Introduction
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are found in the central nervous system and play a critical role in modulating cell excitability and synaptic transmission
[1].
Glutamate, shown in Figure 1, is a negatively charged polar amino acid that is the main neurotransmitter in the brain. Glutamate activates 8 different types of metabotropic glutamate receptors
[2].
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2 (mGlu2) is a member of the
Class C GPCRFamily and can further be classified into the Group II subgroup of metabotropic receptors. Since mGlu2 is a part of the Class C GPCR family, it undergoes small conformational changes to the transmembrane domain (TMD) to move from the inactive to the fully active structure.
Class A and
Class B GPCR Families, however, experience more substantial conformational changes to the TMD
[1]. mGlu2 functionality is dependent on the concentration of glutamate where higher concentrations of glutamate will promote stronger signal transduction from the extracellular domain(ECD) to the TMD
[1].
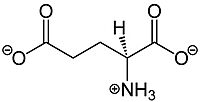
Figure 1.Structure of glutamate. Glutamate binding promotes stronger signal transduction to aid in G-protein activation by mGlu2.
mGlu2 plays vital roles in memory formation, pain management, and addiction, which makes it an important drug target for Parkinson’s Disease,Schizophrenia, cocaine dependence, and many other neurological conditions.
Structure
Overall Structure
Cryo-EM studies of mGlu2 have yielded adequate structural maps of mGlu2 in various activation states. These maps provided clearer understanding of the conformational changes between the inactive and active states of mGlu2[1]. The conformational changes allow mGlu2 to move from an inactive active conformation. The overall of the mGlu2 is composed of 3 main parts. First, a ligand binding , that binds two glutamates which are the agonists. This is followed by a that links the VFT to the TMD. The CRD is helpful in relaying signals for conformational changes in the TMD induced by agonist binding in the VFT[1]. The VFT and CRD are located in the intracellular domain(ICD), while the TMD is located in the ECD (Figure 2). Finally the contains 7 α-helices (7TM) on both the α and β chains. The TMD aids in the binding of the G-protein.
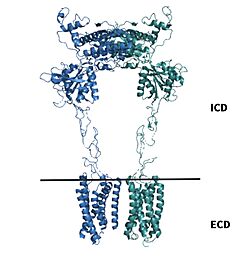
Figure 2.Shown above the line is the intracellular region containing the VFT and CRD. Shown below the line is the extracellular region containing the TMD of mGlu2.
mGlu2 is a homodimer. Dimerization of mGlu2 is required to relay glutamate binding from the ECD to its TMD. The homodimer of mGlu2 contains an . Occupation of both ECDs with the agonist, glutamate, is necessary for a fully active mGlu2[3]. However, only one chain in the dimer is responsible for activation of the G-protein, this suggests an asymmetrical signal transduction mechanism for mGlu2[1].
Due to conformational changes, mGlu2 moves between different states: inactive, intermediate, PAM bound, and active (Figure 3).
Inactive State
A few hallmarks of the of mGlu2 are the in the open conformation, well separated , and distinct orientation of the 7TM. The most critical component of the inactive form is the formed by the 7 α-helices in the α and β chains of the 7TM. The inactive structure of mGlu2 is mediated mainly by helices 3 and 4 on both the α and β chains of the dimer through hydrophobic interactions. These between both transmembrane helices stabilize inactive conformation of mGlu2[1].
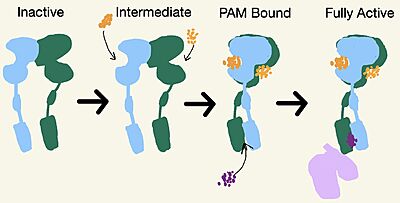
Figure 3. Demonstrates the conformational changes of mGlu2.
Intermediate Form
No Cryo-EM structures are currently available for the intermediate form, but it is an important state for the full activation of mGlu2. While in the intermediate form, glutamate binds the agonist binding site. The is formed by both lobes of the VFT. To stabilize the intermediate state, one glutamate will bind, which will cause the closure of one lobe of the VFT [2]. mGlu2 will still remain inactive after a glutamate is bound. The binding of glutamate promotes signaling down the receptor [1].
