This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Journal:JBIC:16
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
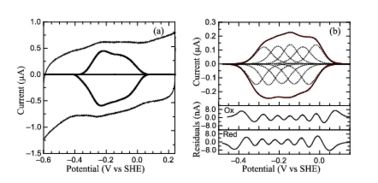
[[Image:figur5.jpg|left|378px|thumb|PFV of ''S. oneidensis'' ccNiR (a) Typical signal on a graphite electrode. (b) Baselinesubtracted non-turnover voltammogram]] | [[Image:figur5.jpg|left|378px|thumb|PFV of ''S. oneidensis'' ccNiR (a) Typical signal on a graphite electrode. (b) Baselinesubtracted non-turnover voltammogram]] | ||
The Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion within <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/14'>conserved site</scene> is coordinated in bidentate fashion by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/15'>Glu205</scene>, and in monodentate fashion by the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/16'>Tyr206 and Lys254</scene> backbone carbonyls, and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/17'>Gln256</scene> side-chain carbonyl. In the ''S. oneidensis'' structure only <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/18'>one water molecule</scene> is assigned to the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion in subunit B. In subunit A the difference electron density that represents this water molecule is very close to the noise level, and it is difficult to identify even one water molecule there. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/14'>carbonyl side chain of Asp242 and the hydroxyl of Tyr235</scene> come near to the open calcium coordination sites, but are not within bonding distance. Instead they interact with the water molecule that is weakly coordinated to the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion. The ccNiR calcium ions appear to play a vital role in organizing the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/13'>active site</scene> (as was mentioned above <font color='magenta'><b>hemes-1</b></font> are the active sites). | The Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion within <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/14'>conserved site</scene> is coordinated in bidentate fashion by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/15'>Glu205</scene>, and in monodentate fashion by the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/16'>Tyr206 and Lys254</scene> backbone carbonyls, and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/17'>Gln256</scene> side-chain carbonyl. In the ''S. oneidensis'' structure only <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/18'>one water molecule</scene> is assigned to the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion in subunit B. In subunit A the difference electron density that represents this water molecule is very close to the noise level, and it is difficult to identify even one water molecule there. The <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/14'>carbonyl side chain of Asp242 and the hydroxyl of Tyr235</scene> come near to the open calcium coordination sites, but are not within bonding distance. Instead they interact with the water molecule that is weakly coordinated to the Ca<sup>2+</sup> ion. The ccNiR calcium ions appear to play a vital role in organizing the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:16/Cv/13'>active site</scene> (as was mentioned above <font color='magenta'><b>hemes-1</b></font> are the active sites). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''PDB reference:''' Laue structure of ''Shewanella oneidensis'' cytochrome-c Nitrite Reductase, [[3ubr]]. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
__NOEDITSECTION__ | __NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Youngblut M, Judd ET, Srajer V, Sayyed B, Goelzer T, Elliott SJ, Schmidt M, Pacheco AA. Laue crystal structure of Shewanella oneidensis cytochrome c nitrite reductase from a high-yield expression system. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Mar 2. PMID:22382353 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0885-0
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.