Sandbox reserved 1752
From Proteopedia
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
<Structure load='2IS4' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='2IS4' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
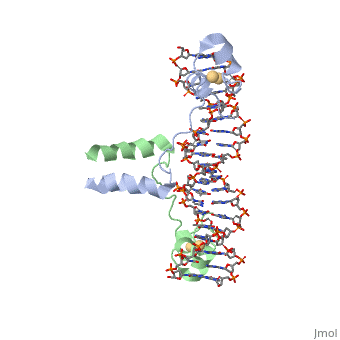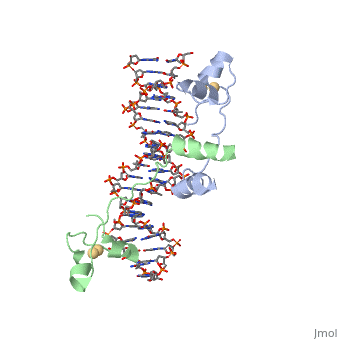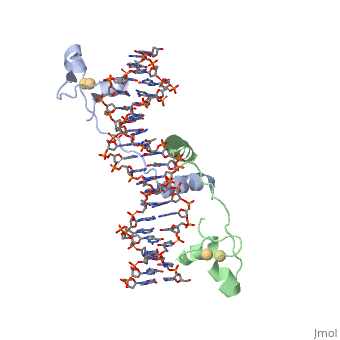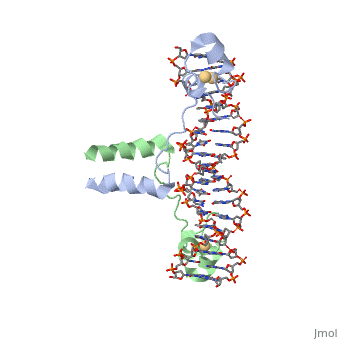
<scene name='92/925553/Uvrd/1'>UvrD</scene>, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. Helicases use energy from nucleoside triphosphate hydrolysis to unwind double helices in metabolic pathways using nucleic acids. A nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is a nucleotide with a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar with 3 phosphates attached. Phosphates are typically used to store energy that is released when breaking bonds to drive catabolic reactions. | <scene name='92/925553/Uvrd/1'>UvrD</scene>, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. Helicases use energy from nucleoside triphosphate hydrolysis to unwind double helices in metabolic pathways using nucleic acids. A nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is a nucleotide with a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar with 3 phosphates attached. Phosphates are typically used to store energy that is released when breaking bonds to drive catabolic reactions. | ||
| - | Helicases are also involved in multiple processes, including RNAs and DNAs, single stranded and double stranded. Helicases were found in the 1970’s to be DNA-dependent ATPases, meaning that they use ATP hydrolysis to complete its interactions with the different types of nucleic acids it comes into contact with. There are multiple types of helicases, with some being for RNA and DNA. Helicase II, also called UvrD is the founding member of SF1, one group of six superfamiliies used to identify helicases. SF1 and SF2 members share seven conserved sequence motifs that are involved in NTP binding. | + | Helicases are also involved in multiple processes, including RNAs and DNAs, single stranded and double stranded. Helicases were found in the 1970’s to be DNA-dependent ATPases, meaning that they use ATP hydrolysis to complete its interactions with the different types of nucleic acids it comes into contact with. There are multiple types of helicases, with some being for RNA and DNA. Helicase II, also called UvrD is the founding member of SF1, one group of six superfamiliies used to identify helicases. SF1 and SF2 members share seven conserved sequence motifs that are involved in NTP binding. UvrD is important in replication, recombination, and repair from ultraviolet damage and mismatched base pairs. Go into NER from the book.. |
| - | There are 7 sequence motifs and a Q motif conserved among the SF1 and the SF2. I, Ia, II-VI | + | There are 7 sequence motifs and a Q motif conserved among the SF1 and the SF2. I, Ia, II-VI are involved in ATP binding. Motifs Ia, III, and V are also involved in ssDNA binding. Motif IV is reported to be unique in SF1. They found in their paper, seven new sequence motifs conserved among UvrD homologs. They are Ib, Ic, Id, IVb, IVc, Va, and VIa. These conserved residues are involved in DNA binding or domain 1B and 2B interactions. |
== UvrD Binding Site for DNA == | == UvrD Binding Site for DNA == | ||
| - | ==UvrD | + | ==UvrD? == |
== UvrD Binding Site for ATP analog == | == UvrD Binding Site for ATP analog == | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 10 October 2022
Contents |
DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX
| |||||||||||
UvrD
|
, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. Helicases use energy from nucleoside triphosphate hydrolysis to unwind double helices in metabolic pathways using nucleic acids. A nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is a nucleotide with a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar with 3 phosphates attached. Phosphates are typically used to store energy that is released when breaking bonds to drive catabolic reactions. Helicases are also involved in multiple processes, including RNAs and DNAs, single stranded and double stranded. Helicases were found in the 1970’s to be DNA-dependent ATPases, meaning that they use ATP hydrolysis to complete its interactions with the different types of nucleic acids it comes into contact with. There are multiple types of helicases, with some being for RNA and DNA. Helicase II, also called UvrD is the founding member of SF1, one group of six superfamiliies used to identify helicases. SF1 and SF2 members share seven conserved sequence motifs that are involved in NTP binding. UvrD is important in replication, recombination, and repair from ultraviolet damage and mismatched base pairs. Go into NER from the book..
There are 7 sequence motifs and a Q motif conserved among the SF1 and the SF2. I, Ia, II-VI are involved in ATP binding. Motifs Ia, III, and V are also involved in ssDNA binding. Motif IV is reported to be unique in SF1. They found in their paper, seven new sequence motifs conserved among UvrD homologs. They are Ib, Ic, Id, IVb, IVc, Va, and VIa. These conserved residues are involved in DNA binding or domain 1B and 2B interactions.
UvrD Binding Site for DNA
UvrD?
UvrD Binding Site for ATP analog
When determining the structure of UvrD, an ATP analog was used. They used an so that the last phosphate can't be cleaved. Using the unhydrolyzable analog is beneficial in locking in the structure to observe.
GIG Motif