PAM and NAM Bound Form
Moving from the intermediate state, a second glutamate will bind in the other lobe of the VFT. This will help close the VFT and move the CRD closer together [2]. A positive allosteric modulator (PAM) or a negative allosteric modulator (NAM) will then come in and bind to mGlu2. PAM and NAM induce different conformational changes, which result in different outcomes. the TMD and promotes greater affinity for the binding of the G-protein. There are different types of PAMs that can bind to the TMD but this page focuses on JNJ-40411813[1]. PAM binds in a binding pocket that is created by helices 3, 5, 6, and 7 in the . Within helix 6, the hydrophobic binding is composed of W773, F776, L777, and F780. Due to spatial hindrance caused by the binding of PAM, helix 6 is shifted downward, causing reorientation of the TMD. This reorientation creates a cleft in the TMD for the G-protein to bind[1]. NAM, however, reduces the affinity for G protein binding. to the same binding pocket as PAM and also interacts with residue W773, but NAM occupies the binding site a little deeper than PAM. This causes NAM to push the side chain of W773 towards helix 7, which does not form the cleft for G-protein binding[1].

Figure 4.PAM binding pocket. PAM, JNJ-40411813, is shown in magenta and colored by atom type, four labelled binding helices (3, 5, 6, and 7) create the binding pocket in the 7TM region for PAM binding. PAM binding promotes G-protein activation by mGLu2.
Active State
The downward shift of helix 6, caused by PAM binding, induces a reorientation of the TMD from its original TM3-TM4 asymmetric dimer interface in the inactive form to an . The downward shift of helix 6 is crucial for the receptor’s transformation from the inactive to the active form for 2 main reasons: (1) reorientation breaks key interactions in the TMD that stabilize the inactive form and (2) repositioning of in the TMD to assist in the binding and recognitions of the . The G-protein is made up of three subunits: , , and a .
G-Protein Recognition
In order for the G-protein to bind to mGlu2, so that it can be fully active, the G-protein has to be recognized by the receptor. Transition to the active state also reorients helix 3 in both monomers to enable binding to the G-protein; Yet only one chain is required for full receptor activation. The intracellular region of helix 3 contributes the main interactions with the α-subunit of the G-protein. Intracellular Loop 2(ICL2) also builds a polar interaction network with the G-protein through its ionic interactions with the of the G-protein. The ionic interactions formed further destabilize the inactive conformation so that the G-protein can be recognized and mGlu2 becomes fully active[1].
G-protein Binding
The PAM induced downward shift of helix 6 coupled with the reorientation of the transmembrane domain to a TM6-TM6 asymmetric interface, opens up a cleft on the intracellular surface of the receptor. This cleft allows a , from terminal 4 residues of the α-subunit of the G-protein to move in adjacent to helix 4 in the TMD. Within this interaction, on the hook participates in hydrophobic interactions with ICL2 and helix 4. These interactions allow the C-terminal region of the G-protein α-subunit to bind in the cleft formed by ICL2 and residues on helix 4[1].The receptor is now with the dimer coupled only to one G-protein. The VFT is in the closed conformation and the TMD helices are also reoriented in both monomers to form an asymmetric dimer interface. These interactions allow the G-protein to bind which causes mGlu2 to be fully active. Now that mGlu2 is active it can regulate different signaling transductions in the cell[1].
Clinical Relevance
mGluRsoccur both presynaptically and postsynaptically in the Central Nervous System [4]. mGluRs play a variety of roles, such as in disease, synaptic plasticity, and modulation of other receptors[4]. Manipulation of these receptors are starting to be used as drug targets for Parkinson's Disease, Fragile X Syndrome, and Schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia
Schizophreniais a chronic brain disorder that affects a person’s ability to think, feel, and behave[5]. The exact cause of Schizophrenia is unknown currently[5]. The symptoms from the disease can vary from patient to patient, but they can be broken down into positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms[6]. Although antipsychotic drugs help to treat Schizophrenia, these drugs only target positive symptoms and have limited efficacy against negative and cognitive symptoms [7]. mGlu2 receptors are a therapeutic target for Schizophrenia, as mGlu2 receptors are expressed in regions associated with Schizophrenia, such as the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, the thalamus, and amygdala [6]. Specifically mGlu2 agonists, LY379268 and LY40439, exhibit antipsychotic properties by increasing dopamine extracellular levels[7]. Increasing dopamine levels improves negative symptoms of Schizophrenia [7]. mGlu2 agonists also increase cortical serotonin levels, which is a property seen in many antipsychotic drugs. These clinical properties give potential for mGlu2 and its agonists as future treatments for Schizophrenia[7].




