We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ricin: Structure and function
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
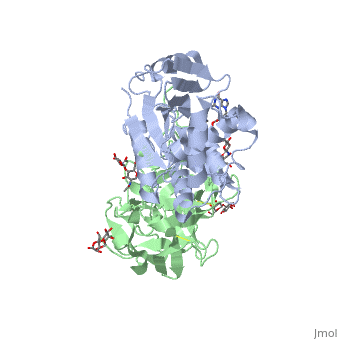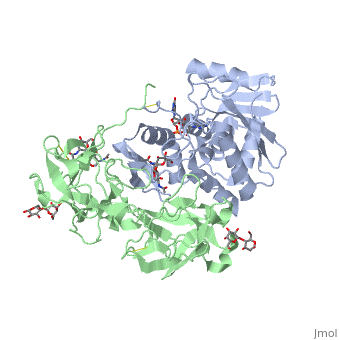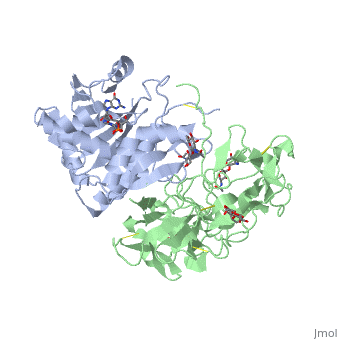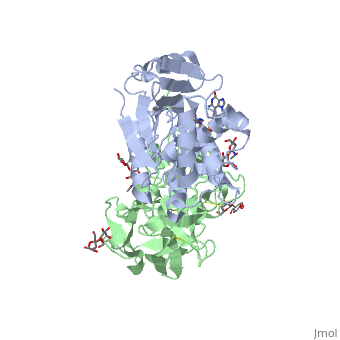
The structure of Ricin consists of two polypeptide chains known as the A and B chain that carry out different functions within the protein due to their amino acid sequences. This heterodimer’s chains are joined by disulfide bonds and have fairly similar molecular weights. In order for ricin to carry out its function, the two chains need to be linked, although they do separate further into the mechanism of action. | The structure of Ricin consists of two polypeptide chains known as the A and B chain that carry out different functions within the protein due to their amino acid sequences. This heterodimer’s chains are joined by disulfide bonds and have fairly similar molecular weights. In order for ricin to carry out its function, the two chains need to be linked, although they do separate further into the mechanism of action. | ||
<scene name='91/910715/Achain/1'>The A chain</scene> (Ricin A) is a globular protein that consists of 8 beta sheets and 8 alpha helices. It is composed of 267 amino acids and is separated into three structural domains. The first domain is made up of parallel and antiparallel beta sheets, the second contains alpha helices, and the third consists of both. These three domains carry out the function of ribosome inactivation within the Golgi apparatus in a cell, as the active site for depurination lies on the second alpha helical domain. The enzymatic activity of this protein is mainly seen on this chain in the ricin loop, where an adenine of a target cell becomes trapped by two tyrosines. This will result in the prevention of mRNA translation. | <scene name='91/910715/Achain/1'>The A chain</scene> (Ricin A) is a globular protein that consists of 8 beta sheets and 8 alpha helices. It is composed of 267 amino acids and is separated into three structural domains. The first domain is made up of parallel and antiparallel beta sheets, the second contains alpha helices, and the third consists of both. These three domains carry out the function of ribosome inactivation within the Golgi apparatus in a cell, as the active site for depurination lies on the second alpha helical domain. The enzymatic activity of this protein is mainly seen on this chain in the ricin loop, where an adenine of a target cell becomes trapped by two tyrosines. This will result in the prevention of mRNA translation. | ||
| - | The B chain (Ricin B) is a lectin that is composed of 262 amino acids and carries out the action of binding through a galactose binding terminal. This chain does not have any alpha helical or beta sheet structure but does fold into two domains. | + | <scene name='91/910715/Bchain/1'>The B chain</scene> (Ricin B) is a lectin that is composed of 262 amino acids and carries out the action of binding through a galactose binding terminal. This chain does not have any alpha helical or beta sheet structure but does fold into two domains. |
These chains are not exclusive to castor plants and they can be found in other non toxic vegetation as well; it is only when these two chains are bound together where they are able to have devastating impacts on an organism<ref>Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID: 8119491.</ref><ref>Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin Poisoning: A Comprehensive Review. JAMA. 2005;294(18):2342–2351. doi:10.1001/jama.294.18.2342</ref>. | These chains are not exclusive to castor plants and they can be found in other non toxic vegetation as well; it is only when these two chains are bound together where they are able to have devastating impacts on an organism<ref>Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID: 8119491.</ref><ref>Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin Poisoning: A Comprehensive Review. JAMA. 2005;294(18):2342–2351. doi:10.1001/jama.294.18.2342</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 29 April 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Etimad, L., Moshiri, M., & Hamid, F. (2019, June 6). Ricin: An ancient story for a timeless plant toxin. RBMB. Retrieved April 23, 2022,
- ↑ Tumer, N. E. (2019). Introduction to the Toxins Special Issue “Ricin Toxins.” Toxins, 12(1).
- ↑ Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID: 8119491.
- ↑ Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin Poisoning: A Comprehensive Review. JAMA. 2005;294(18):2342–2351. doi:10.1001/jama.294.18.2342
- ↑ Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID: 8119491.
- ↑ Gal, Y., Mazor, O., Falach, R., Sapoznikov, A., Kronman, C., & Sabo, T. (2017). Treatments for Pulmonary Ricin Intoxication: Current Aspects and Future Prospects. Toxins, 9(10).