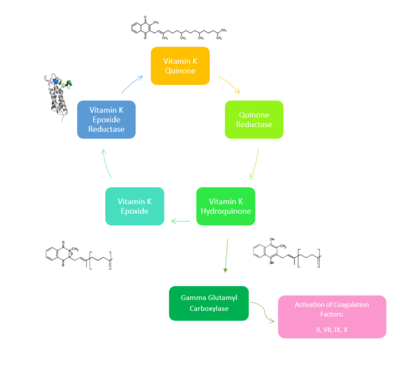
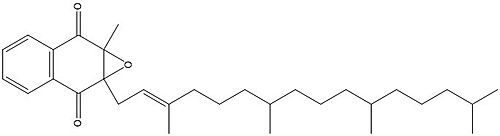
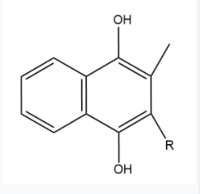
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is found and primarily synthesized in the liver. In the liver, the VKOR enzyme is set in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (Fig.2). The transmembrane helices are located in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Luminal Region, which is the region between the ER Lumen and the Cytosol. The cap region is partially oriented in the ER Lumen. The active site remains within the ER membrane.The Anchor is partially within the ER lumen, and partially embedded in the ER membrane. The anchor is what attaches the cap domain and stabilizes it, which allows the cap domain to cover the active site. Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is unstable in-vitro. To determine its structure an extra protein superfolder green flourescent protein was appended to the N and C termini of Vitamin K Epoxide. For the visualizing VKOR, this protein has been removed from the structural scenes. After superfolder green flourescent protein was removed from the structural scenes, we further took the structure files and resequenced them to better align with the numbering of the protein. In these files the sequence slightly differs between the organisms used to view Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. In the human version, HsVKOR, the catalytic cysteines that play an intricate role in the reduction of Vitamin K Epoxide are cysteines 43, 51, 132, and 135. In the pufferfish version of the file, TrVKORL, the cysteines are 52, 55, 141, and 144. | Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is found and primarily synthesized in the liver. In the liver, the VKOR enzyme is set in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (Fig.2). The transmembrane helices are located in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Luminal Region, which is the region between the ER Lumen and the Cytosol. The cap region is partially oriented in the ER Lumen. The active site remains within the ER membrane.The Anchor is partially within the ER lumen, and partially embedded in the ER membrane. The anchor is what attaches the cap domain and stabilizes it, which allows the cap domain to cover the active site. Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is unstable in-vitro. To determine its structure an extra protein superfolder green flourescent protein was appended to the N and C termini of Vitamin K Epoxide. For the visualizing VKOR, this protein has been removed from the structural scenes. After superfolder green flourescent protein was removed from the structural scenes, we further took the structure files and resequenced them to better align with the numbering of the protein. In these files the sequence slightly differs between the organisms used to view Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. In the human version, HsVKOR, the catalytic cysteines that play an intricate role in the reduction of Vitamin K Epoxide are cysteines 43, 51, 132, and 135. In the pufferfish version of the file, TrVKORL, the cysteines are 52, 55, 141, and 144. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The VKOR enzyme is made up of four transmembrane helices: <scene name='90/904321/Tm1/1'>TM1</scene>, <scene name='90/904321/Tm2/2'>TM2</scene>, <scene name='90/904321/Tm3/2'>TM3</scene>, and <scene name='90/904321/Tm4/2'>TM4</scene> .(Grey/Orange) Each of these helices come together to form a central ligand binding pocket. This central pocket is the active site where conserved Cysteines: C132 and C135 are located. In the cap domain are important regions that are significant for Vitamin K binding, and the overall function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase, including the Anchor(Green), Cap Sequence (Blue), Beta Hairpin (Purple), and 3-4 Loop (Pink). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='90/904321/Anchor/3'>Anchor</scene> attaches to the cap domain of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Enzyme and is partially embedded in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. This both stabilizes the enzyme in the membrane, and stabilizes the cap domain over the active site. