DNA Topoisomerases (TOP) are enzymes capable of solving topological problems in DNA molecules during replication, transcription, recombination and chromatin remodeling by introducing temporary breaks in the DNA. Besides that, these enzymes can modulate the level of DNA supercoiling to facilitate protein interaction with the molecule and to prevent supercoiling relationed stress [1] . There are several types of topoisomerases that are different in structure and function, but basically, the topos are divided based on whether they catalyze single- (type I) or double-stranded (type II) DNA breaks [1].
Within type two topoisomerases there are two classes: A and B. Class B is found only in archaea and type A is present in eukarya and bacteria. Humans have two types of 2A topoisomerases: isoforms alpha and beta. Topoisomerase 2 alpha has a larger role in chromosome segregation and DNA replication and tends to be expressed in more proliferating tissues, which makes topoisomerase 2 alpha a cancer cell marker and the target of anti-cancer drugs. TOP2A is responsible for the selective cleaving, rearranging and religation of DNA strands, which helps untangle the chromosome, thereby changing the state of DNA in the cell [1].
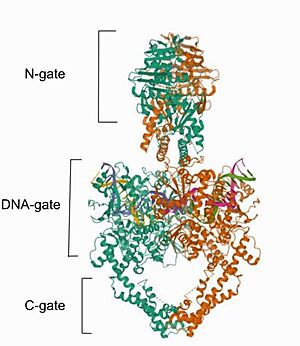
Mammalian DNA topoisomerase IIα (human) (IIA) is a homodimeric protein, in which each subunit structure can be broken down into three major components that are connected by hinged like regions: the N gate, the DNA gate and the C gate [2].
Function
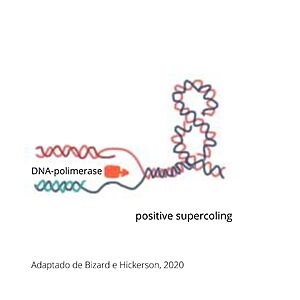
Supercoiling DNA formation
During replication, transcription and cell division, DNA passes for various states of coiling, so sometimes DNA can become too coiled, which, without alleviation, can cause DNA brakes or arrest of the replication, cell division or transcription. To prevent breakages from happening, TOP2a cuts both strands of the DNA duplex, passes another DNA duplex through the cleaved one and relegate the cut duplex to release tension. This is a risky task, once not completed properly, it damages the state of the chromatin and can result in cell death
[3] [4].
In addition to the better-known function of undoing super-coilings in DNA, TOP2a was shown to be important for chromosomal condensation and maintenance of chromosomal structure, since chromatic compaction appears to arise, in part, due to the interaction between TOP2a and complexes of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC complexes).TOP2a is also involved in chromosome segregation during anaphase and in chromatid resolution at ribosomal DNA (rDNA) [3] [5].
Structure
Cryo-EM reconstructions of the TOP2α nucleoprotein complex showed that Mammalian is a homodimeric protein, in whitch each subunit structure can be broken down into three major components that are connected by hinged like regions: the N gate, that contains the ATPase domain, the DNA gate and the C gate
[6]. Biochemical and structural studies have shown that the ATPase domain or N-gate, and the DNA binding/cleavage domain forming the DNA- and C-gates, are allosterically connected, a key feature of its activity
[6]. Furthermore, the literature contains various descriptions of the structures of the N-gate and DNA-gate, but the C-gate is less explored.
The protein DNA Topoisomerase IIα (human) has two one represented in and one in , both bounded to .
The of this protein has and . is what a monomer secondary structure looks like. In other representation, the can be seen in red and dark blue respectively.
