We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Telomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
The reverse transcription process begins by the telomerase RNA binding to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA sequence. Once primed, the G-rich sequence (~6-8 nucleotides) polymerizes the end of the DNA. The RNA primer then translocates down the new DNA sequence and polymerizes again. This process repeats until the entire telomere is formed. After one side of the telomere is formed, the telomerase attaches the complementary nucleotide bases to complete the double-stranded telomere at the end of the DNA double helix. | The reverse transcription process begins by the telomerase RNA binding to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA sequence. Once primed, the G-rich sequence (~6-8 nucleotides) polymerizes the end of the DNA. The RNA primer then translocates down the new DNA sequence and polymerizes again. This process repeats until the entire telomere is formed. After one side of the telomere is formed, the telomerase attaches the complementary nucleotide bases to complete the double-stranded telomere at the end of the DNA double helix. | ||
| + | ==Telomerase 3D structures== | ||
| + | [[Telomerase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
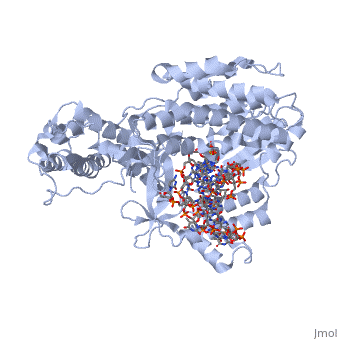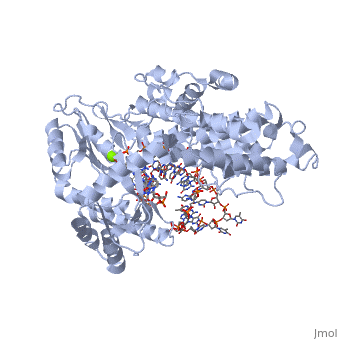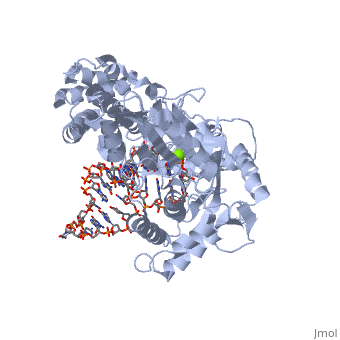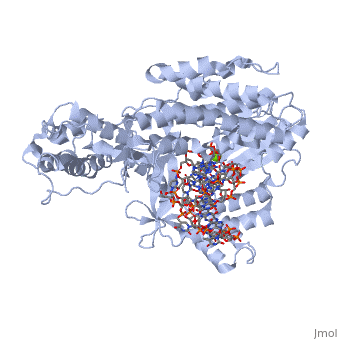
==Telomerase 3D structures== | ==Telomerase 3D structures== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
**[[4mnq]] – hTERT + MHC + b-2-microglobulin + T cell receptor<br /> | **[[4mnq]] – hTERT + MHC + b-2-microglobulin + T cell receptor<br /> | ||
**[[5ugw]] – hTERT thumb domain<br /> | **[[5ugw]] – hTERT thumb domain<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7bg9]], [[7bgb]] – hTERT H/ACA RNP lobe – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7qxa]] – hTERT + TPP1 + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7qxb]], [[7qxs]] – hTERT + TPP1 + POT1 + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[4lmo]] – TERT RNA binding domain - puffer<br /> | **[[4lmo]] – TERT RNA binding domain - puffer<br /> | ||
**[[4o26]] – TERT + telomerase TR – rice fish<br /> | **[[4o26]] – TERT + telomerase TR – rice fish<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3du6]], [[3du5]] - rfbTERT catalytic subunit - red flour beetle<br /> |
| - | **[[6e53]], [[6uso]], [[6usq]], [[6usp]] - rfbTERT + DNA<br /> | + | **[[5cqg]] - rfbTERT + inhibitor <br /> |
| + | **[[3kyl]], [[6e53]], [[6uso]], [[6usq]], [[6usp]] - rfbTERT + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7kqm]], [[7kqn]] - rfbTERT telomerase catalytic subunit + DNA + RNA<br /> | ||
**[[6usr]] - rfbTERT + DNA + G2P<br /> | **[[6usr]] - rfbTERT + DNA + G2P<br /> | ||
**[[2b2a]] - TtTERT telomerase catalytic subunit (mutant) - ''Tetrahymena thermophila''<br /> | **[[2b2a]] - TtTERT telomerase catalytic subunit (mutant) - ''Tetrahymena thermophila''<br /> | ||
**[[2r4g]] - TtTERT telomerase catalytic subunit<br /> | **[[2r4g]] - TtTERT telomerase catalytic subunit<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7lma]], [[7lmb]] – TtTERT + telomerase-associated protein + RNA + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6d6v]] – TtTERT + telomerase-associated protein + TEB2 + RNA + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[6d6v]] – TtTERT + telomerase-associated protein + TEB2 + RNA + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[5c9h]] - TtTERT catalytic subunit + DNA<br /> | **[[5c9h]] - TtTERT catalytic subunit + DNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3du6]], [[3du5]] - TcTERT telomerase catalytic subunit - ''Tribolium castaneum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kyl]] - TcTERT telomerase catalytic subunit + DNA<br /> | ||
**[[5lgf]] - OgTERT N-terminal - ''Ogataea polymorpha'' - NMR<br /> | **[[5lgf]] - OgTERT N-terminal - ''Ogataea polymorpha'' - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[5npt]] – OgTERT N-terminal <br /> | **[[5npt]] – OgTERT N-terminal <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6zd1]], [[6zd2]], [[6zd6]] - CaTERT – ''Candida albicans''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6zdp]], [[6zdq]], [[6zdu]] - CaTERT + RNA <br /> | ||
*Telomerase RNA | *Telomerase RNA | ||
| + | **[[7v99]], [[7v9a]] - hTERC in telomerase holoenzyme – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[1q75]], [[2k96]] – hTERC P2b hairpin (mutant) – human – NMR<br /> | **[[1q75]], [[2k96]] – hTERC P2b hairpin (mutant) – human – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2k95]], [[1na2]] - hTERC P2b hairpin – NMR<br /> | **[[2k95]], [[1na2]] - hTERC P2b hairpin – NMR<br /> | ||
Revision as of 07:32, 19 April 2022
| |||||||||||
Telomerase 3D structures
Updated on 19-April-2022
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Blackburn EH. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113-29. PMID:1497307 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Blackburn EH. Telomeres and telomerase: the means to the end (Nobel lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Oct 4;49(41):7405-21. doi: 10.1002/anie.201002387. PMID:20821774 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201002387
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Corey DR. Telomeres and telomerase: from discovery to clinical trials. Chem Biol. 2009 Dec 24;16(12):1219-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.12.001. PMID:20064431 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.12.001
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Gillis AJ, Schuller AP, Skordalakes E. Structure of the Tribolium castaneum telomerase catalytic subunit TERT. Nature. 2008 Oct 2;455(7213):633-7. Epub 2008 Aug 31. PMID:18758444 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature07283
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Mitchell M, Gillis A, Futahashi M, Fujiwara H, Skordalakes E. Structural basis for telomerase catalytic subunit TERT binding to RNA template and telomeric DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Apr;17(4):513-8. Epub 2010 Mar 28. PMID:20357774 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1777