Introduction
Within the central nervous system (CNS), various membrane receptors exist to detect extracellular signaling molecules and communicate this information intracellularly. Found in eukaryotes and known for its seven transmembrane helices, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) are one type of membrane bound receptors with conserved intracellular signaling via heterotrimeric G-proteins[1]. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGlu), a Class C GPCR, is a receptor utilized in glutamate signaling- which is essential in synaptic plasticity as well as the development and repair of the CNS[2]. These receptors are specifically found in the pre- and postsynaptic neurons of the CNS[2]. Eight different mGlu subtypes exist which are divided into three groups (I, II, III)[2]. While each mGlu has a slightly different function and location, the structures of the different mGlu subtypes are very similar (Table 1) [2]. For each group, binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to the mGlu introduces a conformational change that can activate a G-protein[2].
| Table 1. Classification of mGlu Subtypes[2]
|
| Group
| mGlu Type
| Location
| Function
|
| I
| mGlu1
mGlu5
| Postsynaptic neurons
| Activates calcium channels
Excites adenylyl cyclase
|
| II
| mGlu2
mGlu3
| Presynaptic neurons
| Activates potassium channels
Inhibits calcium channels
Inhibits adenylyl cyclase
|
| III
| mGlu4
mGlu6
mGlu7
mGlu8
| Presynaptic neurons
| Activates potassium channels
Inhibits calcium channels
Inhibits adenylyl cyclase
|

Figure 1. Structure of glutamate under physiological conditions (pH 7.4).
To activate the mGlu transformation, glutamate acts as the protein's main agonist. Glutamate is an acidic, polar amino acid (Figure 1). This agonist binds to the extracellular portion of the glutamate receptor causing the transmembrane spanning region of the homodimer to change conformationally. This change allows for the mGlu to bind to a G-protein. This binding allows for the activation of a G protein which initiates a signaling cascade within the cell that can ultimately lead to a difference in the synapse’s excitability
[3]. In mGlu, the binding affinity of glutamate is also controlled by the binding of either a positive (PAM) or negative (NAM) allosteric modulator to a binding pocket within the seven TMD
[4].
Structural Highlights
mGlu receptors are dimeric proteins consisting of an . While a heterodimer of different mGlu subtypes can form, only homodimeric receptors can become active[3]. Both the alpha and beta chains are comprised of : the venus fly trap (VFT), cysteine rich domain (CRD), and the transmembrane domain (TMD).

Figure 2. Proper orientation of mGlu about the cell membrane.
Domains
: The extracellular location in which the two glutamate agonists bind is known as the VFT. This domain includes a disulfide bond between C121 of the alpha and beta chains. This is shifted down and undergoes an upward movement upon glutamate binding which stabilizes the (Figure 2) Glutamate binds within the through intermolecular forces, specifically hydrogen bonding, with R57, S143, S145, T168, and K377 of the VFT. This binding initiates a closed VFT conformation.
: The portion of the protomer that connects the VFT with the TMD is known as the CRD. As the connecting segment of the protein, it is critical in transmitting the conformational change caused by the binding of glutamate to the TMD. The change resulting from the binding of glutamate in the VFT brings the cysteine-rich domains pf the alpha and beta chain together to alter the configuration of the the seven TMD helices through its interaction with the VFT extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) [3]. This is mediated through interactions with amino acids at the apex of the CRD (e.g. I [3].
: The TMD consists of seven transmembrane helices that are responsible for G-protein interactions and are able to transmit the signal from ligand binding across a membrane. In the , the asymmetric conformation of the helices is mediated by the hydrophobicity of helix 3 and 4 [3]. This allows for a to form between the monomers. Along with the interaction of the CRD with the ECL2 of the TMD, an allosteric modulator must bind within the transmembrane helices to allow for the conformation of the helices to be altered. This conformation allows for an along helix 6 of both protomers [4]. The stabilization of this conformation also enables G protein coupling with ICL2, ICL3, TM Helix 3 and the C terminus [4] (Figure 4).
Conformational Changes
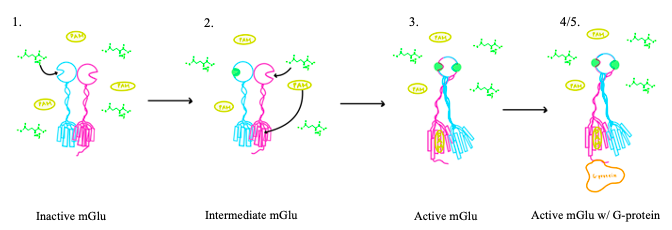
Figure 3. Illustration of mGlu's conformational change process.