The N gate
The N-gate contains an ATPase domain, which was resolved to 1.86 Å by diffraction data of crystals, acquired using synchrotron radiation. The ATPase domain structure contains one dimer per asymmetric unit [7]. The polypeptide chain folds into two discrete structural modules, with the N-terminal module bearing a similarity with the GHKL superfamily, consisting of an eight-stranded, mixed-sheet backed by four -helices. The C-terminal module structure consists of a four-stranded, mixed -sheet with one -helix on one face and two on the other, and has the role of communicating conformational information between the ATPase domain and the DNA gate. The primary dimerization interface involves the nucleotide-binding modules of the two monomers, with two short helices from the N-terminal of the two monomers interacting exclusively with the nucleotide-binding module of the C2 symmetry-related monomer. Furthermore, in each one of the monomers, residues of the nucleotide-binding module form one nucleotide-binding pocket. Loading of ATP onto the ATPase domain triggers dimerization and temporal capture of the DNA strands and that dimerization of the ATPase domain is nucleotide-dependent. Interestingly, the cavity in the domain is not big enough to hold the DNA segment, requesting an extension, but the study indicated that expansion is likely to occur by rigid-body displacement of the transducer module. This movement it is known to cause a retraction of the Lys-378 -amino group from the -phosphat, which is essential for ATPase activity. [8]
The DNA gate
Within the DNA gate there are three important domains: the topoisomerase primases (toprim domain), the winged helix domain (WHD domain or 5Y-CAP)) and the tower domain.
The TOPRIM domain
The TOPRIM domain contains a DxD motif, where metal ion binding occurs due to two aspartates at positions 541 and 543, which coordinates a single magnesium 2 plus ion quelation,and a glutamate residue, that donates a proton to the sugar hydroxyl of the DNA during cleavage and abstracting the proton from the 3ʹ-OH during re-ligation. The TOPRIM domain also contributes to DNA binding, due to conserved residues, namely the EGDS and PLRGK motifs, which interact with the G-segment. Furthermore, the TOPRIM employs a distinct insertion, called insertion 2, composed of a short helix followed by a long loop, known for accommodation of DNA [9].
THE Winged Helix domain
The WHD contains a helix-turn-helix fold, common in DNA-binding proteins, that have catalytic tyrosine residues in the C-terminal helix (also termed the ‘recognition helix’), responsible for forming a reversible covalent bond with the 5ʹ-scissile DNA phosphate. Besides that, The WHD also holds an isoleucine, which intercalates into the G-segment (the first segment of DNA duplex that enter the enzyme) producing a ∼150° bend, promoting DNA cleavage. The cleaving of the DNA backbone occurs in a bipartite active site formed by the TOPRIM DxD motif and the active site tyrosine of the WHD, which physically associate in different orientations during the enzyme's cycle of action [9].
The tower domain
The tower domain (TD) is also involved with DNA binding. G-segment binds with a beta-sheet region, while another region composed by a + b sheets mediates domain-domain interactions [9] .The TD DNA-binding surface juxtaposes with the DNA-intercalating wing-2 motif of WHD, extending the DNA-binding surface of the WHD and anchoring the outer end of the bent G-segment DNA. Interestingly, the structural conservation observed for the fixed packing between the tower domain and WHD suggests their assembly as an integral unit for the production and stabilization of DNA-bending [9] .
Operation
Type II topoisomerases operation involves a complex mechanism of controlled association and dissociation of subunit dimerization elements. Top2A starts out with its N gates dissociated allowing it to bind a DNA duplex passing it through the N gate and binding at the DNA gate (G-segment). Binding at the DNA gate causes a significant one ~150 degree bend, promoted by an isoleucine present in the WHD domain. The N gate contains an ATPase region and ATP binding here triggers the binding of a second DNA duplex at the N gate (T-segment).
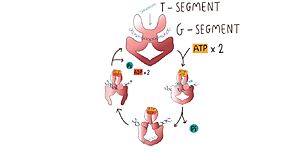
Image adapted from Chang, C.-C., Wang, Y.-R., Chen, S.-F., Wu, C.-C., & Chan, N.-L. (2013). New insights into DNA-binding by type IIA topoisomerases.
Binding of ATP also causes the previously separated N gates to dimerize and close locking in the T-segment. Closing the N gates emulates conformation change that promote the cleavage of the G segment, which is catalyzed by a pair of symmetrically-related tyrosines 9,10, in conjunction with a Mg2+ ion-binding in the TOPRIM fold. Besides that, the 150 degree bend on the duplex puts bonds under significant stress, facilitating the cleavage. Once the G segment has been cleaved, it remains bound at the DNA gate, but the DNA gate opens to allow the T segment to exit through the open C gate. Than, the DNA gate closes again to religate the G segment before releasing it. Strand passage and gate openings are coordinated by defined ATPase domains12–14 which use ATP binding and hydrolysis to promote conformation changes.
