We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Gluconeogenesis
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Under development!''' | '''Under development!''' | ||
| - | Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. | + | Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. In humans the main gluconeogenic precursors are lactate, glycerol (which is a part of the triglyceride molecule), alanine and glutamine. Other glucogenic amino acids and all citric acid cycle intermediates (through conversion to oxaloacetate) can also function as substrates for gluconeogenesis. |
| - | + | ||
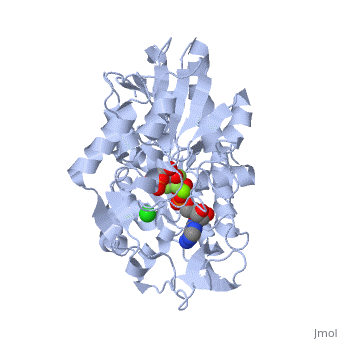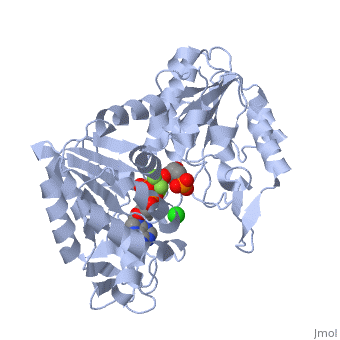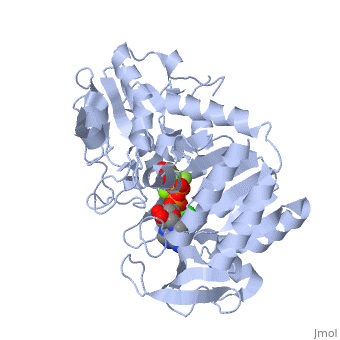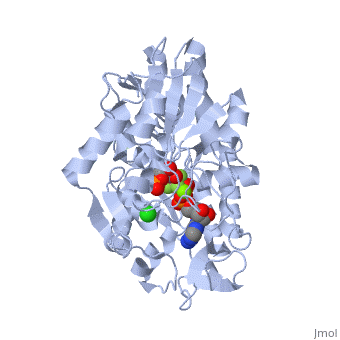
| + | [[Phosphoglycerate Kinase|Phosphoglycerate kinase]] is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible transfer of a phosphate group from <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/5'>1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)</scene> to ADP producing <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/6'>3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG)</scene> and ATP: | ||
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP ⇌ glycerate 3-phosphate + ATP | 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP ⇌ glycerate 3-phosphate + ATP | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 22 November 2022
| |||||||||||