We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
4awl
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
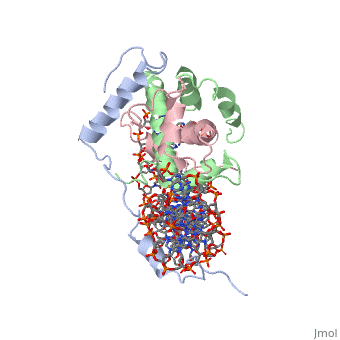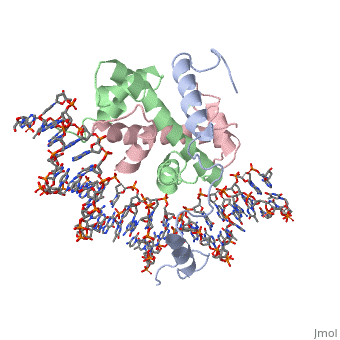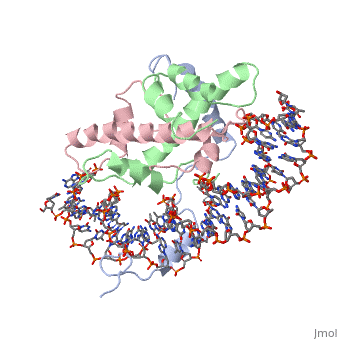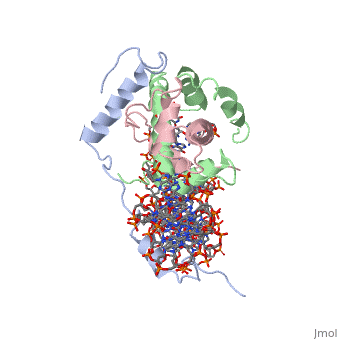
<StructureSection load='4awl' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4awl]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.08Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4awl' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4awl]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.08Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4awl]] is a 5 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4awl]] is a 5 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4AWL OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4AWL FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1n1j|1n1j]]</td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[1n1j|1n1j]]</div></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4awl FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4awl OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4awl PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4awl RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4awl PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4awl ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYA_HUMAN NFYA_HUMAN]] Component of the sequence-specific heterotrimeric transcription factor (NF-Y) which specifically recognizes a 5'-CCAAT-3' box motif found in the promoters of its target genes. NF-Y can function as both an activator and a repressor, depending on its interacting cofactors. NF-YA positively regulates the transcription of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1.<ref>PMID:12741956</ref> [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYC_HUMAN NFYC_HUMAN]] Stimulates the transcription of various genes by recognizing and binding to a CCAAT motif in promoters, for example in type 1 collagen, albumin and beta-actin genes. [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYB_HUMAN NFYB_HUMAN]] Stimulates the transcription of various genes by recognizing and binding to a CCAAT motif in promoters, for example in type 1 collagen, albumin and beta-actin genes. |
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| - | *[[NF-Y Transcription Factor|NF-Y Transcription Factor]] | ||
*[[Nuclear transcription factor Y|Nuclear transcription factor Y]] | *[[Nuclear transcription factor Y|Nuclear transcription factor Y]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 05:48, 25 August 2022
The NF-Y transcription factor is structurally and functionally a sequence specific histone
| |||||||||||
Categories: Human | Large Structures | Bolognesi, M | Donati, G | Forni, C | Fossati, A | Gatta, R | Gnesutta, N | Mantovani, R | Moras, D | Nardini, M | Romier, C | Vonrhein, C | Dna-binding | Nf-y | Transcription-dna complex