This is a default text for your page Max Hideki Oliveira Homma/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) is an enzyme responsible for converting deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) from ribonucleotides (NTPs), as a show in figure 1. It catalyzes this chemical reaction by removing the 2'-hydroxyl group of ribose ring of ribonucleotides. Therefore, this enzyme is also known as ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase (rNDP). In this way, this enzyme promotes the synthesis of precursors for regeneration and construction of DNA.
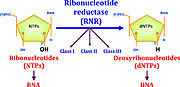
Figure 1: RNRs catalyze the conversion of diphosphated ribonucleotides to their corresponding diphosphate deoxyribonucleotides (Torrents, 2014)
Because of its essential function for the structure of DNA, knowing that all cellular organisms have DNA as a hereditary structure, it is likely that RNR is present in all growing cells of all living beings. In addition, it is also speculated that the RNR played a key role in the transition from the "RNA world" to the "DNA world". In this question, RNR are subdivided into three classes, and the third class can function without oxygen and uses simple structures, thus, it is believed that this class is the oldest.
Classification and distribuition
RNRs can be classified into three distinct classes according to the method of generating thiyl ions triggered by the presence of a particular cofactor. RNRs I are characterized by having a complex quaternary structure and dependence on dioxygen to assemble the cysteine oxidant. RNRs I are present in viruses and in all domains of life and can be subdivided into RNR Ia, Ib, Ic, Id and Ie. RNRs Ia are the best characterized and will receive greater focus on this page. These enzymes present the diiron-tyrosyl radical and are composed of two types of subunits called R1 (or alpha) and R2 (or beta). The biggest difference between the Ia RNRs and the other class I RNRs is in the substitution of diiron-tyrosyl for other cofactors. For example, in RNR Ib, the two ferric ions are replaced by manganese. The cofactors present in the different class I RNRs are shown in the figure.
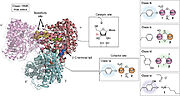
Figure 2: Class I RNRs differ mainly due to the presence of distinct cofactors in the R2 subunit (Ruskoki and Boal, 2021)
Although less studied, there are also class II and III RNRs, which are found only in microorganisms. Class II RNR has adenosylcobalamin, a vitamin B12 derivative, as a cofactor. Class III RNRs, on the other hand, use a [4Fe-4S]-activase to generate a stable glycyl radical capable of leading to the generation of the oxidant Cys at the active site of the RNR. The presence of RNRs of classes II and III is usually related to a better adaptation in environments with low oxygen availability, and RNRs III usually have their activity inhibited by oxygen. Complex eukaryotes, as they generally encode only RNR Ia, have low occupancy in hypoxic environments. Although they share an almost universal ribonucleotide reduction mechanism, the three classes of RNRs have low primary sequence similarity to each other, which may suggest independent emergence.
Several microorganisms are able to encode RNRs of different classes. In the case of Escherichia coli, RNR Ia is preferentially expressed in the growth phase under aerobic conditions, while RNR III is mainly expressed under anaerobic conditions. Furthermore, in environments with low iron availability or when there is biofilm formation, E. coli tends to preferentially express RNR Ib.
Geral structure of RNR Ia
Among the types of RNR, Ia is the best characterized, grouped among the class I RNRs, enzymes Oxygen dependent and found in all eukaryotic organisms and in some prokaryotes and viruses.
The RNR class Ia is a structure that has the diiron-tyrosyl radical and is composed of two subunits, R1 (or alpha) and R2 (or beta). The large R1 structure, also known as alpha2-homodimer, encoded by the NrdA genes, contains the active site for nucleotide binding and reduction and two allosteric sites, involved in the allosteric regulation of substrate specificity and general enzyme activity.
The small R2 structure, also known as beta2-homodimer, encoded by the Nrdb genes, contains a binding site for two iron ions in each polypeptide chain, where the interaction with the metallic cofactor occurs. Metal ion transitions are necessary cofactors to reduce nucleotides, as they generate an oxidant to an active cysteine site (Cys), producing a thiyl radical that is necessary for the initiation of catalysis in all RNRs.
R1 subunit and active site
In Ia RNRs the catalytic site is located in the . This subunit is composed of two identical polypeptide chains, thus forming a homodimer. The secondary structure of each of the that form the R1 subunit is composed of beta sheets and, mainly, alpha helices. Close to the active site an alpha/beta barrel is formed, which is highly conserved among RNR classes. In addition to the active site, two important allosteric sites are also located in the R1 subunit: the specificity site (S site) and the activity site (A site).
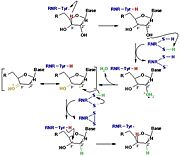
Figure 3: The reduction of ribonucleotides catalyzed by the RNR involves the participation of cysteines present in the active site
The catalysis mechanism performed at the RNR active site is represented in the figure 3 and depends of .Initially, the hydrogen bonded to the 3' carbon of the ribose ribonucleotide is transferred to the thiyl radical of Cys439. As a result, the 2'OH radical becomes more accessible for acid hydrolysis and its protonation is catalyzed by Cys225 and Glu441, resulting in the exit of a molecule from the substrate. After that, a proton is transferred from Cys462 to Cys225 which then transfers a hydrogen to the 2' carbon. Then, the transfer of a hydrogen to the 2' carbon of the substrate occurs concomitantly with the formation of a between the Cys225 and Cys462 of the RNR. Finally, till radical regeneration occurs with the transfer of a hydrogen from Cys439 to the 3' carbon of the substrate, leading to the release of a deoxyribonucleotide. At the end of the catalysis, the disulfide bridge between Cys225 and Cys462 must still be reduced. The electron used in this reduction comes from a redox chain whose initial donor is NADPH. Numerous components participate in this redox chain, including Cys 754 and Cys759 from R1 itself. The reduction of the disulfide bridge between Cys225 and Cys462 would be very difficult to occur if there was a radical very close to the disulfide bridge, since the tendency would be for this radical to be reduced instead of the disulfide bridge. This is a likely explanation for the existence of a second subunit in the RNR, as the R2 subunit harbors a tyrosyl radical that is difficult to reduce.