In more simple terms, in the type IIA reaction cycle, one double-stranded DNA is bound and cleaved by the enzyme, while a second duplex is transported through the break [3].
Relevance
As mentioned before, TOP2 mechanism of DNA cleavage is not simple, and errors can result in cell death. This aspect of TOP2 has been explored by anticancer studies, which showed that TOP2 inhibitors increase the steady-state level of cleavage complexes, promoting the formation of cytotoxic DNA lesions in cancer cells [10]. TOP2-targeting agents are divided into two categories: "Topo poisons" and "Topo inhibitors", based on their mechanisms of action. TOP2 poisons do not prevent TOP2-DNA interaction, but convert the essential enzyme into a highly cytotoxic DNA-damaging agent, due to a stabilized linked DNA strand-passing intermediate, allowing the generation of double strand breaks, but not religation of the strands. "TOP2 inhibitors" interrupt the binding of TOP2 and DNA by binding enzymes to inhibit TOP2 catalytic activity but do not generate increases in the levels of TOP2 covalent complexes [11].
It has been shown that TOP2α is a better target than TOP2β, once targeting the last one was responsible for the development of secondary malignancy. Besides, TOP2α is found more in rapidly growing cancer cells, once its essential for cell growth. So, in conclusion, specific inhibition of TOP2α resulted in significant antitumor action, suggesting that TOP2α-targeted therapy is a valuable approach for cancer chemotherapy and shows the importance of studying the enzyme itself [11].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 McKie SJ, Neuman KC, Maxwell A. DNA topoisomerases: Advances in understanding of cellular roles and multi-protein complexes via structure-function analysis. Bioessays. 2021 Apr;43(4):e2000286. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000286. Epub 2021 Jan, 22. PMID:33480441 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.202000286
- ↑ Alonso-Sarduy L, Roduit C, Dietler G, Kasas S. Human topoisomerase II-DNA interaction study by using atomic force microscopy. FEBS Lett. 2011 Oct 3;585(19):3139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.08.051. Epub, 2011 Sep 6. PMID:21907712 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.08.051
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Wendorff TJ, Schmidt BH, Heslop P, Austin CA, Berger JM. The Structure of DNA-Bound Human Topoisomerase II Alpha: Conformational Mechanisms for Coordinating Inter-Subunit Interactions with DNA Cleavage. J Mol Biol. 2012 Dec 7;424(3-4):109-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.014. Epub 2012, Jul 25. PMID:22841979 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.014
- ↑ Champoux JJ. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:369-413. PMID:11395412 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.369
- ↑ Nielsen CF, Zhang T, Barisic M, Kalitsis P, Hudson DF. Topoisomerase IIalpha is essential for maintenance of mitotic chromosome structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 2;117(22):12131-12142. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.2001760117. Epub 2020 May 15. PMID:32414923 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2001760117
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Vanden Broeck A, Lotz C, Drillien R, Haas L, Bedez C, Lamour V. Structural basis for allosteric regulation of Human Topoisomerase IIalpha. Nat Commun. 2021 May 20;12(1):2962. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23136-6. PMID:34016969 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23136-6
- ↑ Wei H, Ruthenburg AJ, Bechis SK, Verdine GL. Nucleotide-dependent domain movement in the ATPase domain of a human type IIA DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 4;280(44):37041-7. Epub 2005 Aug 12. PMID:16100112 doi:10.1074/jbc.M506520200
- ↑ Schmidt BH, Osheroff N, Berger JM. Structure of a topoisomerase II-DNA-nucleotide complex reveals a new control mechanism for ATPase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Nov;19(11):1147-54. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2388. Epub 2012, Sep 30. PMID:23022727 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2388
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Chang CC, Wang YR, Chen SF, Wu CC, Chan NL. New insights into DNA-binding by type IIA topoisomerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Feb;23(1):125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.11.011., Epub 2012 Dec 21. PMID:23265999 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2012.11.011
- ↑ Wu CC, Li YC, Wang YR, Li TK, Chan NL. On the structural basis and design guidelines for type II topoisomerase-targeting anticancer drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep 14. PMID:24038465 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt828
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Chen W, Qiu J, Shen YM. Topoisomerase IIalpha, rather than IIbeta, is a promising target in development of anti-cancer drugs. Drug Discov Ther. 2012 Oct;6(5):230-7. PMID:23229142