Introduction
is a large transmembrane protein of approximately 230kDa encoded by the dysferlin gene (DYSF omim) highly expressed in striated skeletal and cardiac muscle, but can be found in kidney, placenta, lung and brain tissues (3). Dysferlin is a protein that belongs to the same family of genes as Caenorhabditis elegans ferlin, also known as ferlin-like proteins, therefore the name it was given, and can also be known as ferlin 1-like 1 (Fer1L1). It is common to this family the presence of type II transmembrane domains, where the most part of the protein faces de cytoplasm (3). This protein is critical for repair of muscle membranes after damage and its mutation lead to a progressive muscle dystrophy, since in its absence the membrane tear is not adequately repaired leading to myofiber necrosis and gradual and progressive loss of muscle tissue (1;5). The protein rapidly responds to injury with a calcium (Ca2+) influx mechanism which aids the repair. Dysferlin-deficient muscle fibers demonstrate a primary defect in Ca2+-dependent vesicle-mediated membrane repair (5).
Structure and Function
Structure
has seven tandem C2 domains (, B, D, E and G), three Fer domains (FerA, FerB and FerI) which are short conserved regions found only in the ferlin protein family and are not yet shown to be folded domains (2), two and a C-terminal transmembrane domain with a helix embedded in a patching vesicle.
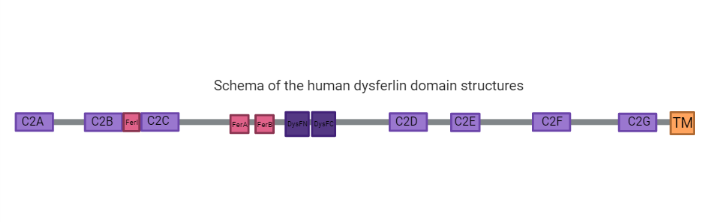
DysF Domain
One Dysf domain is inserted into the other Dysf domain forming an inner Dysf domain (not represented in the image below) and a two part outer Dysf domain (N-terminal DysFN and C-terminal DysFC), and it is woth mentioning that the Dysf domain is held together by arginine/ aromatic sidechain stacking. The crystal structure of the human dysferlin inner DysF domain with a resolution of 1.9 Ångstroms by X-Ray diffraction (2).
C2 Domains
C2 domains are independently membrane-binding modules of about 130 residues found in a large and diverse set of eukaryotic proteins that share a common overall fold: a single compact greek-key motif organized as an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sandwich consisting of a pair of four-stranded β-sheets (6, 7).
Function
Many dysferlinopathy causing mutations fall in the DysF domains (2). It's important to notice that dysferlin function is linked with calcium-activated membrane repair caused by fusing aggregated intracellular vesicles with the sarcolemma at the site of injury(2).
It has been shown that dysferlin deficiency delays myoblast (undifferentiated mononuclear muscle cells) fusion/maturation in vitro, suggesting that dysferlin may also participate in muscle differentiation and regeneration process (3).
C2 Domains function
C2 domains are calcium sensitive phospholipid binding domains with an approximate length of 130 amino acids (5), while the function of the Dysf domain remains unclear (1;2). The presence of the C2 domains is common to ferlin-like proteins, in which only the C2A domain binds strongly to lipids in a calcium dependent way. The other domains have weaker bonds or are calcium independent. Also, C2A, E and F domains have shown a relevant function in the protein activity (5).
Disease
Dysferlinopathies are caused by mutations in dysferlin and most of these mutations are part of aromatic/arginine stacks that hold the Dysf domain in a folded conformation (2). LGMDs (Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies) are a group of muscular dystrophies characterized by predominant weakness and wasting of muscles of the pelvic and shoulder girdle (4). LGMD2B (Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B) is a predominantly proximal muscular dystrophy with an onset in the late teens, in which are identified mutations in the N terminus of Dysf gene that results in dysferlin-reactive amyloid fibrils in the muscle fibers, as a result of a destabilization of the protein (3).
As for Miyoshi Myopathy (MM), it is a predominantly distal muscular dystrophy with early involvement of the posterior compartments of the lower limb and the disease onset is generally in the late teens with an initial involvement of the muscles of the distal lower limbs. Thus, in both diseases, muscles of the limb and girdle are primarily affected, the symptoms usually appear in the late teens, the diseases progress slowly and high levels of creatine kinase, a skeletal-muscle-specific enzyme, are detected in the serum of the patients (4). It is suggested that both diseases could be a result of the same mutations in the Dysf gene, and the phenotypic differences would be accounted for by modifier genes or other factors that could vary its expression (3). With the association of both dystrophies and dysferlin, and its known function of maintaining the integrity of the cells, it is suggested that it also plays an important role in facilitating the repair of cell membranes in skeletal tissues (5).
It is also associated with dysferlin mutations the DMAT (distal myopathy with anterior tibial onset).
Gene Function and Molecular Genetics
Analyzing human fetal tissue, it was concluded that dysferlin is expressed in the earliest stages of development, in the embryonic ages of 5 to 6 weeks, which is the time where the limbs start its differentiation, which agrees with the limb dystrophies associated with the Dysf genes mutations. Also, the analysis of the amino acids sequences of the protein showed its relation with Caveolin-3, a skeletal muscle protein associated with forming caveolae. Dysferlin was associated with 7 sites of caveolin-3 binding motifs, which suggests its function with signaling caveolae functioning (3).
Wild Type dysferlin is degraded by ubiquitin/proteasome endoplasmic reticulum degradation systems.
Both MM and LGMD2B were mapped to the same chromosomal region and it suggests that the dystrophies are given by allelic disorders, as affected people with both diseases seem to have the same haplotype, suggesting that phenotypic differences are given by differential expression driven by modifying factors.

