Tetanus toxin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
*Tetanus toxin light chain | *Tetanus toxin light chain | ||
| - | **[[1yvg]] - CtTeNT Lc – ''Clostridium tetani''<br /> | + | **[[1yvg]] - CtTeNT Lc 1-427 – ''Clostridium tetani''<br /> |
| - | **[[1z7h]], [[4j1l]] - CtTeNT Lc (mutant) | + | **[[1z7h]], [[4j1l]], [[7by5]] - CtTeNT Lc (mutant) |
| + | **[[7ce2]], [[7oh0]], [[7oh1]] - CtTeNT Lc 11-451 + antibody<br /> | ||
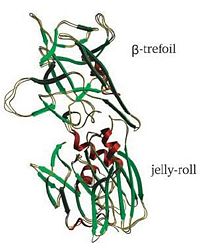
| - | *Tetanus toxin heavy chain | + | *Tetanus toxin heavy chain; Domains – translocation 459-865; receptor binding (RBD) 865-1315 |
| - | **[[1a8d]], [[1af9]] - CtTeNT Hc (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[5n0b]], [[5n0c]] - CtTeNT (mutant)<br /> |
| + | **[[1a8d]], [[1af9]] - CtTeNT Hc RBD (mutant)<br /> | ||
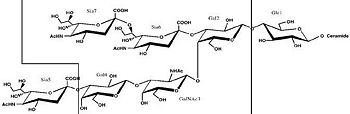
**[[1dfq]], [[1yyn]] – CtTeNT Hc + sialic acid <br /> | **[[1dfq]], [[1yyn]] – CtTeNT Hc + sialic acid <br /> | ||
**[[1diw]] - CtTeNT Hc + galactose<br /> | **[[1diw]] - CtTeNT Hc + galactose<br /> | ||
**[[1dll]] - CtTeNT Hc + lactose<br /> | **[[1dll]] - CtTeNT Hc + lactose<br /> | ||
**[[1d0h]] - CtTeNT Hc (mutant) + N-acetyl-galactosamine<br /> | **[[1d0h]] - CtTeNT Hc (mutant) + N-acetyl-galactosamine<br /> | ||
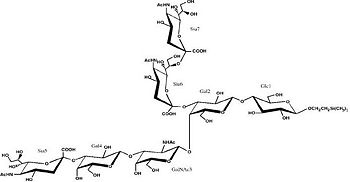
| - | **[[1fv2]], [[1fv3]] - CtTeNT Hc + ganglioside analog<br /> | + | **[[1fv2]], [[1fv3]] - CtTeNT Hc RBD + ganglioside analog<br /> |
| - | **[[1yxw]] - CtTeNT Hc + tripeptide<br /> | + | **[[1yxw]] - CtTeNT Hc RBD + tripeptide<br /> |
| - | **[[3hmy]] - CtTeNT Hc + GT2<br /> | + | **[[3hmy]] - CtTeNT Hc RBD + GT2<br /> |
| - | **[[3hn1]] - CtTeNT Hc + GT2 + lactose | + | **[[3hn1]] - CtTeNT Hc RBD + GT2 + lactose |
| + | **[[7bxx]] - CtTeNT translocation domain (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7by4]] - CtTeNT RBD <br /> | ||
| - | *Tetanus toxin light+heavy chain | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5n0b]] - CtTeNT <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5n0c]] - CtTeNT (mutant)<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 19 April 2022
| |||||||||||
3D structures of tetanus toxin
Updated on 19-April-2022
References
- ↑ Hatheway CL. Toxigenic clostridia. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):66-98. PMID:2404569
- ↑ Bizzini B. Tetanus Toxin. Microbiological Reviews.1979 June;43(2):224-236.[1]
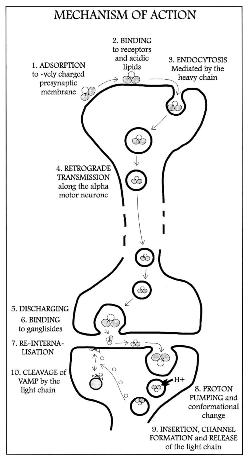
- ↑ Mechanism of Action of Tetanospasmin (Dr. Arnab K Rana) [image on the internet]. 2005[updated 2005 Dec 26; cited 2011 Apr 20]. Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Mechanism_of_action_of_tetanospasmin.gif
- ↑ Lalli G, Schiavo G. Analysis of retrograde transport in motor neurons reveals common endocytic carriers for tetanus toxin and neurotrophin receptor p75NTR. J Cell Biol. 2002 Jan 21;156(2):233-9. Epub 2002 Jan 21. PMID:11807088 doi:10.1083/jcb.200106142
- ↑ Mocchetti I. Exogenous gangliosides, neuronal plasticity and repair, and the neurotrophins. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2283-94. PMID:16158191 doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5188-y
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Chen C, Fu Z, Kim JJ, Barbieri JT, Baldwin MR. Gangliosides as high affinity receptors for tetanus neurotoxin. J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 25;284(39):26569-77. Epub 2009 Jul 14. PMID:19602728 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.027391
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Fotinou C, Emsley P, Black I, Ando H, Ishida H, Kiso M, Sinha KA, Fairweather NF, Isaacs NW. The crystal structure of tetanus toxin Hc fragment complexed with a synthetic GT1b analogue suggests cross-linking between ganglioside receptors and the toxin. J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 24;276(34):32274-81. Epub 2001 Jun 19. PMID:11418600 doi:10.1074/jbc.M103285200