We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Carbon Fixation
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
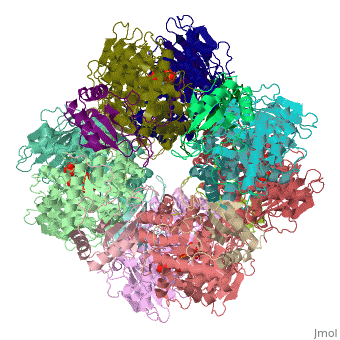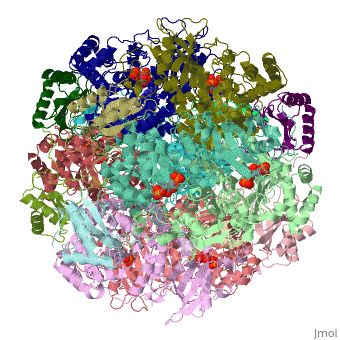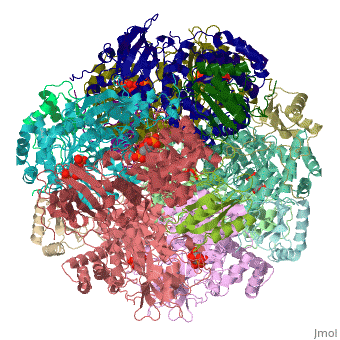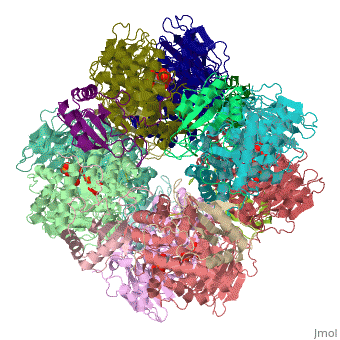
The enzyme [[RuBisCO]] catalyses the carboxylation of <scene name='94/942630/Cv/1'>ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate</scene>, RuBP, a 5-carbon compound, by carbon dioxide (a total of 6 carbons) in a two-step reaction. The product of the first step is enediol-enzyme complex that can capture CO2 or O2. Thus, enediol-enzyme complex is the real carboxylase/oxygenase. The CO2 that is captured by enediol in second step produces an unstable six-carbon compound called 2-carboxy 3-keto 1,5-biphosphoribotol (CKABP) (or 3-keto-2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate) that immediately splits into 2 molecules of <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/6'>3-phosphoglycerate</scene>, a 3-carbon compound. | The enzyme [[RuBisCO]] catalyses the carboxylation of <scene name='94/942630/Cv/1'>ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate</scene>, RuBP, a 5-carbon compound, by carbon dioxide (a total of 6 carbons) in a two-step reaction. The product of the first step is enediol-enzyme complex that can capture CO2 or O2. Thus, enediol-enzyme complex is the real carboxylase/oxygenase. The CO2 that is captured by enediol in second step produces an unstable six-carbon compound called 2-carboxy 3-keto 1,5-biphosphoribotol (CKABP) (or 3-keto-2-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate) that immediately splits into 2 molecules of <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/6'>3-phosphoglycerate</scene>, a 3-carbon compound. | ||
| + | *[[RuBisCO]] | ||
| + | *[[Rubisco and Crop Output]] | ||
| + | *[[RuBisCO (Hebrew)]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 19 December 2022
| |||||||||||