Introduction
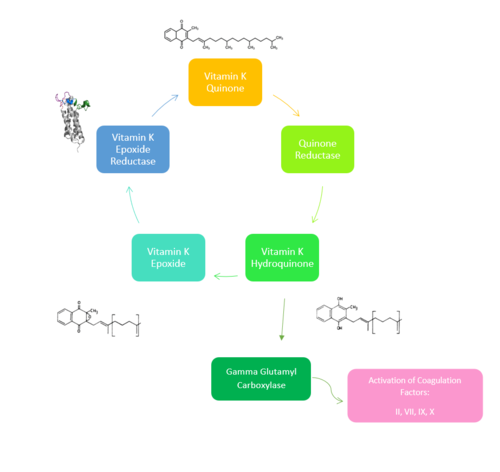
Figure 1. Overview of Vitamin K Cycle: The cycle begins with
Vitamin K Quinone. Vitamin K Quinone is reduced by enzyme Quinone Reductase. This leaves Vitamin K Hydroquinone which can either lead to
Gamma Carboxylaseactivity that will activate Blood Coagulation Factors II, VII, IX, and X. After this, Vitamin K Epoxide is left over. Vitamin K Epoxide is reduced by the enzyme Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase to reform Vitamin K Quinone.
(VKOR) is an endoplasmic membrane enzyme that generates the active form of Vitamin K to support blood coagulation[1]. VKOR homologs are integral membrane thiol oxidoreductases Thiol OxidoReductase due to the function of VKOR being dependent on thiol residues and disulfide bonding. The Vitamin K Cycle and the VKOR enzyme specifically are common drug targets for thromboembolic diseases. This is because, as pictured, the vitamin K cycle is required to activate blood coagulant factors II, VII, IX, and X. Coagulant factor activation promotes blood clotting, which in high amounts can be dangerous and cause thromboembolic diseases such as stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and/or pulmonary embolism.
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is found and primarily synthesized in the liver .
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is unstable in-vitro. To determine its structure an extra protein superfolder green flourescent protein (sGFP) was appended to the N and C termini of Vitamin K Epoxide. For the visualizing VKOR, this protein has been removed from the structural scenes. After sGFP was removed from the structural scenes, we further took the structure files and resequenced them to better align with the numbering of the protein. In these files the sequence slightly differs between the organisms used to view Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. In the human version, HsVKOR, the catalytic cysteines that play an intricate role in the reduction of Vitamin K Epoxide are 43, 51, 132, and 135. In the pufferfish version of the file, TrVKORL, the cysteines are 52, 55, 141, and 144.
Structure
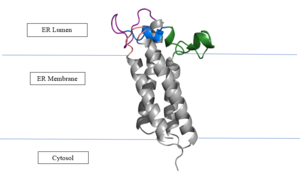
Figure 2: Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase in the Endoplasmic Membrane In the liver, the VKOR enzyme is set in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (Fig.2). The transmembrane helices are located in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Luminal Region, which is the region between the ER Lumen and the Cytosol. The cap region is partially oriented in the ER Lumen. The active site remains within the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane.The Anchor is partially within the ER lumen, and partially embedded in the ER membrane. The anchor is what attaches the cap domain and stabilizes it, which allows the cap domain to cover the active site.[2]
The VKOR enzyme is made up of four transmembrane helices (Fig.2): , , , and (Grey/Orange). Each of these helices come together to form a central ligand binding pocket. This central pocket is the active site where conserved Cysteines: C132 and C135 are located. In the cap domain are important regions that are significant for Vitamin K binding, and the overall function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase, including the Anchor(Green), Cap Sequence (Blue), Beta Hairpin (Purple), and 3-4 Loop (Pink). [2]
The attaches to the cap domain of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Enzyme and is partially embedded in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane. This both stabilizes the enzyme in the membrane, and stabilizes the cap domain over the active site. [2]
