This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1714
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
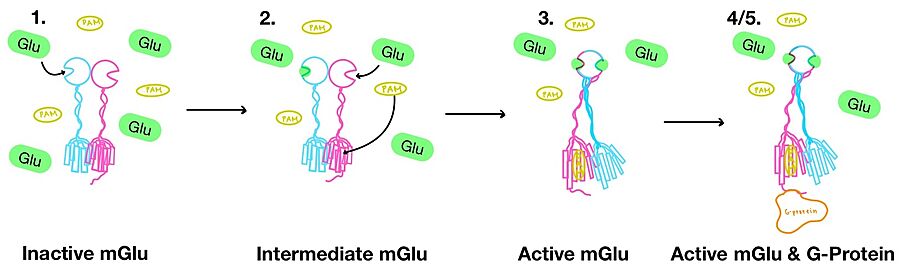
'''3.''' A second glutamate then binds to the other <scene name='90/904320/Active_site_interactions/4'>binding pocket</scene> of the VFT. Mediated by L639, F643, N735, W773, and F776, a <scene name='90/904320/Pam/8'>positive allosteric modulator</scene> (PAM) also binds within the seven TMD helices of the alpha chain <ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. This closed conformation of the VFT now has an inter-lobe angle of 25° is considered to be in the <scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/6'>active conformation</scene><ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. The binding of these ligands allows the CRDs to compact and come together. This transformation causes the TMD to form a separate, active asymmetric conformation with a <scene name='90/904319/Active_helices/23'>TM6-TM6 interface</scene> between the chains<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. | '''3.''' A second glutamate then binds to the other <scene name='90/904320/Active_site_interactions/4'>binding pocket</scene> of the VFT. Mediated by L639, F643, N735, W773, and F776, a <scene name='90/904320/Pam/8'>positive allosteric modulator</scene> (PAM) also binds within the seven TMD helices of the alpha chain <ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. This closed conformation of the VFT now has an inter-lobe angle of 25° is considered to be in the <scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/6'>active conformation</scene><ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. The binding of these ligands allows the CRDs to compact and come together. This transformation causes the TMD to form a separate, active asymmetric conformation with a <scene name='90/904319/Active_helices/23'>TM6-TM6 interface</scene> between the chains<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. | ||
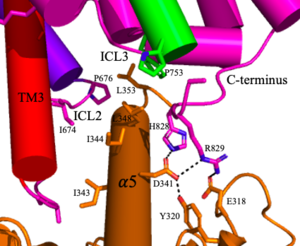
| - | '''4.''' The crossover of the helices from the alpha and beta chains allows for intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) and the C-terminus to be properly ordered to interact with a single G protein<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. While hydrogen bonding is present between the C-terminus and alpha helix 5 of the G-protein, this coupling is primarily driven by the hydrophobic interactions in the interface with the ɑ5 helix of the G protein<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>(Figure 4). This <scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/5'>mGlu/G-protein coupling | + | '''4.''' The crossover of the helices from the alpha and beta chains allows for intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) and the C-terminus to be properly ordered to interact with a single G protein<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. While hydrogen bonding is present between the C-terminus and alpha helix 5 of the G-protein, this coupling is primarily driven by the hydrophobic interactions in the interface with the ɑ5 helix of the G protein<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>(Figure 4). This <scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/5'>mGlu/G-protein coupling PAM as the pocket in which the coupling occurs would be completely closed in its absence<ref name="Seven">PMID:34194039</ref>. |
'''5.''' Upon binding, the G protein can become active through the receptor catalyzed reaction of GDP to GTP on the alpha subunit of the G protein. Depending on the type of mGlu present, this activation causes different signaling cascades to occur within the cell <ref name="Lin">PMID:34135510</ref>. These cascades are necessary for cellular function as they can play primary roles in regulating metabolic molecules, ion channels, transporter molecules, and several other parts of the cell; if these proteins are mutated, various diseases can occur<ref name="Crupi">PMID:30800054</ref>. | '''5.''' Upon binding, the G protein can become active through the receptor catalyzed reaction of GDP to GTP on the alpha subunit of the G protein. Depending on the type of mGlu present, this activation causes different signaling cascades to occur within the cell <ref name="Lin">PMID:34135510</ref>. These cascades are necessary for cellular function as they can play primary roles in regulating metabolic molecules, ion channels, transporter molecules, and several other parts of the cell; if these proteins are mutated, various diseases can occur<ref name="Crupi">PMID:30800054</ref>. | ||
Current revision
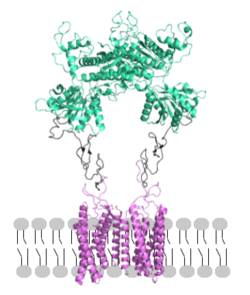
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor
| |||||||||||
Student Contributors
- Courtney Vennekotter
- Cade Chezem