We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Transketolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
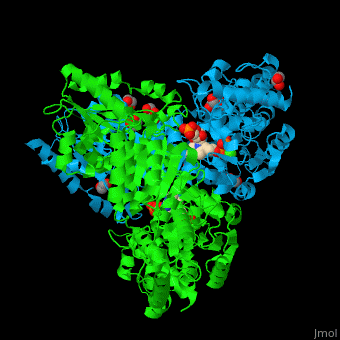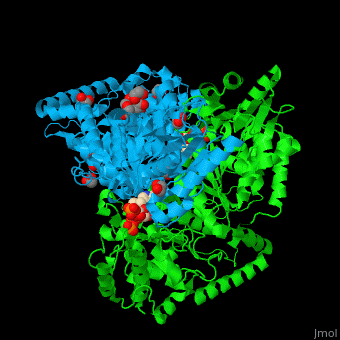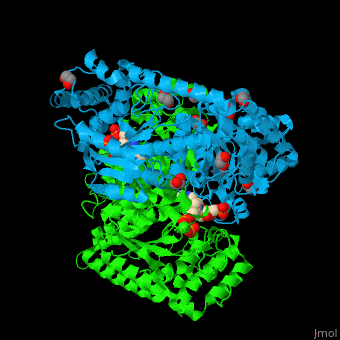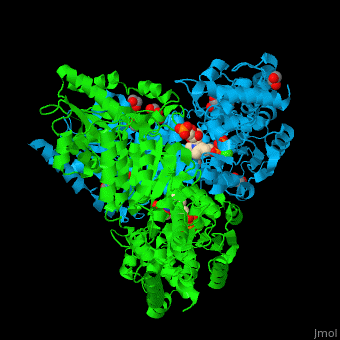
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='E. coli transketolase 1 dimer complex with xylulose-5-phosphate-thiamine diphosphate adduct, ethylene glycol and Ca+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[2r8o]]).' scene='46/466534/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='E. coli transketolase 1 dimer complex with xylulose-5-phosphate-thiamine diphosphate adduct, ethylene glycol and Ca+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[2r8o]]).' scene='46/466534/Cv/1'> | ||
| + | _TOC_ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Transketolase''' (TKT) catalyzes two opposite reactions. The synthesis of sedoheptulose-7-P in the pentose phosphate pathway using thiamine diphosphate (TPP) as co-factor; and the conversion of sedoheptulose-7-P and glyceraldehyde-3-P to aldose and ketose in the Calvin cycle<ref>PMID:8369276</ref>. '''Split-gene TKT''' is found in the hyperthermophilic bacterium ''Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans'' and is reconstituted from 2 separate polypeptide chains<ref>PMID:33193259</ref>. | '''Transketolase''' (TKT) catalyzes two opposite reactions. The synthesis of sedoheptulose-7-P in the pentose phosphate pathway using thiamine diphosphate (TPP) as co-factor; and the conversion of sedoheptulose-7-P and glyceraldehyde-3-P to aldose and ketose in the Calvin cycle<ref>PMID:8369276</ref>. '''Split-gene TKT''' is found in the hyperthermophilic bacterium ''Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans'' and is reconstituted from 2 separate polypeptide chains<ref>PMID:33193259</ref>. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
The <scene name='46/466534/Cv/7'>active site of TKT contains a ligand-cofactor adduct</scene>.<ref>PMID:17914867</ref> Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='46/466534/Cv/8'>Ca coordination site</scene>. | The <scene name='46/466534/Cv/7'>active site of TKT contains a ligand-cofactor adduct</scene>.<ref>PMID:17914867</ref> Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='46/466534/Cv/8'>Ca coordination site</scene>. | ||
| + | [[Transketolase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 16 May 2022
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of transketolase
Updated on 16-May-2022
References
- ↑ Verschueren KH, Kingma J, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Janssen DB, Dijkstra BW. Crystallographic and fluorescence studies of the interaction of haloalkane dehalogenase with halide ions. Studies with halide compounds reveal a halide binding site in the active site. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):9031-7. PMID:8369276
- ↑ James P, Isupov MN, De Rose SA, Sayer C, Cole IS, Littlechild JA. A 'Split-Gene' Transketolase From the Hyper-Thermophilic Bacterium Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans: Structure and Biochemical Characterization. Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 30;11:592353. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.592353., eCollection 2020. PMID:33193259 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.592353
- ↑ Asztalos P, Parthier C, Golbik R, Kleinschmidt M, Hubner G, Weiss MS, Friedemann R, Wille G, Tittmann K. Strain and near attack conformers in enzymic thiamin catalysis: X-ray crystallographic snapshots of bacterial transketolase in covalent complex with donor ketoses xylulose 5-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate, and in noncovalent complex with acceptor aldose ribose 5-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 30;46(43):12037-52. Epub 2007 Oct 3. PMID:17914867 doi:10.1021/bi700844m