The is two parts: The cap helix and the cap loop. When the enzyme is reducing Vitamin K Epoxide or being inhibited by Vitamin K Antagonists, this cap region swings downward over the active site. The cap region is directly attached to the anchor. [2]
The is only seen in the closed conformation of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. When in the open conformation the beta hairpin is referred to as the (yellow). The Beta hairpin is significant due to the fact that it contains the other two conserved cysteines necessary for the function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase: Cysteine43 and Cysteine51. The beta hairpin/luminal helix is directly connected to the cap region. [2]
The is the sequence of residues between Transmembrane Helix 3 and Transmembrane Helix 4. In the open conformation the loop does not have significant interactions with the rest of the cap domain, however in the closed conformation Loop 3-4 has many hydrogen reactions with the Cap Loop. This allows for the stabilization when VKOR is closed. [2]
Vitamin K Epoxide
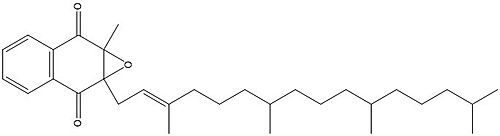
Figure 3. Vitamin K Epoxide structure
As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle and required for blood coagulation. In the cycle, VKOR reduces Vitamin K epoxide to Vitamin K Quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. In this conversion, VKOR donates electrons to Vitamin K epoxide from the S-H of the active pair of cysteines, C132-C135. The mediated cysteine pair, C43-C51, has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate to occur.
Two other notable structures are Vitamin K Quinone (Fig. 5) and Vitamin K Hydroquinone (Fig. 6). Vitamin K Quinone is the product that is released after the reaction with Vitamin K Epoxide and VKOR. (Fig. 1)
Figure 4. Vitamin K Quinone structure
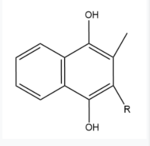
Figure 5. Vitamin K Hydroquinone structure
Binding
In its resting state, VKOR is in its . The Vitamin K epoxide enters through the . The tunnel is located between .[3] The carbonyls on the VK epoxide bind to on VKOR. With Vitamin K epoxide bound, the conformation transitions from open to closed, where the catalytic process will begin.
Catalytic Cycle
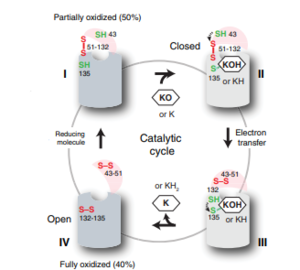
Figure 6: The catalytic cycle of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase [2] Step I
VKOR is the second enzyme in the Vitamin K Cycle (Fig. 1), and has its own catalytic cycle as well. of reforming Vitamin K Epoxide (Fig. 3) through the enzyme Vitamin K Reductase (VKOR) begins in a partially oxidized open conformation. In this state, catalytic cysteines 51 and 132 form a disulfide bond. Cysteines 43 and 135 are considered "free" because they are not bound to anything in this state. The (highlighted in hot pink) is also empty because Vitamin K Epoxide has not bound yet. In order to get to the next step, Vitamin K epoxide will enter through the isoprenyl-chain tunnel.[2]
Step II
After Vitamin K Epoxide enters through the isoprenyl-chain tunnel, this begins . This binding induces a conformation change that "closes" the enzyme.Asn80 on TM2 and Tyr139 on TM4 . to Vitamin K Epoxide. When Vitamin K Epoxide binds, there is a shift in the bonds between the cap domain, beta hairpin, and anchor. also forms a disulfide bond with the 3' OH group on Vitamin K Epoxide.
Step III
is within this partially and free Cys43 forms a bond with Cys 51. Cys51 kicks its electrons to Cys132, and Cys 132 forms a disulfide bond with Cys135. Cys135 then reduces the epoxide ring on Vitamin K Epoxide after donating its electrons. The epoxide ring opens and reforms Vitamin K Quinone (Fig.3).
