|
Function
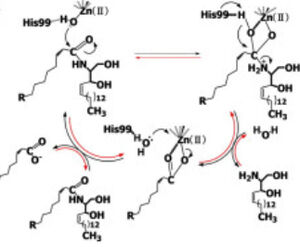 Figure 1 Proposed mechanisms of the zinc-dependent hydrolysis of C2-ceramide (Black arrows) and the zinc-dependent synthesis of C2-ceramide from palmitate and sphingosine (Red arrows) by CerN . Figure adapted from Inoe et al.(2009) [1] CerN is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of the Sphingolipid at the , producing .[2] [1] As a neutral ceramidase, optimal catalytic activity of CerN occurs between pH 6.5-8.5.[2] CerN cleaves the N-acyl linkage within ceramides via zinc-dependent hydrolysis and the enzyme is also capable of synthesizing ceramide from sphingosine and palmitic acid by the reverse mechanism.[1][3] The zinc ion within the is coordinated by His97, His204, Glu411, Tyr448, and a water molecule. His97 and Tyr448 are required for zinc binding within the active site. Ligand binding within the active site is recognized by Gly25, His99, Arg160, and Tyr460.[1] Ser27 and Gly25 stabilize ceramide within the active site by forming a water-mediated hydrogen bond with the central OH of ceramide, and the carbonyl oxygen is stabilized by the Tyr448 and Tyr460.
Upon ligand binding, CerN enters the conformation. [1] His99 and Arg160 function in the catalysis of ceramide hydrolysis, as they deprotonate their coordinated water molecule to produce a hydroxide ion.[1] The carbonyl carbon of ceramide undergoes a nucleophilic attack by the hydroxide ion (Figure 1).[1] The carbonyl oxygen stabilized by Tyr448 and Tyr460 is then passed to the zinc ion, allowing for the breakage of the N-acyl linkage.[1] Sphingosine is then released from the active site while the fatty acid remains bound to the zinc ion until it is replaced by a new water molecule, shifting CerN into the conformation.[1] The synthesis of ceramide from palmitate and sphingosine occurs via the same mechanism but in reverse (Figure 1). [1]
Structural highlights
CerN consists of two domains: a .[1] Three β-sheets, each formed from four β-strands, compose a β-prism fold at the center of the N-terminal domain.[1] Surrounding the β-prism fold are 11 α-helices, forming an .[1] The immunoglobulin-like C-terminal domain is composed of two β-sheets, containing four β-strands each, forming a .[1] Between the N- and C-terminal domains is a magnesium/calcium ion binding site that links together the two domains.[1] His37, Asp579, Asp581, and Thr854 interact with divalent cations within the .[1] A is located within the N-terminal domain active site, where it is coordinated by His97, His204, Glu411, and a water molecule.[1]
Full crystallographic information for 2zxc (Closed) is available from OCA.Full crystallographic information for 2zws (Open) is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
| | Ligands: | , , , , |
| Activity: | Ceramidase, with EC number 3.5.1.23 |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, ProSAT |
Role of Ceramide and CerN in Bacterial Infections
Sphingolipids play key role in eukaryotic cell membrane structure and function.[4][5] Additionally, sphingolipids act as signaling molecules for eukaryotic processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, cell migration, and pathogen defense.[5] Ceramide is considered as the central molecule in sphingolipid metabolism, as it can be converted to more complex sphingolipids or be broken down for the production of sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate.[6] [7] [8] Eukaryotes utilize ceramide in the formation of lipid rafts, lipid-protein platforms that alter the biophysical properties of cell membranes as well as localize receptors for signal amplification.[5] [7] Sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, the products of ceramide catabolism, are important for pathogen defense by functioning as a potent anti-microbial and activating signal for host-immune responses, respectively.[6]
Due to its abundance in eukaryotic cell membranes and role in pathogen defense, pathogens have evolved mechanisms to use host ceramides for their own pathogenesis.[7] Ceramide-rich membrane platforms on human-epithelial cells serve as sites for the attachment and invasion of bacterial pathogens such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae.[7] Pseudomonas aeruginosa is capable of detecting host-derived sphingosine, resulting in activation of P. aeruginosa sphingosine-responsive genes.[9] The products of P. aeruginosa sphingosine-responsive genes are used for the detoxification of sphingosine, as well as its production from other host-derived sphingolipids, making P. aeruginosa sphingosine tolerant.[9] Loss of P. aeruginosa sphingosine-responsive genes results in the inability of the bacteria to survive in the presence of sphingosine in vitro or in the murine lung.[9] CerN is one of the proteins encoded by P. aeruginosa sphingosine-responsive genes used for the production of sphingosine from ceramide, with the added ability of functioning as a ceramide synthase.[2][3][9] It has been hypothesized that the hydrolysis of host-membrane ceramide via CerN facilitates P. aeruginosa intracellular invasion, similar to other bacterial pathogens.[2] CerN is also involved in P. aeruginosa biofilm production, a major virulence trait of the pathogen.[10] Sphingosine production via CerN-mediated hydrolysis of host ceramide induces a biofilm formation at sites of infection, biofilm accumulation yields more ceramide hydrolysis, creating a positive-feedback loop for P. aeruginosa virulence.[10]
