User:Arthur Migliatti/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
</ref>. As it is shown in this <scene name='91/911850/Conservation/1'>image</scene>, both Cys32 and Cys 35 were highly conserved during evolution(<font color='mediumvioletred'><b>dark pink</b></font> = highly conserved, <span style="color:white;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">white</span> = average, <font color='deepskyblue'><b>blue</b></font> = variable). One of the most important proteins that Trx reduces is '''[[Peroxiredoxin]]'''(Prx), which catalyses the reduction of Hidrogen Peroxide(H2O2) to water. Since high concentrations of H2O2 produces other potent oxidizing molecules, such as hydroxyl radical, Prx's action, and so Trx's also, are fundamental for the cell to have a redox homeostasis and to have low amount of damage. | </ref>. As it is shown in this <scene name='91/911850/Conservation/1'>image</scene>, both Cys32 and Cys 35 were highly conserved during evolution(<font color='mediumvioletred'><b>dark pink</b></font> = highly conserved, <span style="color:white;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">white</span> = average, <font color='deepskyblue'><b>blue</b></font> = variable). One of the most important proteins that Trx reduces is '''[[Peroxiredoxin]]'''(Prx), which catalyses the reduction of Hidrogen Peroxide(H2O2) to water. Since high concentrations of H2O2 produces other potent oxidizing molecules, such as hydroxyl radical, Prx's action, and so Trx's also, are fundamental for the cell to have a redox homeostasis and to have low amount of damage. | ||
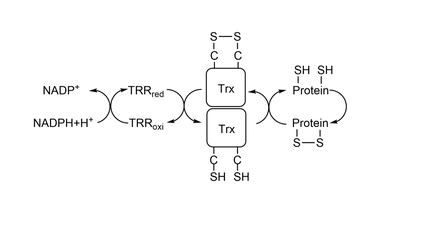
| - | [[Image:ThioredoxinSystem.png| | + | [[Image:ThioredoxinSystem.png|thumb|center|540x240px|Thioredoxin System.]] |
To reduce other proteins, first happens an attack from Cys32, creating an intermolecular dissulfide bond, represented <scene name='91/911850/C32_s-s_c206/1'>here</scene> between residue Cys32 from Trx1 and residue Cys206 from '''[[MsrA]]'''.After it, residue Cys35 attacks Cys32, creating a <scene name='91/911850/Trx_cys_-_oxidized_-_diss_bond/4'>dissulfide bond</scene> between the two cysteines in Trx1's catalytic site. To study the mechanism of reduction by Trx1 it is commom to use a wild-type Trx1 Cys35Ser. Since there is no other Cys to make a dissulfide bond with Cys32, Trx1 is mainteined bonded to the other protein being studied by a intermolecular dissulfide bond. | To reduce other proteins, first happens an attack from Cys32, creating an intermolecular dissulfide bond, represented <scene name='91/911850/C32_s-s_c206/1'>here</scene> between residue Cys32 from Trx1 and residue Cys206 from '''[[MsrA]]'''.After it, residue Cys35 attacks Cys32, creating a <scene name='91/911850/Trx_cys_-_oxidized_-_diss_bond/4'>dissulfide bond</scene> between the two cysteines in Trx1's catalytic site. To study the mechanism of reduction by Trx1 it is commom to use a wild-type Trx1 Cys35Ser. Since there is no other Cys to make a dissulfide bond with Cys32, Trx1 is mainteined bonded to the other protein being studied by a intermolecular dissulfide bond. | ||
Revision as of 18:35, 26 July 2022
Introduction
| |||||||||||