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='90/904321/Cap_sequence/1'>Cap Sequence</scene> is two parts: The cap helix and the cap loop. When the enzyme is reducing Vitamin K Epoxide or being inhibited by Vitamin K Antagonists, this cap region swings downward over the active site. The cap region is directly attached to the anchor. | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | The <scene name='90/904321/Beta_hairpin/1'>Beta Hairpin</scene> is only seen in the closed conformation of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. When in the open conformation the beta hairpin is referred to as the luminal helix (yellow). The Beta hairpin is significant due to the fact that it contains the other two conserved cysteines necessary for the function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase: Cysteine43 and Cysteine51. The beta hairpin/luminal helix is directly connected to the cap region. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='90/904321/3-4_loop/2'>Loop 3-4</scene> is the sequence of residues between Transmembrane Helix 3 and Transmembrane Helix 4. In the open conformation the loop does not have significant interactions with the rest of the cap domain, however in the closed conformation Loop 3-4 has many hydrogen reactions with the Cap Loop. This allows for the stabilization when VKOR is closed. | ||
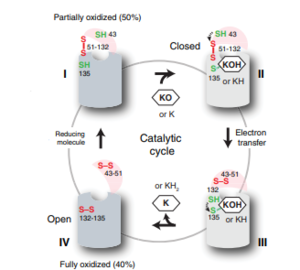
==Catalytic Cycle== | ==Catalytic Cycle== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 45: | ||
===Step II=== | ===Step II=== | ||
After Vitamin K Epoxide enters through the isoprenyl-chain tunnel, Asn80 on TM2 and Tyr139 on TM4 <scene name='90/904322/Tyr_asn_binding_warfarin/2'>hydrogen bond</scene>. to Vitamin K Epoxide. When Vitamin K Epoxide binds, there is a shift in the bonds between the cap domain, beta hairpin, and anchor. <scene name='90/904321/Vkobound_cys/1'>Cys135</scene> also forms a disulfide bond with the 3' OH group on Vitamin K Epoxide. | After Vitamin K Epoxide enters through the isoprenyl-chain tunnel, Asn80 on TM2 and Tyr139 on TM4 <scene name='90/904322/Tyr_asn_binding_warfarin/2'>hydrogen bond</scene>. to Vitamin K Epoxide. When Vitamin K Epoxide binds, there is a shift in the bonds between the cap domain, beta hairpin, and anchor. <scene name='90/904321/Vkobound_cys/1'>Cys135</scene> also forms a disulfide bond with the 3' OH group on Vitamin K Epoxide. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Structure == | ||
| - | |||
| - | The VKOR enzyme is made up of four transmembrane helices: <scene name='90/904321/Tm1/1'>TM1</scene>, <scene name='90/904321/Tm2/2'>TM2</scene>, <scene name='90/904321/Tm3/2'>TM3</scene>, and <scene name='90/904321/Tm4/2'>TM4</scene> .(Grey/Orange) Each of these helices come together to form a central ligand binding pocket. This central pocket is the active site where conserved Cysteines: C132 and C135 are located. In the cap domain are important regions that are significant for Vitamin K binding, and the overall function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase, including the Anchor(Green), Cap Sequence (Blue), Beta Hairpin (Purple), and 3-4 Loop (Pink). | ||
| - | |||
| - | The <scene name='90/904321/Anchor/3'>Anchor</scene> attaches to the cap domain of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Enzyme and is partially embedded in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. This both stabilizes the enzyme in the membrane, and stabilizes the cap domain over the active site. | ||
| - | |||
| - | The <scene name='90/904321/Cap_sequence/1'>Cap Sequence</scene> is two parts: The cap helix and the cap loop. When the enzyme is reducing Vitamin K Epoxide or being inhibited by Vitamin K Antagonists, this cap region swings downward over the active site. The cap region is directly attached to the anchor. | ||
| - | ''' | ||
| - | The <scene name='90/904321/Beta_hairpin/1'>Beta Hairpin</scene> is only seen in the closed conformation of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. When in the open conformation the beta hairpin is referred to as the luminal helix (yellow). The Beta hairpin is significant due to the fact that it contains the other two conserved cysteines necessary for the function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase: Cysteine43 and Cysteine51. The beta hairpin/luminal helix is directly connected to the cap region. | ||
| - | |||
| - | The <scene name='90/904321/3-4_loop/2'>Loop 3-4</scene> is the sequence of residues between Transmembrane Helix 3 and Transmembrane Helix 4. In the open conformation the loop does not have significant interactions with the rest of the cap domain, however in the closed conformation Loop 3-4 has many hydrogen reactions with the Cap Loop. This allows for the stabilization when VKOR is closed. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 15:35, 15 April 2022
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase
| |||||||||||