Sandbox Reserved 1750
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
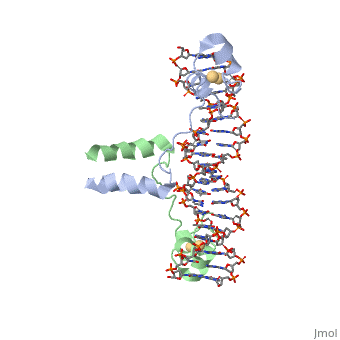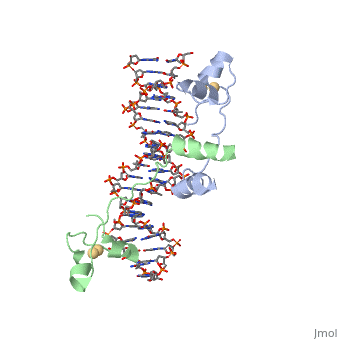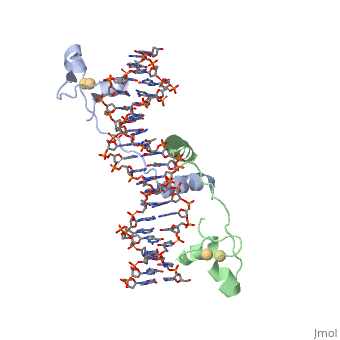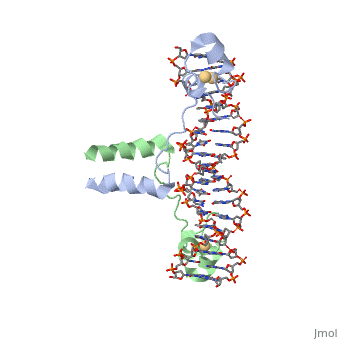
| - | + | Displayed</scene></scene>==DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX== | |
<StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1d66]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.70Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1d66]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.70Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 00:14, 4 October 2022
Displayed</scene></scene>==DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX==
| |||||||||||
STRUCTURE OF Cas9 IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN COMPLEX WITH gRNA
Cas9 Overview
CRISPR is a bacterial immune response to bacteriophages to prevent subsequent infections and is a form of acquired immunity. Within the CRISPR system, Cas9 is a protein responsible for cutting the viral DNA rendering it inert. structure in Staphylococcus aureus (SaCas9) utilizes a single stranded guide RNA (sgRNA) to bind the target DNA that will be cut. The target DNA must also have a PAM sequence to bind to Cas9 to be cut. Cas9 has four main mechanisms that are important for successful cleavage including recognition of the sgRNA-target heteroduplex, recognition of the PAM sequence, recognition of the sgRNA scaffold, and endonuclease activity by HNH and RuvC.