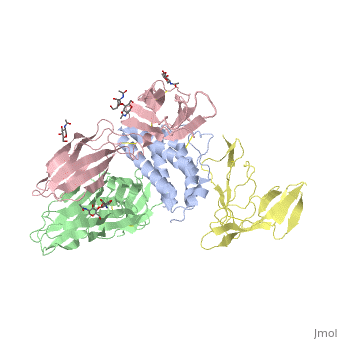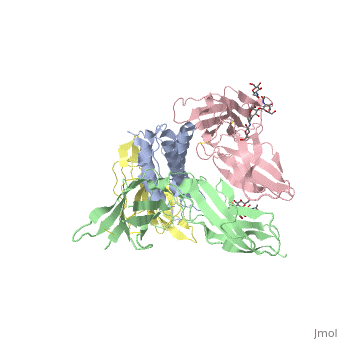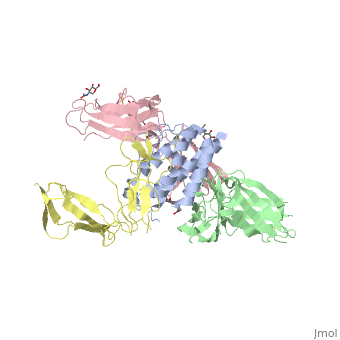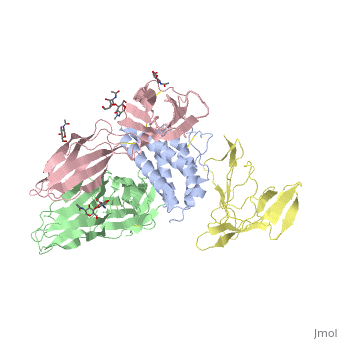This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Interleukin receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='2b5i' size='340' side='right' caption='Glycosylated interleukin-2 receptor α (yellow), β (green), γ (pink) chains complex with interleukin-2 (grey), [[2b5i]]' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2b5i' size='340' side='right' caption='Glycosylated interleukin-2 receptor α (yellow), β (green), γ (pink) chains complex with interleukin-2 (grey), [[2b5i]]' scene=''> | ||
'''Interleukin receptors''' (ILR) are cytokine receptor which are classified into type I, type II and others. '''ILR type I''' are cell surface receptors which recognize cytokines with four α-helical strands. '''ILR type II''' are similar to type I but lack the former’s signature sequence: WXSWS. Interleukin-1 receptor belongs to the ILR of immunoglobulin family. IL1R contains two types. Type I (IL1R1) binds interleukin-1 (IL1) transmitting its inflammatory effect. Interleukin-1 receptor type II (IL1R2) suppresses IL1 activity. Another suppressor of IL1R activity is the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1R1A). | '''Interleukin receptors''' (ILR) are cytokine receptor which are classified into type I, type II and others. '''ILR type I''' are cell surface receptors which recognize cytokines with four α-helical strands. '''ILR type II''' are similar to type I but lack the former’s signature sequence: WXSWS. Interleukin-1 receptor belongs to the ILR of immunoglobulin family. IL1R contains two types. Type I (IL1R1) binds interleukin-1 (IL1) transmitting its inflammatory effect. Interleukin-1 receptor type II (IL1R2) suppresses IL1 activity. Another suppressor of IL1R activity is the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1R1A). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''TYPE-1 INTERLEUKIN-1 RECEPTOR COMPLEXED WITH INTERLEUKIN-1 BETA''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interleukin-1_receptor Interleukin-1 receptor] complex with ligand and go through the plasma membrane. <scene name='57/571319/Scene_2/2'> Type 1 Interleukin-1 receptor complex with Interleukin-1 beta</scene> 3D structure is showing here. Ribbon diagram of s-IL 1R complex to IL-1β. The complex has approximate dimensions of 97Å × 52Å ×35Å with one s-IL1R molecule wrapping around the IL-1β molecule with 1:1 ratio. In the <scene name='57/571319/Scene_2/3'>complex</scene>, domain 3 provides a 'lid' which covers most of the top of the IL-1β β-barrel, whereas domains 1 and 2 from a groove which binds to the lower rim of the barrel. Here, Domains 1,2 and 3 of s-IL 1R are colored light, medium and dark blue, respectively. IL-1β is yellow, with site A residues in green and site B residues in red. The structure is oriented so that the carboxy terminus of s-IL 1R and the cell membrane are at the bottom of the picture. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''STRUCTURE OF THE INTERLEUKIN-1BETA SIGNALING COMPLEX''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Ternary complex paradigm.png||250px|right|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='57/571319/Scene_3/1'> Interleukin-1 beta signal complex</scene> 3D structure was showed here, and the cartoon (right) showed the formation of the ternary complex paradigm, the primary receptors ('''IL-1R''') first bind their corresponding cytokine ligands ('''IL-1β''') and then engage the accessory receptor ('''IL-1RAcP''') (which is incapable of binding cytokines by itself). The overall ternary architecture of the IL-1β–IL-1RI–IL-1RAcP signaling complex has the cytoplasmic TIR domain necessary for signal transduction. The IL-1RI-IL-1RAcP interface was most hydrogen-bonded and signal was transferred through the highly packed hydrophobic region between receptor accessory and IL-1R liganded with IL-1β. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The dimer complex with conserved area was showed when you <scene name='57/571319/Scene_3/2'>click here</scene>. The insert are ligands (IL-1β), which are present as conserved structure as well as green ribbon. The two IL-1Rs and two IL-1RAcPs are colored as purple and blue, respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Clinical significance== | ||
| + | Why are people interested in IL-1? Because IL-1 cytokines family are usually over-expressed at tumor sites or inflammatory, these cytokines could be used as bio-markers to help diagnose in advance. Also, since IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-1ra all have the ability to bind to the type 1 IL-1 receptor (IL-1R), and the binding of IL-1α or IL-1β to IL-1R is an early step in IL-1 signal transduction, blocking this interaction may therefore be a useful target for the development of new drugs. | ||
See also: | See also: | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 1 May 2022
| |||||||||||