R2 subunit and cofactor
In Ia RNRs, the cofactor binding site is located on the R2 subunit, also known as β. The R2 subunit may be associated with the R1 protein in dimeric or oligomeric forms, and there may be one or more R2 subunits in the same enzyme. The , similarly to the R1 subunit, is formed by two polypeptide chains, with each formed by beta structures and, mainly, alpha helices.
It contains the essential metal cofactor binding site for the initiation of nucleotide reduction, the ionic transition that occurs with the metallofactor at the R2 subunit site promotes the formation of the radical that will later be transferred through long-range radical transfer to the alpha subunit, where it will generate the thiol radical at the active site of the enzyme, where the two cysteine loops reduce NTP.
The R2 protein has a binding site for two Iron atoms on each of its two identical protomers and a nearby potential tyrosyl radical site (Y122 in E.coli). The general structure of the protein is mainly α-helix and each of the di-iron centers are coordinated by aspartate (D84), two histidines (H118 and H241) and three glutamate residues (E115, E204 and E238) that are brought together within a bundle of four helices. This structure is conserved in all subclasses of RNR I, with very few exceptions.
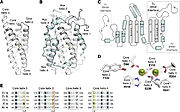
Figue 4: The diiron cofactor present in the R2 subunit of RNR Ia is located in a core formed by four alpha helices
All R2 subunits belong to the ferritin structural superfamily, with a core composed of a package of four central helices that connect to assemble the active oxidant. In class Ia, this core unit is symmetrical, with two α-helix pairs arranged in a head-to-tail direction to sink the Metallocofactor, FeIII-O-FeIII in this class, into the β structure and protect it from the solvent. Each of the helices in the pair confer a linker region with the cofactor. In addition to cofactor protection, the helical structure also provides second-sphere side chains that contribute to cofactor assembly and reactivity.
Regulation
The regulation of RNRs is very refined and occurs at several levels. In microorganisms, a transcription factor, called NrdR, was identified, which is capable of binding to NrdR-box, a consensus sequence present in the promoters of nrd genes, which encode RNRs. The NrdR is composed of two domains, the Zn-finger, which binds to DNA, and the ATP-cone, which has ATP and/or dATP binding sites. Although its regulatory mechanism has not been fully elucidated, it is proposed (figure 5) that the binding of dATP to the ATP-cone causes NrdR to dimerize and interact more with the NrdR-boxes sequences, leading to reduced transcription of nrd genes.
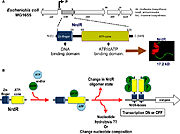
Figure 5: proposed model of how NrdR modulates the expression of nrd genes in bacteria (Torrents, 2014)
The activity of the already translated RNR is also finely regulated. Although RNRs are capable of reducing the 4 ribonucleotides, the binding of dATP (or ATP), dGTP, dCTP and dUTP to the S site of the R1 subunit changes which ribonucleotide will be preferentially reduced by the enzyme. For example, in Ia RNRs, the binding of dATP or ATP to the S site causes the enzyme to reduce CDP and UDP while inhibiting the reduction of ADP (figure 6).
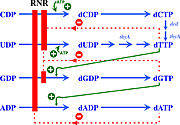
Figure 6: Modulation of RNR Ia activity by binding deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates to the S site (Torrents, 2014).
In addition to the S site, the A site is also capable of regulating RNR Ia activity. In this sense, ATP binding to this site will stimulate the general activity of the enzyme. On the other hand, the binding of of the R1 subunit inhibits the activity of RNR Ia by altering its oligomerization state, forming a composed of 2 R1 subunits and two R2 subunits. However, because dATP binds with a much higher affinity to the S site than to the A site, its inhibitory effect is only significant when this molecule is in high concentrations.
Due to the cellular importance of RNRs and the possibility of regulating their activity, inhibitors of these enzymes have been used for therapeutic purposes. Inhibition of Ia RNRs seems to be a particularly interesting strategy in the fight against cancer, as it leads to the interruption of cell proliferation. An alternative R2 subunit, called p53R2, was also identified in mammalian cells, which is associated with the DNA repair system and is often not functioning correctly in cancer cells.
Inhibitors of Ia RNRs can be divided into three main groups. The first group consists of inhibitors that bind to the R1 subunit, either at the active site or at allosteric sites. The second group comprises inhibitors that act on the R2 subunit, usually being iron-chelating or radical-scavenging compounds. Finally, the third group is composed of inhibitors that form hairpins with the mRNA transcribed from the nrd genes, preventing their translation. In addition to these three groups, there are also inhibitors that prevent the union between the R1 and R2 subunits.