1. In its resting state, mGlu is in an . In this conformation, the receptor is considered open with an inter-lobe angle of 44°[3]. The structure has two free glutamate binding sites in the VFT, the CRDs are separated, and the TMD is not interacting with a G protein[3].
2. In the intermediate activation state, also known as the open-closed conformation, one glutamate is bound in one binding pocket of VFT. This single is still considered inactive as the receptor has not changed the conformations in the CRD and thus the TMD. With the same asymmetric transmembrane helices formation, a is still present and mGlu cannot interact with a G protein[3].
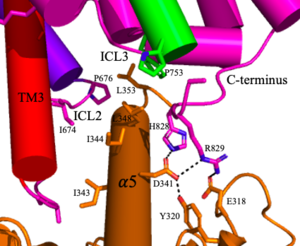
Figure 4. The interaction between an active mGlu (magenta/lime/purple/crimson) and a G-protein (orange). Hydrogen bonds are shown through black dashes
3. A second glutamate then binds to the other of the VFT. Mediated by L639, F643, N735, W773, and F776, a (PAM) also binds within the seven TMD helices of the alpha chain [3]. This closed conformation of the VFT now has an inter-lobe angle of 25° is considered to be in the [3]. The binding of these ligands allows the CRDs to compact and come together. This transformation causes the TMD to form a separate, active asymmetric conformation with a between the chains[3].
4. The crossover of the helices from the alpha and beta chains allows for intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) and the C-terminus to be properly ordered to interact with a single G protein[3]. While hydrogen bonding is present between the C-terminus and alpha helix 5 of the G-protein, this coupling is primarily driven by the hydrophobic interactions in the interface with the ɑ5 helix of the G protein[3](Figure 4). This can only occur in the presence of a as the pocket in which the coupling occurs would be completely closed in its absence[3].
5. Upon binding, the G protein can become active through the receptor catalyzed reaction of GDP to GTP on the alpha subunit of the G protein. Depending on the type of mGlu present, this activation causes different signaling cascades to occur within the cell [4]. These cascades are necessary for cellular function as they can play primary roles in regulating metabolic molecules, ion channels, transporter molecules, and several other parts of the cell; if these proteins are mutated, various diseases can occur[5].
Clinical Relevance
Glutamate is a major neurotransmitter in the brain and is known for its role in memory, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal development[5]. Thus, mGlus are located throughout the CNS and play key roles in various neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease (AD), Huntington's Disease (HD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)[5]. Also, due to the key role of glutamate in the brain, mGlus are also being studied for their role in psychiatric disorders like anxiety and depression[5]. In many of these diseases, the overexpression of glutamate can lead to the overstimulation of mGlus and excitotoxicity [6]. However, an exception to this is the under stimulation of mGlus which can result in schizophrenia[7]. Research is ongoing, but studies have proven that agonists, antagonists, PAMs, and NAMs of mGlus are potential treatments for these diseases[5].
3D Structures
7epa, mGlu Inactive
7mtr, mGlu Active
7mts, mGlu Active G Protein Bound
References
- ↑ Katritch V, Cherezov V, Stevens RC. Structure-function of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53:531-56. doi:, 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-032112-135923. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PMID:23140243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-032112-135923
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Niswender CM, Conn PJ. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:295-322. doi:, 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533. PMID:20055706 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 Seven AB, Barros-Alvarez X, de Lapeyriere M, Papasergi-Scott MM, Robertson MJ, Zhang C, Nwokonko RM, Gao Y, Meyerowitz JG, Rocher JP, Schelshorn D, Kobilka BK, Mathiesen JM, Skiniotis G. G-protein activation by a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 2021 Jun 30. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3. PMID:34194039 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Lin S, Han S, Cai X, Tan Q, Zhou K, Wang D, Wang X, Du J, Yi C, Chu X, Dai A, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Liu H, Liu J, Yang D, Wang MW, Zhao Q, Wu B. Structures of Gi-bound metabotropic glutamate receptors mGlu2 and mGlu4. Nature. 2021 Jun;594(7864):583-588. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03495-2. Epub 2021, Jun 16. PMID:34135510 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03495-2
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Crupi R, Impellizzeri D, Cuzzocrea S. Role of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Neurological Disorders. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb 8;12:20. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00020. eCollection , 2019. PMID:30800054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00020
- ↑ Bordi F, Ugolini A. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: implications for brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 1999 Sep;59(1):55-79. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00095-1. PMID:10416961 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00095-1
- ↑ Conn PJ, Lindsley CW, Jones CK. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors as a novel approach for the treatment of schizophrenia. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Jan;30(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.10.006. Epub, 2008 Dec 6. PMID:19058862 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2008.10.006




