User:Isabela de Aquino Zogbi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
====C2 Domains==== | ====C2 Domains==== | ||
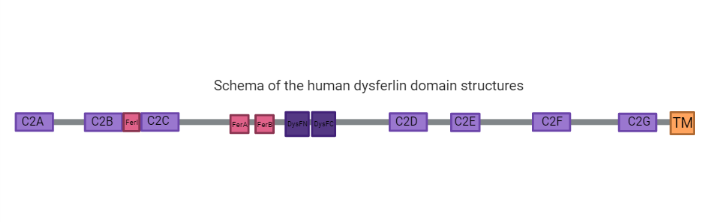
| - | C2 domains are independently membrane-binding modules of about 130 residues found in a large and diverse set of eukaryotic proteins that share a common overall fold: a single compact greek-key motif organized as an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sandwich consisting of a pair of four-stranded β-sheets <ref name="ref6"> Lek, A., Evesson, F.J., Sutton, R.B., North, K.N. and Cooper, S.T. Ferlins: Regulators of Vesicle Fusion for Auditory Neurotransmission, Receptor Trafficking and Membrane Repair. Traffic, 13: 185-194 (2012) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01267.x </ref> <ref> Corbalan-Garcia, S., Gómez-Fernández, J. C. Signaling through C2 domains: More than one lipid target. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, Volume 1838, Issue 6, Pages 1536-1547, ISSN 0005-2736 (2014) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005273614000108?via%3Dihub </ref>. For example, its seen in the structure the <scene name='91/915204/4ihbc2a/1'>C2A</scene> resolved to 2.04 Å by X-Ray diffraction the pair of four-stranded <scene name='91/915204/ | + | C2 domains are independently membrane-binding modules of about 130 residues found in a large and diverse set of eukaryotic proteins that share a common overall fold: a single compact greek-key motif organized as an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sandwich consisting of a pair of four-stranded β-sheets <ref name="ref6"> Lek, A., Evesson, F.J., Sutton, R.B., North, K.N. and Cooper, S.T. Ferlins: Regulators of Vesicle Fusion for Auditory Neurotransmission, Receptor Trafficking and Membrane Repair. Traffic, 13: 185-194 (2012) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01267.x </ref> <ref> Corbalan-Garcia, S., Gómez-Fernández, J. C. Signaling through C2 domains: More than one lipid target. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, Volume 1838, Issue 6, Pages 1536-1547, ISSN 0005-2736 (2014) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005273614000108?via%3Dihub </ref>. For example, its seen in the structure the <scene name='91/915204/4ihbc2a/1'>C2A</scene> resolved to 2.04 Å by X-Ray diffraction the pair of four-stranded <scene name='91/915204/4ihbc2asheet/1'>β-sheets</scene>. |
====Fer Domains==== | ====Fer Domains==== | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 19 June 2022
Dysferlin
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 https://www.omim.org/entry/603009?search=dysferlin&highlight=dysferlin
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 de Morrée A., Hensbergen P.J., van Haagen H. H. H. B. M., Dragan I., Deelder A. M., ’t Hoen P. A. C., et al. Proteomic Analysis of the Dysferlin Protein Complex Unveils Its Importance for Sarcolemmal Maintenance and Integrity. PLoS ONE 5(11): e13854 (2010) https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0013854
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Harsini, F. M., A. Bui, A. A., Rice, A. M., Chebrolu, S., Fuson, K. L., Turtoi, A., Bradberry, M., Chapman, E. R., Sutton, R. B. Structural Basis for the Distinct Membrane Binding Activity of the Homologous C2A Domains of Myoferlin and Dysferlin. Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 431, Issue 11, Pages 2112-2126, ISSN 0022-2836 (2019) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022283619301883
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Sula, A., Cole, A.R., Yeats, C. et al. Crystal structures of the human Dysferlin inner DysF domain. BMC Struct Biol 14, 3 (2014) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/1472-6807-14-3
- ↑ Ono, H., Suzuki, N., Kanno, S., Kawahara, G., Izumi, R., Takahashi, T., Kitajima, Y., Osana, S., Nakamura, N., Akiyama, T., Ikeda, K., Shijo, T., Mitsuzawa, S., Nagatomi, R., Araki, N., Yasui, A., Warita, H., Hayashi, Y. K., Miyake, K., Aoki, M. AMPK Complex Activation Promotes Sarcolemmal Repair in Dysferlinopathy. Molecular Therapy, Volume 28, Issue 4, Pages 1133-1153, ISSN 1525-0016,(2020) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1525001620300927
- ↑ Abdullah, N., Padmanarayana, M., Marty, N. J., Johnson, C. P. Quantitation of the Calcium and Membrane Binding Properties of the C2 Domains of Dysferlin Biophysical Journal, Volume 106, Issue 2, Pages 382-389, ISSN 0006-3495,(2014) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006349513057536
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Lek, A., Evesson, F.J., Sutton, R.B., North, K.N. and Cooper, S.T. Ferlins: Regulators of Vesicle Fusion for Auditory Neurotransmission, Receptor Trafficking and Membrane Repair. Traffic, 13: 185-194 (2012) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01267.x
- ↑ Corbalan-Garcia, S., Gómez-Fernández, J. C. Signaling through C2 domains: More than one lipid target. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, Volume 1838, Issue 6, Pages 1536-1547, ISSN 0005-2736 (2014) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005273614000108?via%3Dihub
- ↑ https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/bi400432f
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Bansal, D., Campbell, K. P. Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy. Trends in Cell Biology, Volume 14, Issue 4, Pages 206-213, ISSN 0962-8924 (2004) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0962892404000546
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Han, R., Campbell, K. P .Dysferlin and muscle membrane repair. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, Volume 19, Issue 4, Pages 409-416, ISSN 0955-0674 (2007) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955067407000993