We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Transaldolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
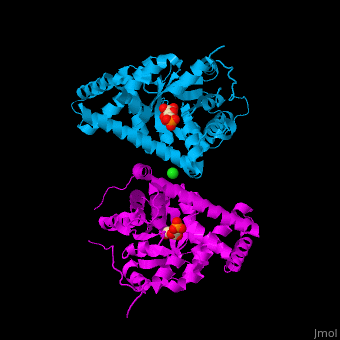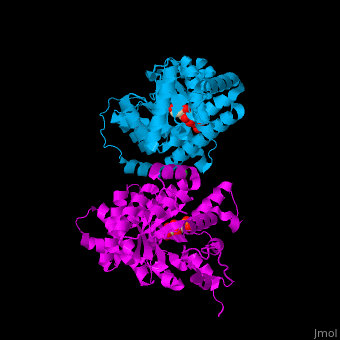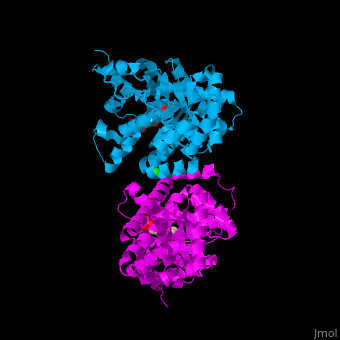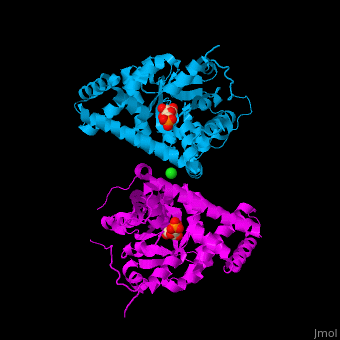
<StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='47/477090/Cv/1' caption='Transaldolase dimer complex with sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and Cl- (green) ion, [[3tno]]' pspeed='8'> | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='47/477090/Cv/1' caption='Transaldolase dimer complex with sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and Cl- (green) ion, [[3tno]]' pspeed='8'> | ||
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Transaldolase''' (TAL) is part of the pentose phosphate pathway. It catalyzes the transformation of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to erythrose 4-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate<ref>PMID:15960612</ref>. | '''Transaldolase''' (TAL) is part of the pentose phosphate pathway. It catalyzes the transformation of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to erythrose 4-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate<ref>PMID:15960612</ref>. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
{{Template:ColorKey_Loop}}, | {{Template:ColorKey_Loop}}, | ||
{{Template:ColorKey_Turn}}). The <scene name='47/477090/Cv/9'>active site contains a Schiff-base-bound phosphosugar</scene> at <scene name='47/477090/Cv/10'>Lys135</scene><ref>PMID:24531488</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='47/477090/Cv/11'>Cl coordination site</scene>. | {{Template:ColorKey_Turn}}). The <scene name='47/477090/Cv/9'>active site contains a Schiff-base-bound phosphosugar</scene> at <scene name='47/477090/Cv/10'>Lys135</scene><ref>PMID:24531488</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='47/477090/Cv/11'>Cl coordination site</scene>. | ||
| + | == 3D Structures of transaldolase == | ||
| + | [[Transaldolase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of transaldolase == | == 3D Structures of transaldolase == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
*Transaldolase | *Transaldolase | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1f05]] – TAL – human<br /> |
| + | **[[2cwn]], [[2e1d]] – TAL (mutant) – mouse<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3clm]], [[6zwf]], [[6zwh]], [[6zwj]], [[6zx4]], [[7b0l]], [[7odo]], [[7odp]], [[7odq]] –NgTAL – ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7bbw]], [[7bbx]], [[7oey]] - NgTAL (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[3cwn]], [[1onr]], [[1ucw]] - EcTAL B – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | **[[3cwn]], [[1onr]], [[1ucw]] - EcTAL B – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
**[[3kof]], [[1i2n]], [[1i2o]], [[1i2p]], [[1i2q]], [[1i2r]], [[4rz5]], [[4rz6]] - EcTAL B (mutant)<br /> | **[[3kof]], [[1i2n]], [[1i2o]], [[1i2p]], [[1i2q]], [[1i2r]], [[4rz5]], [[4rz6]] - EcTAL B (mutant)<br /> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 34: | ||
**[[3r8r]] – TAL – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | **[[3r8r]] – TAL – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | ||
**[[3r5e]] – TAL – ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''<br /> | **[[3r5e]] – TAL – ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1f05]] – TAL – human<br /> | ||
**[[1vpx]] – TAL – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | **[[1vpx]] – TAL – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | ||
**[[1wx0]] – TAL – ''Thermus thermophilus''<br /> | **[[1wx0]] – TAL – ''Thermus thermophilus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[6yre]] - TaTAL – ''Thermoplasma acidophilum''<br /> |
*Transaldolase binary complexes | *Transaldolase binary complexes | ||
| Line 44: | Line 48: | ||
**[[4s2c]], [[4s1f]] - EcTAL B + fructose 6-phosphate<br /> | **[[4s2c]], [[4s1f]] - EcTAL B + fructose 6-phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4rxf]], [[4rxg]], [[4rz4]] - EcTAL B (mutant) + fructose 6-phosphate<br /> | **[[4rxf]], [[4rxg]], [[4rz4]] - EcTAL B (mutant) + fructose 6-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4xz9]] - | + | **[[4xz9]] - TaTAL + glycerol 3-phosphate <br /> |
| - | + | **[[6yr3]] - TaTAL + fructose 6-phosphate <br /> | |
| + | **[[6yrh]], [[6yrm]], [[6yrt]] - TaTAL (mutant) + fructose 6-phosphate<br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 07:55, 27 April 2022
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of transaldolase
Updated on 27-April-2022
References
- ↑ Caillau M, Paul Quick W. New insights into plant transaldolase. Plant J. 2005 Jul;43(1):1-16. PMID:15960612 doi:http://dx.doi.org/TPJ2427
- ↑ Qian Y, Banerjee S, Grossman CE, Amidon W, Nagy G, Barcza M, Niland B, Karp DR, Middleton FA, Banki K, Perl A. Transaldolase deficiency influences the pentose phosphate pathway, mitochondrial homoeostasis and apoptosis signal processing. Biochem J. 2008 Oct 1;415(1):123-34. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080722. PMID:18498245 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20080722
- ↑ Light SH, Minasov G, Duban ME, Anderson WF. Adherence to Burgi-Dunitz stereochemical principles requires significant structural rearrangements in Schiff-base formation: insights from transaldolase complexes. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Feb;70(Pt 2):544-52. doi:, 10.1107/S1399004713030666. Epub 2014 Jan 31. PMID:24531488 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713030666