Evolutionary Conservation
 Figure 2 Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment of neutral ceramidases from Pseudomonas aeruginosahumans, rats, fruit flies, and zebrafish Ceramidases are classified into three groups based upon primary structure and the optimal pH for their catabolic activity: acidic, neutral, and alkaline.[11] Neutral ceramidases function optimally between pH 6.5-8.5 and can be found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, while acidic and alkaline ceramidases are restricted to eukaryotes.[11] The primary structure of neutral ceramidases is conserved from bacteria to humans, neutral ceramidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and humans share 32% identity and 47% similarity.[11] The amino acids responsible for the catalytic activity of neutral ceramidases, primarily His99 and Arg160, are conserved in P. aeruginosa, humans, rats, fruit flies, and zebrafish, suggesting that the enzymatic mechanism is also shared (Figure 2).[2][11] Furthermore, the crystal structure of Human neutral ceramidase (Figure 3) is similar to that of P. aeruginosa, aligning with an RMSD value of 0.890 Å (Figure 4). However, the location of neutral ceramidase expression differs between bacteria/invertebrates and vertebrates.[11] Neutral ceramidases from bacteria, slime molds, and fruit flies are secreted proteins, while the enzyme is primarily membrane-bound in vertebrates.[11] Vertebrate ceramidases contain a serine/threonine/proline-rich domain, or mucin box, within the N-terminal region which is necessary for anchoring to the plasma membrane.[11]
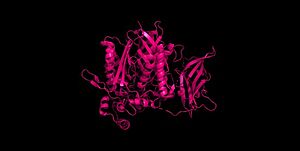 Figure 3 Human neutral ceramidase 4wgk 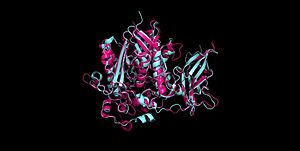 Figure 4 Alignment of Human neutral ceramidase 4wgk (pink) and P. aeruginosa neutral ceramidase 2zws (blue) RMSD=0.890 Å
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 Inoue T, Okino N, Kakuta Y, Hijikata A, Okano H, Goda HM, Tani M, Sueyoshi N, Kambayashi K, Matsumura H, Kai Y, Ito M. Mechanistic insights into the hydrolysis and synthesis of ceramide by neutral ceramidase. J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 3;284(14):9566-77. Epub 2008 Dec 16. PMID:19088069 doi:10.1074/jbc.M808232200
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Okino N, Tani M, Imayama S, Ito M. Purification and characterization of a novel ceramidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14368-73. PMID:9603946
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kita K, Okino N, Ito M. Reverse hydrolysis reaction of a recombinant alkaline ceramidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 31;1485(2-3):111-20. doi:, 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00029-9. PMID:10832092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00029-9
- ↑ Futerman AH, Hannun YA. The complex life of simple sphingolipids. EMBO Rep. 2004 Aug;5(8):777-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400208. PMID:15289826 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400208
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;9(2):139-50. doi: 10.1038/nrm2329. PMID:18216770 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm2329
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Wu Y, Liu Y, Gulbins E, Grassme H. The Anti-Infectious Role of Sphingosine in Microbial Diseases. Cells. 2021 May 4;10(5). pii: cells10051105. doi: 10.3390/cells10051105. PMID:34064516 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cells10051105
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Seitz AP, Grassme H, Edwards MJ, Pewzner-Jung Y, Gulbins E. Ceramide and sphingosine in pulmonary infections. Biol Chem. 2015 Jun;396(6-7):611-20. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0285. PMID:25720061 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2014-0285
- ↑ Harrison PJ, Dunn TM, Campopiano DJ. Sphingolipid biosynthesis in man and microbes. Nat Prod Rep. 2018 Sep 19;35(9):921-954. doi: 10.1039/c8np00019k. PMID:29863195 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c8np00019k
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 LaBauve AE, Wargo MJ. Detection of host-derived sphingosine by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is important for survival in the murine lung. PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1003889. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003889. Epub, 2014 Jan 23. PMID:24465209 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003889
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Sinha M, Ghosh N, Wijesinghe DS, Mathew-Steiner SS, Das A, Singh K, Masry ME, Khanna S, Inoue H, Yamazaki K, Kawada M, Gordillo GM, Roy S, Sen CK. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Theft Biofilm Require Host Lipids of Cutaneous Wound. Ann Surg. 2021 Oct 12. pii: 00000658-900000000-93230. doi:, 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005252. PMID:35129518 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000005252
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 Ito M, Okino N, Tani M. New insight into the structure, reaction mechanism, and biological functions of neutral ceramidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1841(5):682-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.09.008., Epub 2013 Sep 21. PMID:24064302 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.09.008
|