Step IV
is the last step of this cycle. A bond between Cys43 and Cys51 causes an electron transfer to Cys132. In its reduced form Cys132 will attack Cys135, and the extra electrons are kicked to Vitamin K Epoxide. This opens the epoxide ring on Vitamin K Epoxide so that it may be reformed into Vitamin K Quinone. Vitamin K Quinone is released from Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. VKOR is in a fully oxidized open conformation. This process is repeated over and over unless interrupted by inhibitors known as Vitamin K Antagonists or VKAs. Vitamin K Quinone will exit the central binding pocket and the open conformation will form. VKOR is in its fully oxidized state after donating its electrons to Vitamin K Epoxide. This is when the luminal helix will be visible. The cycle then repeats at Step I to keep reducing Vitamin K Epoxide to Vitamin K Quinone. [2]
Warfarin
Warfarin is the most common Vitamin K antagonist (VKA). Warfarin is a competitive inhibitor, taking the place of Vitamin K Epoxide (VKO) in the active site of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKOR). When warfarin binds in the active site, it causes VKOR to go into the closed conformation.
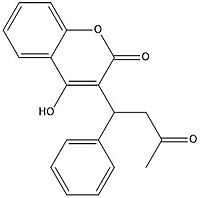
Figure 7. Warfarin structure
Binding
Warfarin still forms Hydrogen bonds with . The specific bonds are between Asn80 and the 2-ketone group of warfarin and Tyr139 with the 4-hydroxyl group of warfarin. The rest of the pocket is hydrophobic interactions. The H bonds are necessary for the recognition of the ligand in the binding site of VKOR.
There is a slight difference in the way in which warfarin binds compared to VKO. Warfarin binds are a slightly different angle (Fig.7). This creates a difference in how the cap loop and anchor domain interact, and that noticeable difference is with . With VKO, Arg58, located in the cap loop, directly interacts with when VKO is bound. When warfarin binds, Arg58 is found inserted between of the anchor domain.[2]
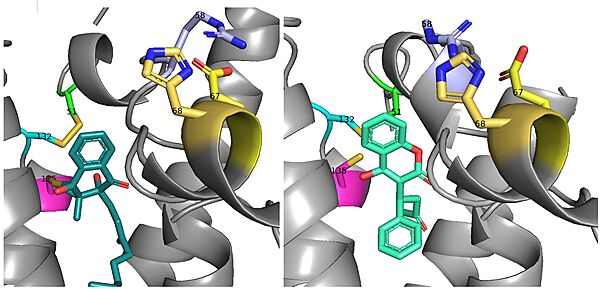
Figure 8. Vitamin K Epoxide and Warfarin Binding Angles: There is a slight angle of around 30 degrees in which VKO(left) and warfarin(right) bind. The location of the cap domain and the interactions between amino acid residues changes based on this slight difference in binding.
Disease
Vitamin K Antagonists play a big role in the treatment of thromboembolic diseases, like a stroke or heart attack.[4] Warfarin is the most common medication for this treatment, acting as a blood thinner. Warfarin binding in VKOR overall prevents the triggering of coagulation factors that form blood clots.
References
- ↑ Shen G, Cui W, Cao Q, Gao M, Liu H, Su G, Gross ML, Li W. The catalytic mechanism of vitamin K epoxide reduction in a cellular environment. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100145. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401. Epub 2020, Dec 10. PMID:33273012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel AM, Li W. Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science. 2020 Nov 5. pii: science.abc5667. doi: 10.1126/science.abc5667. PMID:33154105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667
- ↑ Li W, Schulman S, Dutton RJ, Boyd D, Beckwith J, Rapoport TA. Structure of a bacterial homologue of vitamin K epoxide reductase. Nature. 2010 Jan 28;463(7280):507-12. PMID:20110994 doi:10.1038/nature08720
- ↑ Goy J, Crowther M. Approaches to diagnosing and managing anticoagulant-related bleeding. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012 Oct;38(7):702-10. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1326788. Epub, 2012 Oct 3. PMID:23034830 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1326788








